Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\sqrt{x^2-x}=\sqrt{3-x}\)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x\ge0\\3-x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\le3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3}\\x=-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: ...

đkxđ: \(z\ge1;x\ge2;y\ge3\)
Đặt \(a=\sqrt{z-1}\ge0;b=\sqrt{x-2}\ge0;c=\sqrt{y-3}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow z=a^2+1;x=b^2+2;y=c^2+3\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{a}{a^2+1}+\dfrac{b}{b^2+2}+\dfrac{c}{c^2+3}\)
Do các biến \(a,b,c\) độc lập nhau nên ta xét từng phân thức một.
Đặt \(f\left(a\right)=\dfrac{a}{a^2+1}\) \(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right).a^2-a+f\left(a\right)=0\) (*)
Nếu \(f\left(a\right)=0\) thì \(a=0\), rõ ràng đây không phải là GTLN cần tìm.
Xét \(f\left(a\right)\ne0\)
Để pt (*) có nghiệm thì \(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4\left[f\left(a\right)\right]^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+2f\left(a\right)\right)\left(1-2f\left(a\right)\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}\le f\left(a\right)\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(f\left(a\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{a}{a^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow a^2+1=2a\Leftrightarrow a=1\) (nhận)
Vậy \(max_{f\left(a\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2}\).
Tiếp đến, gọi \(g\left(b\right)=\dfrac{b}{b^2+2}\) \(\Rightarrow g\left(b\right).b^2-b+2g\left(b\right)=0\) (**)
Tương tự nếu \(b=0\) thì vô lí. Xét \(b\ne0\). Khi đó để (**) có nghiệm thì \(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-8\left[g\left(b\right)\right]^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-2\sqrt{2}g\left(b\right)\right)\left(1+2\sqrt{2}g\left(b\right)\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\le g\left(b\right)\le\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
\(g\left(b\right)=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b}{b^2+2}=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\Leftrightarrow b^2+2=2\sqrt{2}b\Leftrightarrow b=\sqrt{2}\) (nhận)
Vậy \(max_{g\left(b\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
Làm tương tự với \(h\left(c\right)=\dfrac{c}{c^2+3}\), ta được \(max_{h\left(c\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}\), xảy ra khi \(c=\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy GTLN của A là \(\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{6+3\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{3}}{12}\), xảy ra khi \(\left(a,b,c\right)=\left(1,\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3}\right)\) hay \(\left(x,y,z\right)=\left(2,4,6\right)\).

Bài làm của bạn chưa đúng nhé:
Đến đoạn
$|x-3|=3-x$
$\Leftrightarrow |3-x|=3-x$
$\Leftrightarrow 3-x\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow x\leq 3$
Vậy pt có nghiệm $x\leq 3, x\in\mathbb{R}$
----------------------------
Bạn nhớ 1 tính chất này: Nếu $|a|=a$ thì $a\geq 0$.

\(\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}=8\left(x\ge0;x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2\sqrt{x}=8\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2\sqrt{x}=8\sqrt{x}-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2\sqrt{x}-8\sqrt{x}+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-6\sqrt{x}+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}-2=0\\\sqrt{x}-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=2\\\sqrt{x}=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=16\end{matrix}\right.\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: ...
\(\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}=8\left(x\ge0,x\ne1\right)\\ < =>x+2\sqrt{x}=8\sqrt{x}-8\\ < =>x-6\sqrt{x}+8=0\\ < =>\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-4\right)=0\\ =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}-2=0\\\sqrt{x}-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=16\end{matrix}\right.\left(TMDK\right)\)
\(=>S=\left\{4;16\right\}\)


Bạn nên gõ đề bằng công thức toán (biểu tượng $\sum$ góc trái khung soạn thảo) để mọi người hiểu đề của bạn hơn nhé. Viết thế này khó đọc quá.

