x.(2x-1)- (2x^2 +x) =-2 giải hộ mình với. Cảm ơn ah !
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 4:
a, \(\sqrt{3x+4}-\sqrt{2x+1}=\sqrt{x+3}\) (ĐK: \(x\ge\dfrac{-1}{2}\))
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\left(\sqrt{3x+4}-\sqrt{2x+1}\right)^2\) = x + 3
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(3x+4+2x+1-2\sqrt{\left(3x+4\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(4x+2=2\sqrt{6x^2+11x+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x+1=\sqrt{6x^2+11x+4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(4x^2+4x+1=6x^2+11x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x^2+7x+3=0\)
\(\Delta=7^2-4.2.3=25\); \(\sqrt{\Delta}=5\)
Vì \(\Delta\) > 0; theo hệ thức Vi-ét ta có:
\(x_1=\dfrac{-7+5}{4}=\dfrac{-1}{2}\)(TM); \(x_2=\dfrac{-7-5}{4}=-3\) (KTM)
Vậy ...
Các phần còn lại bạn làm tương tự nha, phần d bạn chuyển \(-\sqrt{2x+4}\) sang vế trái rồi bình phương 2 vế như bình thường là được
Bài 5:
a, \(\sqrt{x+4\sqrt{x}+4}=5x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)^2}=5x+2\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\sqrt{x}+2=5x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(5x-\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{x}\left(5\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=0\\5\sqrt{x}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{25}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
Phần b cũng là hằng đẳng thức thôi nha \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}=\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}=x-1\); \(\sqrt{x^2+4x+4}=\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)^2}=x+2\) rồi giải như bình thường là xong nha!
VD1:
a, \(\sqrt{2x-1}=\sqrt{2}-1\) (x \(\ge\) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x-1=\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)^2\) (Bình phương 2 vế)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x-1=2-2\sqrt{2}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x=4-2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=2-\sqrt{2}\) (TM)
Vậy ...
Phần b tương tự nha
c, \(\sqrt{3}x^2-\sqrt{12}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{3}x^2=\sqrt{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
Vậy ...
d, \(\sqrt{2}\left(x-1\right)-\sqrt{50}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\sqrt{2}\left(x-1\right)=\sqrt{50}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-1=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=6\)
Vậy ...
VD2:
Phần a dễ r nha (Bình phương 2 vế rồi tìm x như bình thường)
b, \(\sqrt{x^2-x}=\sqrt{3-x}\) (\(x\le3\); \(x^2\ge x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2-x=3-x\) (Bình phương 2 vế)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=\pm\sqrt{3}\) (TM)
Vậy ...
c, \(\sqrt{2x^2-3}=\sqrt{4x-3}\) (x \(\ge\) \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x^2-3=4x-3\) (Bình phương 2 vế)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(KTM\right)\\x=2\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
Chúc bn học tốt! (Có gì không biết cứ hỏi mình nha!)

a) \(\left(x+2\right)^2=4\left(2x-1\right)^2\)
\(\left(x+2\right)^2-4\left(2x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\left(x+2\right)^2-\left[2\left(2x-1\right)\right]^2=0\)
\(\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(4x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\left(x+2-4x+2\right)\left(x+2+4x-2\right)=0\)
\(6x\left(-3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow6x=0\) hoặc \(-3x+4=0\)
*) \(6x=0\)
\(x=0\)
*) \(-3x+4=0\)
\(3x=4\)
\(x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Vậy \(x=0;x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
b) \(4x\left(x-2019\right)-x+2019=0\)
\(4x\left(x-2019\right)-\left(x-2019\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-2019\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2019=0\) hoặc \(4x-1=0\)
*) \(x-2019=0\)
\(x=2019\)
*) \(4x-1=0\)
\(4x=1\)
\(x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{1}{4};x=2019\)

