Cho phương trình . Tổng tất cả các nghiệm thuộc đoạn của phương trình bằng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Chọn C
Ta có: ![]() nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
Cách 1:
Xét: ![]()
![]() nên (3) vô nghiệm.
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 2:
Điều kiện có nghiệm của phương trình: sin x + cos x = 2 là: 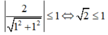
(vô lý) nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 3:
Vì 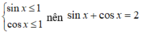
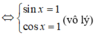
nên (3) vô nghiệm.

\(cosx-\left(3sinx-4sin^3x\right)=\sqrt{2}\left(cosx-sinx\right)sin4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sinx+2sinx\left(2sin^2x-1\right)=\sqrt{2}\left(cosx-sinx\right)sin4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx-sinx-2sinx\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx\right)=\sqrt{2}\left(cosx-sinx\right)sin4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(1-2sinx\left(sinx+cosx\right)-\sqrt{2}sin4x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(1-2sin^2x-2sinx.cosx-\sqrt{2}sin4x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cos2x-sin2x-\sqrt{2}sin4x=0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left[sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-2x\right)-sin4x\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

1.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cos2x-1\right)\left(sinx-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\sinx=3>1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
2. Bạn kiểm tra lại đề, pt này về cơ bản ko giải được.
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{3\left(sinx+\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}\right)}{\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}-sinx}-2cosx=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(1+cosx\right)}{1-cosx}+2\left(1+cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+cosx\right)\left(\dfrac{3}{1-cosx}+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-1\left(loại\right)\\cosx=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm

a.
\(\left(sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}+cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2-2sin^2\dfrac{x}{2}cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2-\left(2sin\dfrac{x}{2}cos\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-sin^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
b.
\(\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)^3-3sin^2x.cos^2x\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)=\dfrac{7}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(2sinx.cosx\right)^2=\dfrac{7}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16-12.sin^22x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-4sin^22x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-2\left(1-cos4x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos4x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=\pm\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)

\(sin^2x-2m.sinx.cosx-sinx.cosx+2mcos^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(sinx-cosx\right)-2mcosx\left(sinx-cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sinx-cosx\right)\left(sinx-2m.cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=cosx\\sinx=2m.cosx\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=1\\tanx=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(tanx=1\) ko có nghiệm đã cho nên \(tanx=2m\) phải có nghiệm trên khoảng đã cho
\(\Rightarrow tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)< 2m< tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow1< 2m< \sqrt[]{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\) (hoặc có thể 1 đáp án là tập con của tập này cũng được)

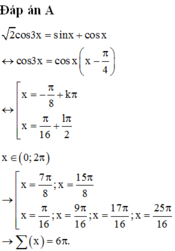

Chọn D.
Phương pháp:
- Sử dụng các công thức nhân ba, phân tích tích thành tổng để biến đổi đơn giản phương trình.
- Giải phương trình, tìm nghiệm thỏa mãn bài toán và tính tổng các nghiệm.