2x² + 6x =0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ΔMAB đều \(\Rightarrow \hat{A M B} = 6 0^{0}\)
Theo tính chất 2 tiếp tuyến, ta có MO là phân giác \(\hat{A M B}\)
\(\Rightarrow \hat{A M O} = \frac{1}{2} \hat{A M B} = 3 0^{0}\)
Trong tam giác vuông OAM:
\(t a n \hat{A M O} = \frac{O A}{A M} \Rightarrow O A = A M . t a n \hat{A M O} = 15 \sqrt{3} . t a n 3 0^{0} = 15 \left(\right. c m \left.\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow 2 R = 2 O A = 30 \left(\right. c m \left.\right)\)

2:
a: Xét tứ giác ABOC có \(\widehat{OBA}+\widehat{OCA}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên ABOC là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>A,B,O,C cùng thuộc một đường tròn
b: Xét (O) có
AB,AC là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: AB=AC
=>A nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(1)
Ta có: OB=OC
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra AO là đường trung trực của BC
=>AO\(\perp\)BC tại H và H là trung điểm của BC
Xét ΔOBA vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(OH\cdot OA=OB^2=R^2\) không đổi
c: Xét (O) có
\(\widehat{ABM}\) là góc tạo bởi tiếp tuyến BA và dây cung BM
\(\widehat{BNM}\) là góc nội tiếp chắn cung BM
Do đó: \(\widehat{ABM}=\widehat{BNM}\)
Xét ΔABM và ΔANB có
\(\widehat{ABM}=\widehat{ANB}\)
\(\widehat{BAM}\) chung
Do đó: ΔABM~ΔANB
=>\(\dfrac{AB}{AN}=\dfrac{AM}{AB}\)
=>\(AM\cdot AN=AB^2\left(3\right)\)
Xét ΔOBA vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(AH\cdot AO=AB^2\left(4\right)\)
Từ (3),(4) suy ra \(AM\cdot AN=AH\cdot AO\)
Gọi I là giao điểm của BA và CD
Xét (O) có
ΔBCD nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBCD vuông tại C
=>BC\(\perp\)DI tại C
=>ΔBCI vuông tại C
Ta có: \(\widehat{ACI}+\widehat{ACB}=\widehat{BCI}=90^0\)
\(\widehat{AIC}+\widehat{ABC}=90^0\)(ΔBCI vuông tại C)
mà \(\widehat{ABC}=\widehat{ACB}\)(ΔBCA cân ạti A)
nên \(\widehat{ACI}=\widehat{AIC}\)
=>AI=AC
mà AB=AC
nên AB=AI(5)
TA có: CE\(\perp\)BD
IB\(\perp\)BD
Do đó: CE//IB
Xét ΔDAB có EK//AB
nên \(\dfrac{EK}{AB}=\dfrac{DK}{DA}\left(6\right)\)
Xét ΔDAI có KC//AI
nên \(\dfrac{KC}{AI}=\dfrac{DK}{DA}\left(7\right)\)
Từ (5),(6),(7) suy ra EK=KC
=>K là trung điểm của EC

a: Xét (O) có
ΔADC nội tiếp
AC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔADC vuông tại D
=>AD\(\perp\)MC tại D
=>\(\widehat{ADM}=90^0\)
Xét (O) có
MA,MB là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: MA=MB
=>M nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(1)
Ta có: OA=OB
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra MO là đường trung trực của AB
=>MO\(\perp\)AB tại H và H là trung điểm của AB
=>\(\widehat{MHA}=90^0=\widehat{MDA}\)
=>MDHA nội tiếp
b: Xét ΔOAM vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(MH\cdot MO=MA^2\left(3\right)\)
Xét ΔACM vuông tại A có AD là đường cao
nên \(MD\cdot MC=MA^2\left(4\right)\)
Từ (3),(4) suy ra \(MH\cdot MO=MD\cdot MC\)

Xét (O) có
ΔACB nội tiếp
AB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔACB vuông tại C
=>BC\(\perp\)AM tại C
Xét (O) có
ΔADB nội tiếp
AB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔADB vuông tại D
=>AD\(\perp\)MB tại D
Xét ΔMAB có
AD,BC là các đường cao
AD cắt BC tại I
Do đó: I là trực tâm của ΔMAB
=>MI\(\perp\)AB
mà MH\(\perp\)AB
và MI,MH có điểm chung là M
nên M,I,H thẳng hàng
Xét tứ giác MCID có \(\widehat{MCI}+\widehat{MDI}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên MCID là tứ giác nội tiếp đường tròn đường kính MI
=>MCID nội tiếp (K)
=>KC=KI
=>ΔKCI cân tại K
=>\(\widehat{KCI}=\widehat{KIC}\)
mà \(\widehat{KIC}=\widehat{MIC}=\widehat{CAB}\left(=90^0-\widehat{AMH}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{KCI}=\widehat{CAB}\)
ΔOBC có OB=OC
nên ΔOBC cân tại O
=>\(\widehat{OCB}=\widehat{OBC}\)
\(\widehat{KCO}=\widehat{KCB}+\widehat{OCB}=\widehat{CAB}+\widehat{CBA}=90^0\)
Xét tứ giác KCOH có \(\widehat{KCO}+\widehat{KHO}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên KCOH là tứ giác nội tiếp

Bài 2:
a: Xét (O) có
ΔCNM nội tiếp
CM là đường kính
Do đó: ΔCNM vuông tại N
=>CN\(\perp\)BN tại N
Xét tứ giác CNAB có \(\widehat{CNB}=\widehat{CAB}=90^0\)
nên CNAB là tứ giác nội tiếp
b: Xét (O) có
\(\widehat{DNM};\widehat{DCM}\) là các góc nội tiếp cùng chắn cung DM
=>\(\widehat{DNM}=\widehat{DCM}\)
mà \(\widehat{DNM}=\widehat{ANB}=\widehat{ACB}\)(CNAB nội tiếp)
nên \(\widehat{DCA}=\widehat{BCA}\)
=>CA là phân giác của góc BCD
c: C,E,D,N cùng thuộc (O)
=>CEDN nội tiếp
=>\(\widehat{CED}+\widehat{CND}=180^0\)
mà \(\widehat{CND}+\widehat{CBA}=180^0\)(CNAB nội tiếp)
nên \(\widehat{CED}=\widehat{CBA}\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc ở vị trí đồng vị
nên ED//AB
=>ABED là hình thang

a: Thay x=1 và y=-2 vào (P), ta được:
\(a\cdot1^2=-2\)
=>\(a\cdot1=-2\)
=>a=-2
b: Khi a=-2 thì \(y=a\cdot x^2=-2x^2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
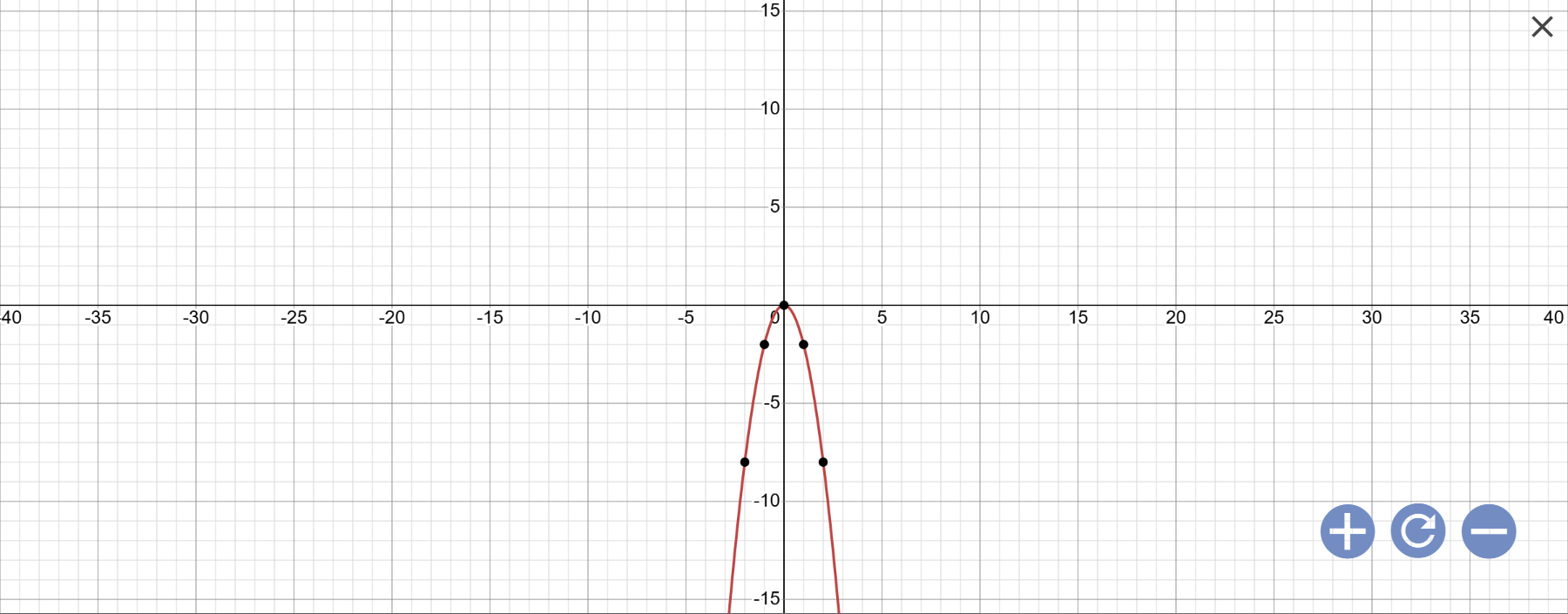
c: Thay x=2 vào (P), ta được:
\(y=-2\cdot2^2=-8\)

a: Thay m=1 vào (1), ta được:
\(x^2-1\cdot x+1-3=0\)
=>\(x^2-x-2=0\)
=>(x-2)(x+1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-m\right)^2-4\left(m-3\right)\)
\(=m^2-4m+12\)
\(=m^2-4m+4+8=\left(m-2\right)^2+8>=8>0\forall m\)
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=6\)
=>\(m^2-2\left(m-3\right)-6=0\)
=>\(m^2-2m=0\)
=>m(m-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(2x^2-3x+1=0\\ \Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot2\cdot1=1>0\\ x_1=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-3\right)-1}{2\cdot2}=0,5\\ x_2=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-3\right)+1}{2\cdot2}=1\\ \text{vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm là }x_1=0,5;x_2=1\)
\(2x^2-3x+1=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot2\cdot1=1\left(>0\right)\)
Do \(\Delta>0\) nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
x1 = \(\frac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{-\left(-3\right)+\sqrt1}{4}=\frac{3+1}{4}=1\)
x2 = \(\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{-\left(-3\right)-\sqrt1}{4}=\frac{3-1}{4}=\frac24=\frac12\)


2x² + 6x = 0
2x(x + 3) = 0
2x = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
*) 2x = 0
x = 0
*) x + 3 = 0
x = -3
Vậy S = {-3; 0}
2x² + 6x = 0
2x(x + 3) = 0
2x = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
+) 2x = 0
x = 0
+) x + 3 = 0
x = -3
Vậy S = {-3 và 0}