Bài 14. Chỉ dung nước và dung dịch phenolphtalein, hãy trình bày phương pháp để nhận biết 4 chất rắn sau: Na2O, P2O5, MgO, Al2O3. Viết PTHH xảy ra.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Dưới đây là cách nhận biết các chất khí CH₄, O₂, C₂H₄, và H₂ bằng phương pháp hóa học.
1. Nhận biết khí CH₄ (Methane)
- Phương pháp: Dùng chứng chỉ nhiên liệu.
- Phản ứng: Đưa khí CH₄ vào một lửa. Khi cháy, nó tạo ra ánh sáng và âm thanh, đồng thời có mùi mặn của khí NO₂.
- Kết quả: Tạo ra khí CO₂ và H₂O.
2. Nhận biết khí O₂ (Oxygen)
- Phương pháp: Dùng hợp chất cháy.
- Phản ứng: Đưa một que que có mẩu than hồng vào lọ chứa khí O₂.
- Kết quả: Que sẽ bùng cháy và sáng rực lên. O₂ hỗ trợ việc cháy.
3. Nhận biết khí C₂H₄ (Ethylene)
- Phương pháp: Dùng thuốc thử brom.
- Phản ứng: Thêm dung dịch brom vào khí C₂H₄.
- Kết quả: Màu vàng của brom sẽ mất đi do xảy ra phản ứng cộng.
4. Nhận biết khí H₂ (Hydrogen)
- Phương pháp: Thí nghiệm que diêm.
- Phản ứng: Đưa que diêm hoặc que gỗ gần khí H₂ và đốt.
- Kết quả: Khi H₂ cháy, có tiếng “nổ” nhỏ và tạo thành nước.
đây là phương pháp hóa học để nhận biết các chất khí CH4, O2, C2H4 và H2:
1. Dùng que diêm có tàn đỏ:
- O2: Làm que diêm bùng cháy.
- CH4, C2H4, H2: Không làm que diêm bùng cháy.
2. Dẫn các khí còn lại qua dung dịch brom:
- C2H4: Làm dung dịch brom mất màu.
- CH4, H2: Không làm dung dịch brom mất màu.
3. Đốt cháy 2 khí còn lại, dẫn sản phẩm qua dung dịch Ca(OH)2:
- CH4: Khi đốt tạo ra CO2, làm vẩn đục dung dịch Ca(OH)2.
- H2: Khi đốt cháy tạo ra H2O, không làm vẩn đục dung dịch Ca(OH)2.
Phương trình hóa học:
- Đốt CH4: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
- Đốt H2: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
- Dẫn CO2 qua Ca(OH)2: CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
- C2H4 tác dụng với dung dịch brom: C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2

4. Tính thể tích khí và lượng kết tủa khi đốt cháy hỗn hợp \(C_{3} H_{8}\) và \(C_{4} H_{8}\)
Giả sử đề bài cho số mol hoặc khối lượng hỗn hợp, bạn cần cung cấp dữ kiện cụ thể (số mol, khối lượng hoặc tỉ lệ hai khí, điều kiện phản ứng, thể tích dung dịch phản ứng với sản phẩm, v.v.).
Nếu chỉ hỏi phương trình phản ứng:
- Phản ứng đốt cháy:
- \(C_{3} H_{8} + 5 O_{2} \rightarrow 3 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)
- \(C_{4} H_{8} + 6 O_{2} \rightarrow 4 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)
- Tính thể tích khí CO2 (nếu biết số mol):
- Số mol CO2 = \(3 n_{C_{3} H_{8}} + 4 n_{C_{4} H_{8}}\)
- Thể tích khí CO2 ở đktc: \(V_{C O_{2}} = \left(\right. 3 n_{C_{3} H_{8}} + 4 n_{C_{4} H_{8}} \left.\right) \times 22.4\) lít
- Lượng kết tủa khi cho CO2 vào dung dịch Ca(OH)2 dư:
- \(C O_{2} + C a \left(\right. O H \left.\right)_{2} \rightarrow C a C O_{3} \downarrow + H_{2} O\)
- Số mol kết tủa \(C a C O_{3}\) = số mol CO2
- Khối lượng kết tủa: \(m_{C a C O_{3}} = n_{C O_{2}} \times 100\) (g)
Bạn hãy bổ sung dữ kiện cụ thể để mình giải chi tiết nhé!

