Cho tam giác ABC với các đỉnh A,B,C và các cạnh đối diện với các đỉnh tương ứng là a,b,c. Chứng minh: a^(2)=b^(2)+c^(2)-2bc cosA ai giúp mik với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
$x^3+5x^2+6x=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x^2+5x+6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x[x(x+2)+3(x+2)]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x+2)(x+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$ hoặc $x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-2$ hoặc $x=-3$
Vậy PT có tập nghiệm $\left\{0; -2; -3\right\}$

1A. Để biết cặp số nào là nghiệm của PT bậc nhất hai ẩn $2x-5y=19$, bạn thay giá trị $(x_0,y_0)$ tương ứng vào PT $2x-5y=19$ xem có thỏa mãn không. Nếu thỏa mãn nghĩa là cặp số $(x_0,y_0)$ là nghiệm của PT đã cho.
Trong các cặp số đã cho, khi thay giá trị ta thấy cặp $(12;1)$ và $(2;-3)$ thỏa mãn, do:
$2.12-5.1=19$
$2.2-5(-3)=19$
Suy ra $(12;1); (2;-3)$ là nghiệm của PT đã cho.
1B.
a. Ta thấy: $-2-3\neq -1$ nên $(-2;3)$ không là nghiệm của PT $x-y=1$
b. Ta thấy $2(-2)+3.3=5$ nên $(-2;3)$ là nghiệm của PT $2x+3y=5$
c. Ta thấy $2.(-2)+3\neq -4$ nên $(-2;3)$ không là nghiệm của PT $2x+y=-4$
d. Ta thấy $2.(-2)-3=-7$ nên $(-2;3)$ là nghiệm của PT $2x-y=-7$