\(|2x^2-3x+4|-|2x-x^2-1|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow|2x^2-3x+4|=|2x-x^2-1|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4=2x-x^2-1\\2x^2-3x+4=-2x+x^2+1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4-2x+x^2+1=0\\2x^2-3x+4+2x-x^2-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x^2-5x+5=0\\x^2-x+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3\left(x^2-\frac{5}{3}x+\frac{25}{9}-\frac{25}{9}+\frac{5}{3}\right)=0\\x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{4}+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3\left(x-\frac{5}{3}^2\right)-\frac{10}{3}=0\\\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}>0\left(Loai\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)^2-\left(\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}+5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)\left(x\sqrt{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}-5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\sqrt{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}+5\sqrt{3}}{3}=0\\x\sqrt{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}-5\sqrt{3}}{3}=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5+\sqrt{10}}{3}\\x=\frac{5-\sqrt{10}}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ...
\(\left|2x^2-3x+4\right|-\left|2x-x^2-1\right|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x^2-3x+4\right|=\left|2x-x^2-1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4=2x-x^2-1\\2x^2-3x+4=x^2-2x+1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x^2-5x+5=0\\x^2-x+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(TH1:3x^2-5x+5=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=5^2-4.3.5=-35< 0\)(vô nghiệm)
\(TH2:x^2-x+3=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=1^2-4.1.3=-11< 0\)(vô nghiệm)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm

Bạn gõ bằng công thức trực quan để được giúp đỡ nhanh hơn nhé, chứ mình nhìn thế không dịch được (Nhấp vào biểu tượng chữ M nằm ngang)

Vd1:
d) Ta có: \(\sqrt{2}\left(x-1\right)-\sqrt{50}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}\left(x-1-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=6\)

a: Hàm số đồng biến khi x>0 và nghịch biến khi x<0
c: PTHĐGĐ là
2x^2=x+1
=>2x^2-x-1=0
=>2x^2-2x+x-1=0
=>(x-1)(2x+1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-1/2
=>y=2 hoặc y=2*(-1/2)^2=2*1/4=1/2
b: 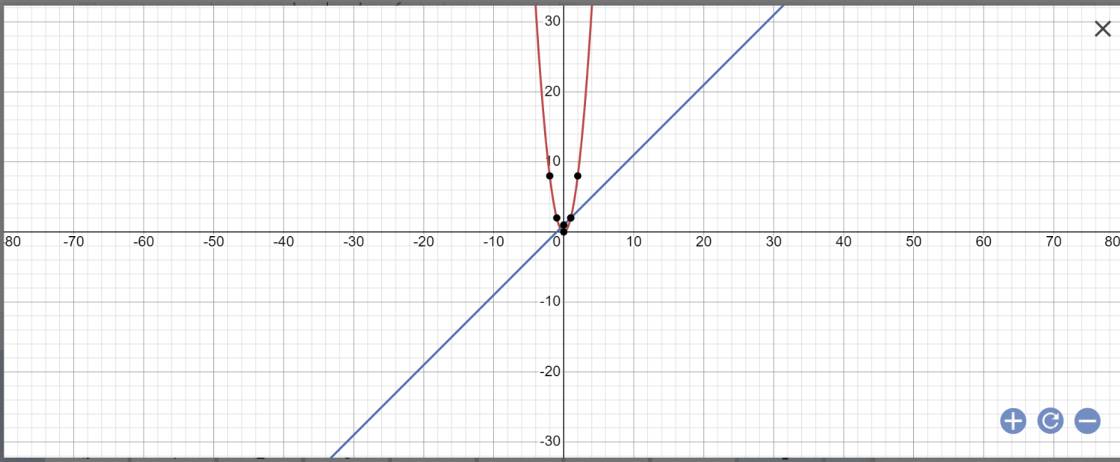

Giả sử con muỗi nặng m (gam), còn con voi nặng V (gam). Ta có
 .
.
Cộng hai về với -2mV. Ta có
 - 2mV +
- 2mV +  =
=  - 2mV +
- 2mV + 
hay  .
.
Lấy căn bậc hai mỗi vế của bất đẳng thức trên, ta được:

Do đó m - V = V - m
Từ đó ta có 2m = 2V, suy ra m = V. Vậy con muỗi nặng bằng con voi (!).
Hướng dẫn giải:
Phép chứng minh sai ở chỗ: sau khi lấy căn bậc hai mỗi vế của đẳng thức  . Ta được kết quả │m - V│ = │V - m│ chứ không thể có m - V = V - m.
. Ta được kết quả │m - V│ = │V - m│ chứ không thể có m - V = V - m.

\(\left(2x-1\right)^2=\left(2x-1\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left[2x-1+1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-1=0\\2x=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=1\\x=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=0\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{\frac{1}{2};0\right\}\)

\(x\left(2x-1\right)-\left(2x^2+x\right)=-2\)
=>\(2x^2-x-2x^2-x=-2\)
=>-2x=-2
=>x=1
x = 1