Dưới đây là lời giải chi tiết cho bài toán hóa học bạn cung cấp từ đường link trên:
Đề bài tóm tắt
- Dẫn 7,437 lít (ở đktc) hỗn hợp X gồm C₃H₈ và C₄H₈ qua dung dịch brom dư, thấy có 16 gam brom phản ứng.
- a. Tính thể tích mỗi khí (ở đktc).
- b. Đốt cháy hết cùng 1 thể tích khí C₃H₈, C₄H₈ rồi cho toàn bộ sản phẩm cháy vào nước vôi trong dư. Lượng kết tủa thu được khi đốt cháy chất nào nhiều hơn? Giải thích.
a. Tính thể tích mỗi khí (ở đktc)
Bước 1: Đặt ẩn số mol
Gọi số mol C₃H₈ là x (mol), C₄H₈ là y (mol).
Ta có:
- Tổng thể tích hỗn hợp:
\(x + y = \frac{7 , 437}{22 , 4} = 0 , 332\) (mol)
Bước 2: Phản ứng với brom
- C₃H₈ (ankan) không phản ứng với Br₂.
- C₄H₈ (anken) phản ứng với Br₂ theo tỉ lệ 1:1:
\(C_{4} H_{8} + B r_{2} \rightarrow C_{4} H_{8} B r_{2}\)
Số mol Br₂ phản ứng = số mol C₄H₈ = y.
Khối lượng Br₂ phản ứng:
\(n_{B r_{2}} = \frac{16}{160} = 0 , 1 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\) \(y = 0 , 1 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)Bước 3: Tìm x
\(x + y = 0 , 332 \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } x = 0 , 332 - 0 , 1 = 0 , 232 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)Bước 4: Tính thể tích mỗi khí
\(V_{C_{3} H_{8}} = 0 , 232 \times 22 , 4 = 5 , 197 \&\text{nbsp};\text{l} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{t}\) \(V_{C_{4} H_{8}} = 0 , 1 \times 22 , 4 = 2 , 24 \&\text{nbsp};\text{l} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{t}\)Đáp số:
- Thể tích C₃H₈: 5,197 lít
- Thể tích C₄H₈: 2,24 lít
b. So sánh lượng kết tủa khi đốt cháy cùng 1 thể tích C₃H₈ và C₄H₈
Bước 1: Viết phương trình cháy
C₃H₈:
\(C_{3} H_{8} + 5 O_{2} \rightarrow 3 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)C₄H₈:
\(C_{4} H_{8} + 6 O_{2} \rightarrow 4 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)Bước 2: Số mol CO₂ tạo thành từ 1 mol mỗi khí
- 1 mol C₃H₈ → 3 mol CO₂
- 1 mol C₄H₈ → 4 mol CO₂
Bước 3: Cùng thể tích (cùng số mol)
- 1 mol C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn 1 mol C₃H₈.
Bước 4: Kết tủa CaCO₃
CO₂ sục vào nước vôi trong dư sẽ tạo kết tủa CaCO₃ theo tỉ lệ 1:1.
- Số mol kết tủa CaCO₃ = số mol CO₂ sinh ra.
=> Đốt cháy cùng thể tích (cùng số mol), C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều kết tủa hơn vì tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn.
Giải thích:
- C₄H₈ có số nguyên tử C nhiều hơn (4C so với 3C trong C₃H₈), nên khi đốt cháy cùng số mol sẽ tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn, dẫn đến lượng kết tủa CaCO₃ nhiều hơn.
Tóm tắt đáp án
a.
- Thể tích C₃H₈: 5,197 lít
- Thể tích C₄H₈: 2,24 lít
b.
- Đốt cháy cùng 1 thể tích, C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều kết tủa CaCO₃ hơn vì tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn (4 mol CO₂ so với 3 mol CO₂ của C₃H₈).