Lời giải:
$B=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\frac{\sqrt{x}-4}{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}$
$=\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}-1)+(\sqrt{x}-4)}{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}$
$=\frac{x-4}{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}$
Do đó:
$A:B=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}: \frac{x-4}{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}$
$=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}.\frac{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)}{(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}+2)}$
$=\frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}$
Để $A:B< \frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow \frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}< \frac{1}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}-\frac{1}{2}<0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{\sqrt{x}-4}{2(\sqrt{x}+2)}<0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}-4<0$
$\Leftrightarrow 0\leq x< 16$
Kết hợp đkxđ suy ra $0\leq x< 16; x\neq 1$
Khi $x=6-2\sqrt{5}=(\sqrt{5}-1)^2$ thì $\sqrt{x}=\sqrt{5}-1$
$A=\frac{\sqrt{5}-1-2}{\sqrt{5}-1+1}=\frac{5-3\sqrt{5}}{5}$
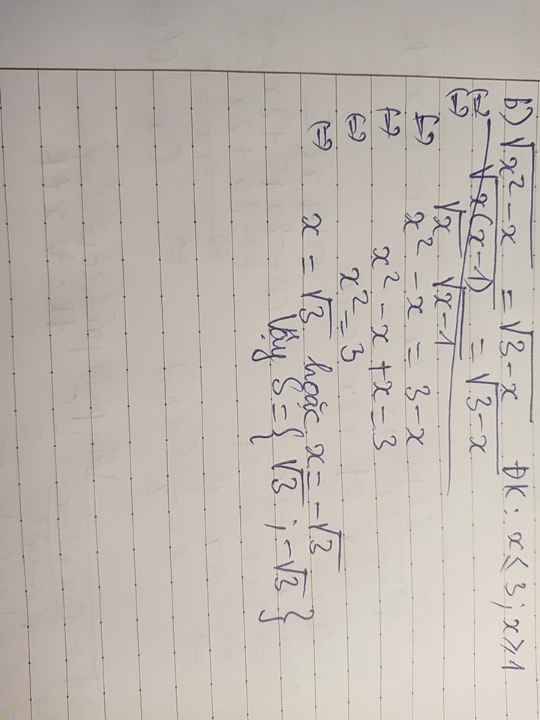

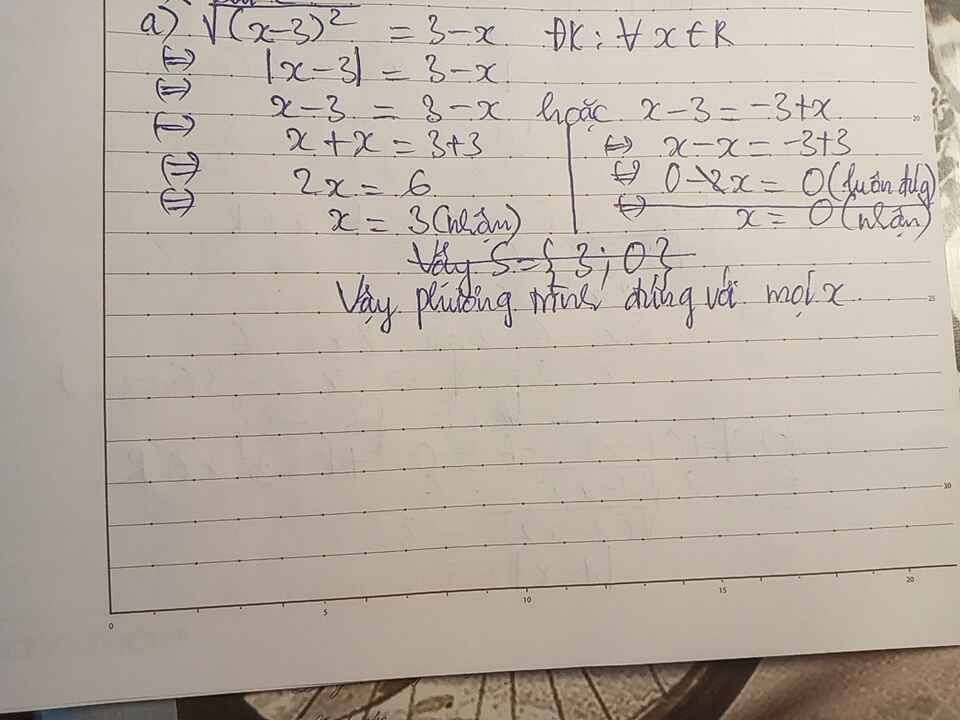

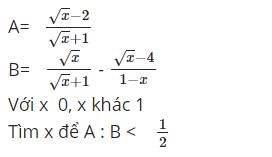 tính giá trị của A khi x= 6 -2
tính giá trị của A khi x= 6 -2
giải dùm mình với mai thi rồi