Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: A(2;4); B(1;0); C(2;2)
vecto AB=(-1;-4)
vecto DC=(2-x;2-y)
Vì ABCD là hình bình hành nên vecto AB=vecto DC
=>2-x=-1 và 2-y=-4
=>x=3 và y=6
c: N đối xứng B qua C
=>x+1=4 và y+0=4
=>x=3 và y=4

các đáp án đúng lần lượt là:
D. Một đường thẳng đi qua gốc tọa độ.
C. 3
C. 𝑃(0; 1)
D. 𝑓(0) = 5

a) Ta thấy \(\overrightarrow{AB}\left(3;2\right)\) và \(\overrightarrow{AC}\left(4;-3\right)\). Vì \(\dfrac{3}{4}\ne\dfrac{2}{-3}\) nên A, B, C không thẳng hàng.
b) Ta có \(\overrightarrow{BC}\left(1;-5\right)\)
Do vậy \(AB=\left|\overrightarrow{AB}\right|=\sqrt{3^2+2^2}=\sqrt{13}\)
\(AC=\left|\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=\sqrt{4^2+\left(-3\right)^2}=5\)
\(BC=\left|\overrightarrow{BC}\right|=\sqrt{1^2+\left(-5\right)^2}=\sqrt{26}\)
\(\Rightarrow C_{ABC}=AB+AC+BC=5+\sqrt{13}+\sqrt{26}\)
c) Gọi M, N, P lần lượt là trung điểm BC, CA, AB.
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\dfrac{x_A+x_B}{2};\dfrac{y_A+y_B}{2}\right)=\left(-\dfrac{3}{2};3\right)\)
\(N=\left(\dfrac{x_A+x_C}{2};\dfrac{y_A+y_C}{2}\right)=\left(-1;\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(M=\left(\dfrac{x_B+x_C}{2};\dfrac{y_B+y_C}{2}\right)=\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
d) Gọi G là trọng tâm tam giác ABC thì \(G=\left(\dfrac{x_A+x_B+x_C}{3};\dfrac{y_A+y_B+y_C}{3}\right)=\left(-\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{5}{3}\right)\)
e) Gọi \(D\left(x_D;y_D\right)\) là điểm thỏa mãn ycbt.
Để ABCD là hình bình hành thì \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{DC}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3;2\right)=\left(1-x_D;-1-y_D\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3=1-x_D\\2=-1-y_D\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_D=-2\\y_D=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow D\left(-2;-3\right)\)
f) Bạn xem lại đề nhé.

Đáp án A
Gọi G là trọng tâm Δ A B C khi đó G 2 ; 1 ; − 3
Ta có M A → + M B → + M C → = 3 M G → = 3 M G đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất khi M là hình chiếu của G 2 ; 1 ; − 3 liên tục Ox. Suy ra M 2 ; 0 ; 0

Gọi \(M\left(0;m\right)\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AM}=\left(-1;m+2\right)\\\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-5;7\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
3 điểm M;A;B thẳng hàng khi:
\(\dfrac{-1}{-5}=\dfrac{m+2}{7}\Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow M\left(0;-\dfrac{3}{5}\right)\)
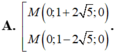
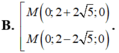
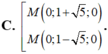
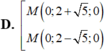
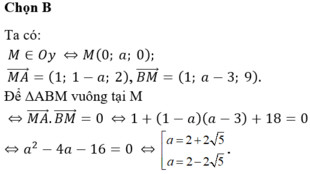
C thuộc Ox nên C(x;0)
CQ=8
=>\(CQ^2=8^2=64\)
=>\(\left(3-x\right)^2+\left(8-0\right)^2=64\)
=>\(\left(3-x\right)^2=0\)
=>3-x=0
=>x=3
=>C(3;0)