Dưới đây là lời giải chi tiết cho bài toán hóa học bạn cung cấp từ đường link trên:
Đề bài tóm tắt
- Dẫn 7,437 lít (ở đktc) hỗn hợp X gồm C₃H₈ và C₄H₈ qua dung dịch brom dư, thấy có 16 gam brom phản ứng.
- a. Tính thể tích mỗi khí (ở đktc).
- b. Đốt cháy hết cùng 1 thể tích khí C₃H₈, C₄H₈ rồi cho toàn bộ sản phẩm cháy vào nước vôi trong dư. Lượng kết tủa thu được khi đốt cháy chất nào nhiều hơn? Giải thích.
a. Tính thể tích mỗi khí (ở đktc)
Bước 1: Đặt ẩn số mol
Gọi số mol C₃H₈ là x (mol), C₄H₈ là y (mol).
Ta có:
- Tổng thể tích hỗn hợp:
\(x + y = \frac{7 , 437}{22 , 4} = 0 , 332\) (mol)
Bước 2: Phản ứng với brom
- C₃H₈ (ankan) không phản ứng với Br₂.
- C₄H₈ (anken) phản ứng với Br₂ theo tỉ lệ 1:1:
\(C_{4} H_{8} + B r_{2} \rightarrow C_{4} H_{8} B r_{2}\)
Số mol Br₂ phản ứng = số mol C₄H₈ = y.
Khối lượng Br₂ phản ứng:
\(n_{B r_{2}} = \frac{16}{160} = 0 , 1 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\) \(y = 0 , 1 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)Bước 3: Tìm x
\(x + y = 0 , 332 \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } x = 0 , 332 - 0 , 1 = 0 , 232 \&\text{nbsp};\text{mol}\)Bước 4: Tính thể tích mỗi khí
\(V_{C_{3} H_{8}} = 0 , 232 \times 22 , 4 = 5 , 197 \&\text{nbsp};\text{l} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{t}\) \(V_{C_{4} H_{8}} = 0 , 1 \times 22 , 4 = 2 , 24 \&\text{nbsp};\text{l} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{t}\)Đáp số:
- Thể tích C₃H₈: 5,197 lít
- Thể tích C₄H₈: 2,24 lít
b. So sánh lượng kết tủa khi đốt cháy cùng 1 thể tích C₃H₈ và C₄H₈
Bước 1: Viết phương trình cháy
C₃H₈:
\(C_{3} H_{8} + 5 O_{2} \rightarrow 3 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)C₄H₈:
\(C_{4} H_{8} + 6 O_{2} \rightarrow 4 C O_{2} + 4 H_{2} O\)Bước 2: Số mol CO₂ tạo thành từ 1 mol mỗi khí
- 1 mol C₃H₈ → 3 mol CO₂
- 1 mol C₄H₈ → 4 mol CO₂
Bước 3: Cùng thể tích (cùng số mol)
- 1 mol C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn 1 mol C₃H₈.
Bước 4: Kết tủa CaCO₃
CO₂ sục vào nước vôi trong dư sẽ tạo kết tủa CaCO₃ theo tỉ lệ 1:1.
- Số mol kết tủa CaCO₃ = số mol CO₂ sinh ra.
=> Đốt cháy cùng thể tích (cùng số mol), C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều kết tủa hơn vì tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn.
Giải thích:
- C₄H₈ có số nguyên tử C nhiều hơn (4C so với 3C trong C₃H₈), nên khi đốt cháy cùng số mol sẽ tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn, dẫn đến lượng kết tủa CaCO₃ nhiều hơn.
Tóm tắt đáp án
a.
- Thể tích C₃H₈: 5,197 lít
- Thể tích C₄H₈: 2,24 lít
b.
- Đốt cháy cùng 1 thể tích, C₄H₈ tạo ra nhiều kết tủa CaCO₃ hơn vì tạo ra nhiều CO₂ hơn (4 mol CO₂ so với 3 mol CO₂ của C₃H₈).

