Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-2\sqrt{2x^2+5x-3}=1+x\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1-2\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}-x\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x-1}\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)-x\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-x\right)\left(\sqrt{2x-1}-2\sqrt{x+3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2x-1}=x\left(x\ge0\right)\\\sqrt{2x-1}=2\sqrt{x+3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=x^2\\2x-1=4\left(x+3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{13}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,ĐK:x\ge\dfrac{4}{3}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x+2=9x^2-24x+16\\ \Leftrightarrow9x^2-25x+14=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{25+\sqrt{569}}{2}\)

\(l,PT\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-3\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\\ 5,ĐK:x\ge-1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2+2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\\ 2,ĐK:x\ge0\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(3\sqrt{x}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\left(3\sqrt{x}+1>0\right)\\ 6,ĐK:x\ge-1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x+1}+1\right)^2}-\sqrt{x+1}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x+1}+2-\sqrt{x+1}=4\left(\sqrt{x+1}+1>0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+1}=2\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)

Gọi \(x\) và \(y\) lần lượt là thời gian (giờ) để vòi 1 và vòi 2 làm đầy bể. Theo đề bài, \(x = y + 3\). Khi mở cả 2 vòi 2 giờ thì bể đầy:
\(2 \left(\right. \frac{1}{x} + \frac{1}{y} \left.\right) = 1 \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \frac{1}{x} + \frac{1}{y} = \frac{1}{2}\)
Thay \(x = y + 3\):
\(\frac{1}{y + 3} + \frac{1}{y} = \frac{1}{2} \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \frac{2 y + 3}{y \left(\right. y + 3 \left.\right)} = \frac{1}{2} \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } 2 \left(\right. 2 y + 3 \left.\right) = y^{2} + 3 y \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } y^{2} - y - 6 = 0\)
Giải phương trình bậc hai: \(y = 3\) (loại nghiệm âm).
Vậy \(x = y + 3 = 6\)


a: =>x>=0 và x^2+x=x^2
=>x=0
a: =>x>=1 và 1-x^2=x^2-2x+1
=>-2x^2+2x=0 và x>=1
=>x=1
a: =>x>=1 và 1-2x^2=x^2-2x+1
=>-3x^2+2x=0 và x>=1
=>\(x\in\varnothing\)
a: ĐKXĐ: x<=2 và x^2-2x=x^2-4x+4
=>x=2
a: =>căn x^2-4=x-2
=>x>=2 và x^2-4=x^2-4x+4
=>x>=2 và 4x=8
=>x=2
b: =>x>=0 và x^2-4x+1=x^2
=>-4x+1=0 và x>=0
=>x=1/4
b: =>x>=-1 và x^2+x+1=x^2+2x+1
=>x=0
c: =>x>=1 và 4x^2-8x+1=x^2-2x+1
=>x>=1 và 3x^2-6x=0
=>x=2
b: =>x>=-1 và 5x^2-2x+2=x^2+2x+1
=>x>=-1 và 4x^2-4x+1=0
=>x=1/2
b: =>căn 4x^2-x+1=2x+3
=>x>=-3/2 và 4x^2-x+1=(2x+3)^2=4x^2+12x+9
=>x>=-3/2 và -13x=8
=>x=-8/13


2:
a: AC=căn 5^2-3^2=4cm
sin B=AC/BC=4/5
cos B=AB/BC=3/5
tan B=4/5:3/5=4/3
cot B=1:4/3=3/4
b: AB=căn 13^2-12^2=5cm
sin B=AC/BC=12/13
cos B=AB/BC=5/13
tan B=12/13:5/13=12/5
cot C=1:12/5=5/12
c: BC=căn 4^2+3^2=5cm
sin B=AC/BC=4/5
cos B=AB/BC=3/5
tan B=4/5:3/5=4/3
cot B=1:4/3=3/4

Gọi số tự nhiên cần tìm là \(\overline{ab}\) ( 0< a; b< 9)
=> Sau khi đổi chỗ ta có số: \(\overline{ba}\)
Theo bài ra ta có: \(\overline{ba}-\overline{ab}=45\)
<=> b.10 + a - a.10 -b = 45
<=> 9 ( b - a ) = 45
<=> b - a = 5
+) a = 1 => b = 6
+) a = 2 => b = 7
+) a = 3 => b = 8
+) a = 4 => b = 9
+) a >4 => b >9 loại
Vậy:...




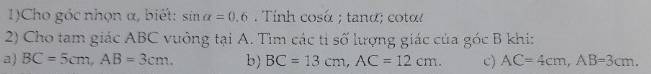
\(3,Đk:x\ge0\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}=2\\\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ 7,ĐK:x\ge0\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{x\left(x+1\right)}\right)+\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-\sqrt{x+1}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)+\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{x+1}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(tm\right)\\x+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(4,ĐK:1\le x\le\sqrt{5}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow5-x^2=x^2-2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-2\left(ktm\right)\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)