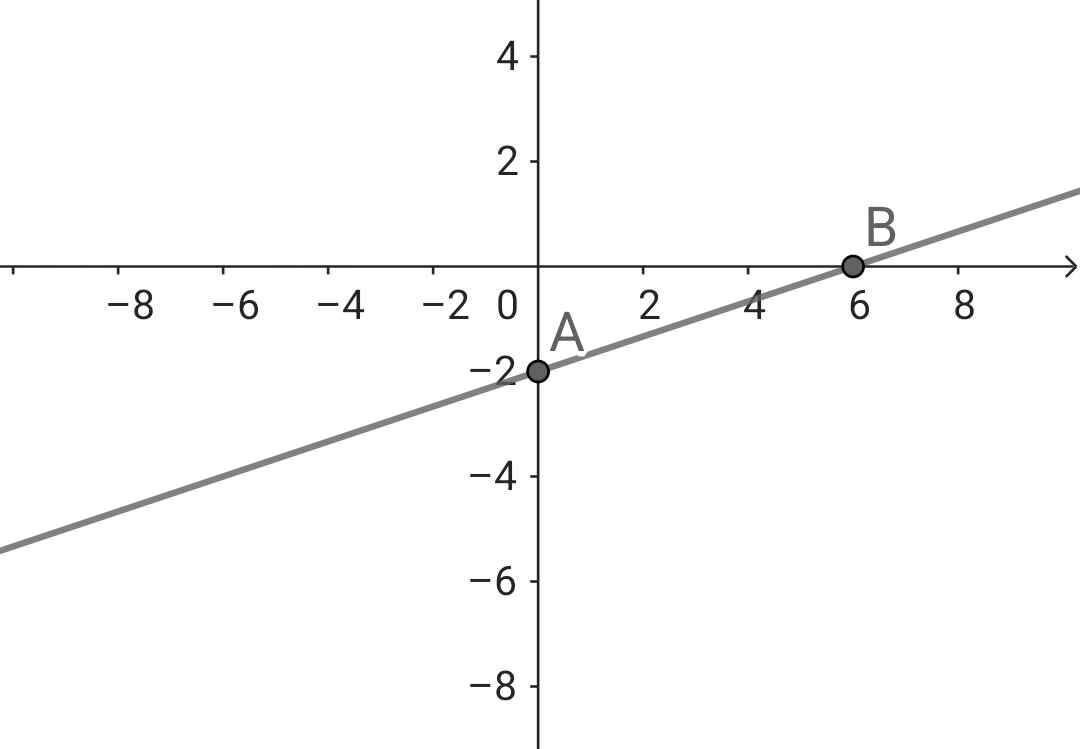
a) x - 3y = 6
x = 6 + 3y
Nghiệm tổng quât của phương trình:
y ∈ R và x = 6 + 3y
Biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên mặt phẳng tọa độ:
b) 3y - 2x = 3
3y = 3 + 2x
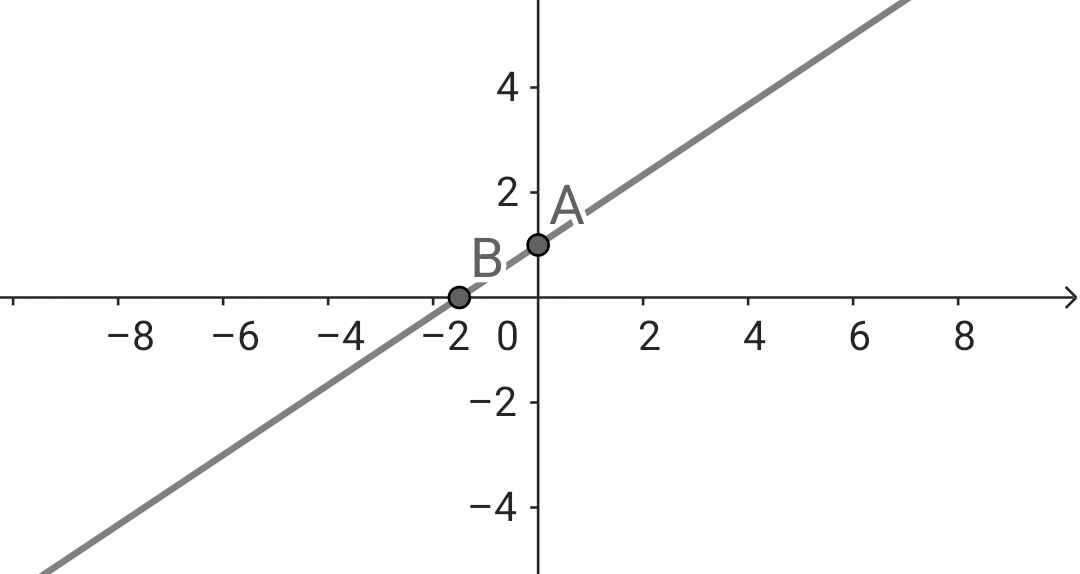
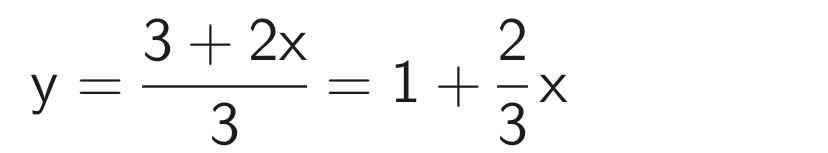 Nghiệm tổng quát của phương trình:
Nghiệm tổng quát của phương trình:
x ∈ R và  Biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên mặt phẳng tọa độ:
Biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên mặt phẳng tọa độ:

Kẻ đường cao AH của tam giác ABC \(\left(H\in BC\right)\). Gọi F là trung điểm của BC.
Khi đó tam giác GBC vuông tại G có trung tuyến GF nên \(GF=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\)
Lại có G là trọng tâm tam giác ABC \(\Rightarrow GF=\dfrac{1}{3}AF\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}BC=\dfrac{1}{3}AF\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{AF}{BC}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{2}{3}AF\) (1)
Mặt khác, tam giác ABH vuông tại H \(\Rightarrow cotB=\dfrac{BH}{AH}\)
Tương tự, \(cotC=\dfrac{CH}{AH}\)
\(\Rightarrow cotB+cotC=\dfrac{BH}{AH}+\dfrac{CH}{AH}=\dfrac{BC}{AH}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{3}AF}{AH}\) \(\ge\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{3}AH}{AH}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
(vì AH, AF là đường vuông góc và đường xiên kẻ từ A đến BC)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow AH=AF\), nghĩa là đường cao bằng đường trung tuyến ứng với đỉnh A \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta ABC\) cân tại A.
Ta có đpcm.

ĐK: \(a\ne-2\); \(a\in\mathbb{Z}\)
\(P=\dfrac{a-1}{a+2}=\dfrac{a+2-3}{a+2}=1-\dfrac{3}{a+2}\)
Để \(P\in\mathbb{Z}\) thì \(\dfrac{3}{a+2}\in\mathbb{Z}\)
\(\Rightarrow3⋮a+2\)
\(\Rightarrow a+2\inƯ\left(3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow a+2\in\left\{1;3;-1;-3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow a\in\left\{-1;1;-3;-5\right\}\) (tmđk)

\(4x^2+4x+1=x^2\\\Leftrightarrow 3x^2+4x+1=0\\\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x+x+1=0\\\Leftrightarrow 3x(x+1)+(x+1)=0\\\Leftrightarrow (3x+1)(x+1)=0 \\\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{array}{} 3x+1=0\\ x+1=0 \end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{array}{} x=-\frac13\\ x=-1 \end{array}\right.\)

Đối với các bài hình học, bạn nên tách lẻ mỗi bài ra một post để mọi người tiện theo dõi và hỗ trợ nhanh hơn nhé.

\(x^2-x-\left(3x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-3\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: ...

Bài 2:
a)
\(C=\dfrac{2x+1}{4x-2}+\dfrac{1-2x}{4x+2}-\dfrac{2}{1-4x^2}\left(x\ne\pm\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\\ =\dfrac{2x+1}{2\left(2x-1\right)}+\dfrac{1-2x}{2\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2}{4x^2-1}\\ =\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)^2}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(1-2x\right)\left(2x-1\right)}{2\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{4}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)^2}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)^2}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}+\dfrac{4}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^2+4}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{4x^2+4x+1-4x^2+4x-1+4}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\dfrac{8x+4}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(2x+1\right)}{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2}{2x-1}\)
b)
\(D=\dfrac{3x+1}{x^2-2x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}+\dfrac{x+3}{1-x^2}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\\ =\dfrac{3x+1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{3x^2+3x+x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-\left(x^2-x+3x-3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+4x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+3x+x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-2x+1}\)
Bài 1:
a. \(A=\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x^2}{1-x^2}\left(dk:x\ne\pm1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1-x-1+2x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-2}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}=2\)
b. \(B=\dfrac{4x^2-3x+17}{x^3-1}+\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{6}{x-1}\left(dk:x\ne1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2-3x+17}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2-3x+17+2x^2-3x+1-6x^2-6x-6}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-12x+12}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-12\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-12}{x^2+x+1}\)
c. \(C=\dfrac{3x+2}{x^2-2x+1}-\dfrac{6}{x^2-1}-\dfrac{3x-2}{x^2+2x+1}\left(dk:x\ne\pm1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}-\dfrac{6\left(x^2-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}-\dfrac{\left(3x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-6x^2+6-\left(3x-2\right)\left(x^2-2x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x^3+6x^2+3x+2x^2+4x+2-6x^2+6-\left(3x^3-6x^2+3x-2x^2+4x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-1\right)^2}\\ =\dfrac{10x^2+10}{x^4-2x^2+1}\)
d. \(D=\dfrac{18}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2-9\right)}-\dfrac{3}{x^2-6x+9}-\dfrac{x}{x^2-9}\left(dk:x\ne\pm3\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{18}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{3\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{18-3x-9-x^2+3x}{\left(x-3\right)^2\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{9-x^2}{\left(x^2-9\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{3-x}\)







Kẻ đường cao BD của tam giác ABC \(\left(D\in AC\right)\)
Khi đó \(AD=AB.cosA=c.cosA\)
\(\Rightarrow CD=AC-AD=b-c.cosA\)
Mặt khác, \(BD=BA.sinA=c\sqrt{1-cos^2A}\)
Tam giác BCD vuông tại D nên:
\(a^2=BC^2=DB^2+DC^2\)
\(=\left(b-c.cosA\right)^2+\left(c\sqrt{1-cos^2A}\right)^2\)
\(=b^2-2bc.cosA+c^2.cos^2A+c^2\left(1-cos^2A\right)\)
\(=b^2+c^2-2bc.cosA\)
Vậy đẳng thức được chứng minh.