Ý 1:
\(Đ_r=\dfrac{V_r}{V_r+V_{H_2O}}.100=\dfrac{50}{50+125}.100=28,57\)
Ý 2:
\(\dfrac{25.500:100}{500+V_{nước.thêm\left(ml\right)}}=16\%\\\Leftrightarrow V_{nước.thêm\left(ml\right)}=281,25\left(ml\right)\\ \Rightarrow V_{r\left(sau.pha\right)}=500+281,25=781,25\left(ml\right)\)


`#1194`
Qtr sx thép:
- Nguyên liệu: gang, sắt, thép phế liệu, khí oxygen
- Cách thực hiện:
+ Khí oxy được thổi từ dưới lò lên để đốt cháy tạp chất trong gang
+ Các oxide tạo thành ở dạng khí \(\left(\text{CO}_2;\text{ }\text{ SO}_2;...\right)\) sẽ thoát ra theo khí thải, các oxide dạng rắn \(\left(\text{SiO}_2;\text{ MnO}_2;...\right)\) sẽ tạo ra xỉ nhẹ, nổi lên trên thép nóng.
- Xỉ được tách ra để thu lấy thép.

Lượng nước cần cung cấp cho Hà Nội mỗi ngày là: V H 2 O = 8000000 . 200 = 1600000000 ( l ) = 1600000 ( m 3 ) Lượng clo cần xử lý là: m C l 2 ( C a n x u l y ) = 5 . 160000 = 8000000 ( g ) = 8000 k g


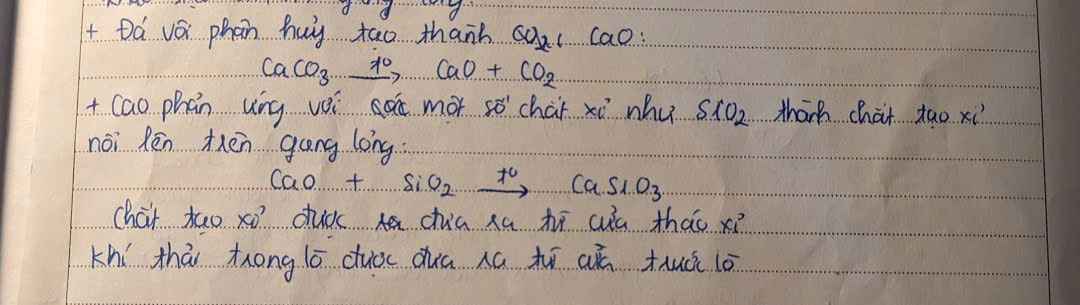
- Trích mẫu thử.
- Hòa tan từng chất vào nước.
+ Tan, làm phenolphtalein hóa hồng: Na2O
PT: Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
+ Tan, phenolphtalein không đổi màu: P2O5
PT: P2O5 + 3H2O → 2H3PO4
+ Không tan: MgO, Al2O3 (1)
- Cho mẫu thử nhóm (1) pư với dd NaOH thu được ở trên.
+ Tan: Al2O3
PT: Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
+ Không tan: MgO
- Dán nhãn.
đây là phương pháp nhận biết 4 chất rắn Na2O, P2O5, MgO, Al2O3 chỉ dùng nước và dung dịch phenolphtalein:
1. Hòa tan vào nước:
2. Nhỏ dung dịch phenolphtalein vào các dung dịch thu được:
3. Nhận biết MgO và Al2O3:
Tóm lại: