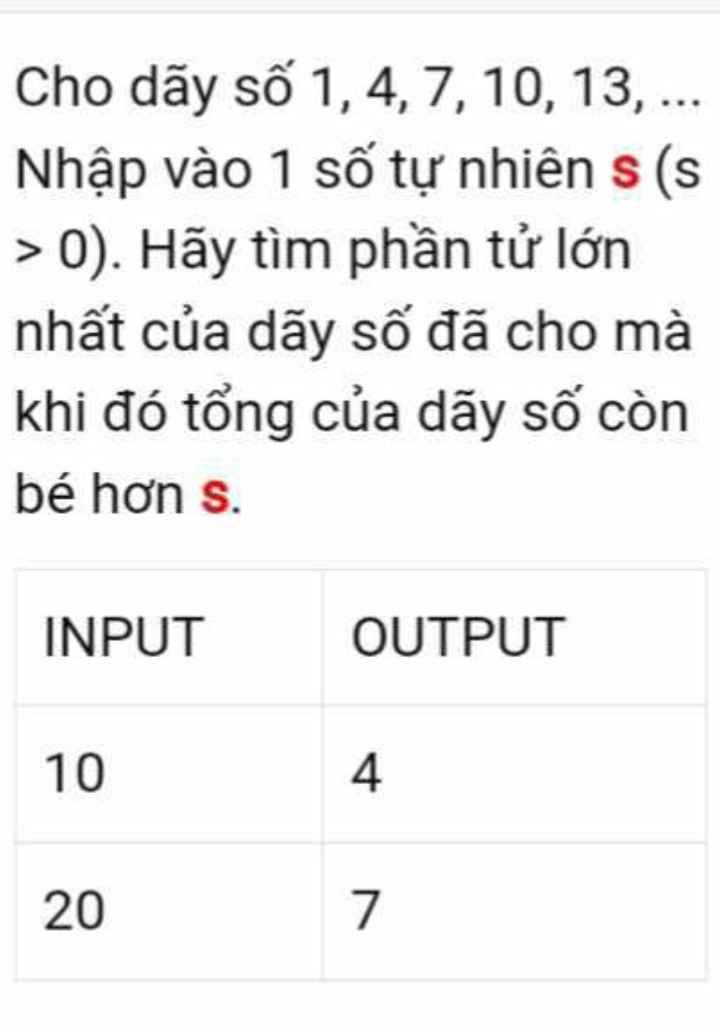
 giúp e với e đang cần gấp lắm ạ
giúp e với e đang cần gấp lắm ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


def viettat(s):
s = s.split(" ")
kq = ""
for i in s:
if i != "":
kq += i[0]
return kq
name = str(input("Nhập vào họ tên: "))
print("Tên viết tắt là: ", viettat(name))
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string viettat(string s)
{
string l="";
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++)
{
if(s[i]>='A' and s[i]<='Z') l+=s[i];
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin, s);
cout<<viettat(s);
}

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a[1000007];
long long n;
void kq()
{
long long ans=-1e18;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
ans=max(ans, a[i]);
}
cout<<ans;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
kq();
}

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int d=0, k=(n-1)/2;
for (int i=0; i<n;i++){
if (i>=k) d++;
cout<<d;
return 0;
}

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1, s2;
getline(cin,s1);
getline(cin,s2);
int n=s1.size(), m=s2.size(),len;
if (n<m) len=m; else len=n;
for (int i=0;i<len;i++){
if (s1[i]!='\0') cout<<s1[i];
if (s2[i]!='\0') cout<<s2[i];
}
return 0;
}

s = input("Nhập dãy số (cách nhau bởi dấu trong project của bạn): ").split()
for i in s: if int(i) < 0: tong_am += init(i)
print(f"Tổng các phần tử âm trong dãy là: {tong_am}")


Ví dụ Input là 23 -> với bài toán của em kết quả sẽ là 23/3+1 = 8
Trong dãy làm gì có số 8 đâu đúng không nè.