cho hàm số f(f(x)+2y)=4x+4y+3 với mọi số thực x, y. Tìm f(x)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Ta có: \(y=f\left(x\right)=4x^2-5\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(3\right)=4.3^2-5=31\\f\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=4.\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-5=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2-5=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\) thì \(f\left(x\right)=-1\)
c) \(\forall x\in R,f\left(x\right)=f\left(-x\right)\Leftrightarrow f\left(-x\right)=4.\left(-x\right)^2-5=4x^2-5=f\left(x\right)\)
Vậy \(\forall x\in R\) thì \(f\left(x\right)=f\left(-x\right)\)
\(a.f\left(3\right)=4.3^2-5=31.\\ f\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}\right)=4.\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}\right)^2-5=-4.\)
\(b.f\left(x\right)=-1.\Rightarrow4x^2-5=-1.\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2=4.\Leftrightarrow x^2=1.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\pm1.\)
\(c.f\left(x\right)=f\left(-x\right).\\ \Rightarrow4x^2-5=4\left(-x\right)^2-5.\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-5=4x^2-5.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\) (luôn đúng).
Vậy với mọi x ∈ R thì f (x)= f (-x).

Đáp án B
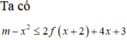
![]()
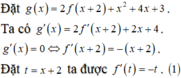
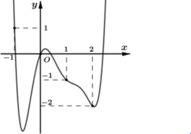
(1) là phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của đồ thị f'(t) và đường thẳng d : y = -t (hình vẽ)
Dựa vào đồ thị của f'(t) và đường thẳng y =-t ta có





Câu 5:
a: Khi m=3 thì \(f\left(x\right)=\left(2\cdot3+1\right)x-3=7x-3\)
\(f\left(-3\right)=7\cdot\left(-3\right)-3=-21-3=-24\)
\(f\left(0\right)=7\cdot0-3=-3\)
b: Thay x=2 và y=3 vào f(x)=(2m+1)x-3, ta được:
\(2\left(2m+1\right)-3=3\)
=>2(2m+1)=6
=>2m+1=3
=>2m=2
=>m=1
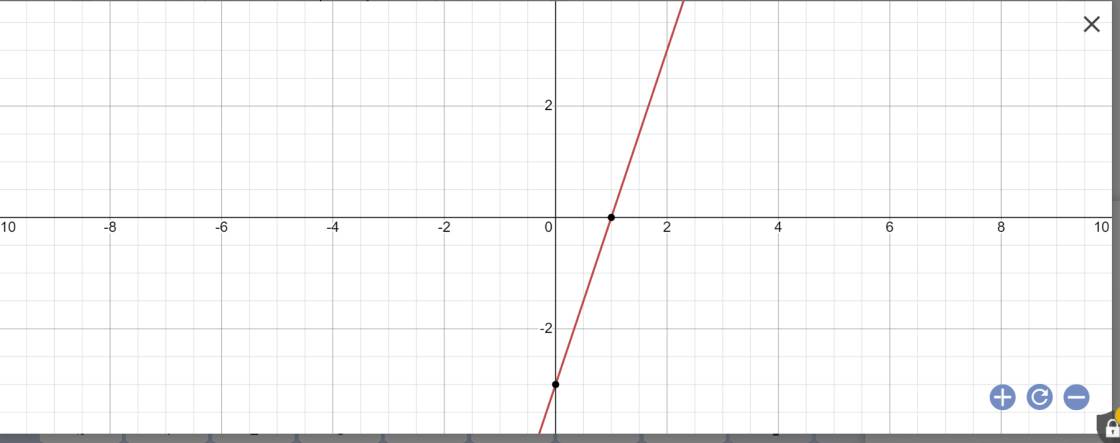
c: Thay m=1 vào hàm số, ta được:
\(y=\left(2\cdot1+1\right)x-3=3x-3\)
*Vẽ đồ thị
d: Để hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 là hàm số bậc nhất thì \(2m+1\ne0\)
=>\(2m\ne-1\)
=>\(m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e: Để đồ thị hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 song song với đường thẳng y=5x+1 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m+1=5\\-3\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2m+1=5
=>2m=4
=>m=2

a) Có: y = f(x) = 4x2 - 3
=> f(-2) = 4 . (-2) - 3
= -11
Vậy f(-2) = -11
b) Có: f(x) = 4x2 - 3
Mà f(x) = 1
=> 4x2 - 3 = 1
<=> 4x2 = 4
<=> x2 = 1
<=> x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Vậy x = 1 hoặc x = -1 thì f(x) = 1.
c) Có: f(x) = 4x2 - 3
Mà f(x) = x
=> 4x2 - 3 = x
<=> 4x2 - 3 - x = 0
<=> (4x2 + 3x) - (4x + 3) = 0
<=> x(4x + 3) - (4x+ 3) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(4x + 3) = 0
<=> x - 1 = 0 hoặc 4x + 3 = 0
<=> x = 1 hoặc 4x = -3
<=> x = 1 hoặc x = \(-\frac{3}{4}\)
Vậy x = 1 hoặc x = \(-\frac{3}{4}\) thì f(x) = x.
Linz
a, \(f\left(-2\right)=4\left(-2\right)^2-3=16-3=13\)
b, \(f\left(x\right)=1\)hay \(f\left(x\right)=4x^2-3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x=\pm1\)
c, \(f\left(x\right)=x\)hay \(4x^2-3=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3-x=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+x^2-3-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x^2-1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[3\left(x+1\right)+x\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=1;-\frac{3}{4}\)
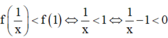
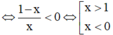
Nhận xét: f(x) là đơn ánh.
Thật vậy, giả sử f(x1)=f(x2) thì: f(f(x1)+2y)=f(f(x2)+2y)
=> 4x1+4y+3=4x2+4y+3<=>x1=x2. Vậy f là đơn ánh
Ta có: f(f(x)+2y)=4x+4y+3=f(f(y)+2x)
Vì f là đơn ánh nên: f(x)+2x=f(y)+2x hay f(x)-2x=f(y)-2y. Với mọi x,y thuộc R
Do đó: f(x)-2x=c, c thuộc R. Thay f(x)=2x+c vào điều kiện ta có c=1
Vậy f(x)=2x+1 (TMĐK)