Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (d) và (d') là:
\(-2x+5=\dfrac{1}{2}x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x-\dfrac{1}{2}x=-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\dfrac{-5}{2}=-5\)
hay \(x=-5:\dfrac{-5}{2}=-5\cdot\dfrac{2}{-5}=2\)
Thay x=2 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=-2\cdot2+5=-4+5=1\)

\(a,-1< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(d'\right)\text{ nghịch biến trên }R\\ b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }x=-x+2\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;1\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(1;1\right)\text{ là giao 2 đths}\\ c,\text{3 đt đồng quy }\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;1\right)\in\left(d''\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow m-1+2m=1\\ \Leftrightarrow3m=2\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

b: Tọa độ giao là:
2x+5=x+3 và y=x+3
=>x=-2 và y=1
c: Thay x=-2 và y=1 vào (d), ta được:
m-3-6=1
=>m=10

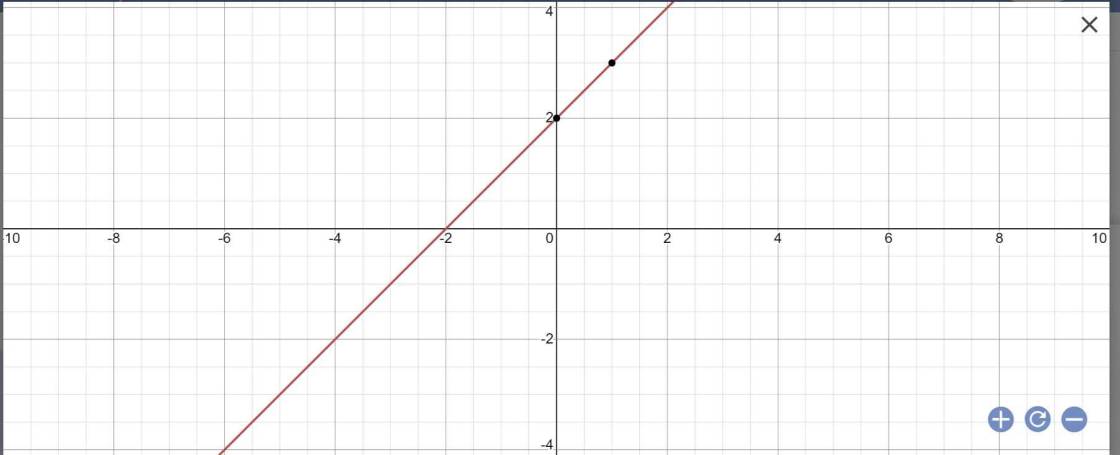
a) Đồ thị:
b) Gọi giao điểm của đồ thị của hàm số y = x - 1 với trục tung, với trục hoành lần lượt là 2 điểm B và C
Thay x = 0 vào hàm số y = x - 1 ta có:
y = 0 - 1 = - 1
⇒ B(0; -1)
Thay y = 0 vào hàm số y = x - 1 ta có:
x - 1 = 0
⇔ x = 1
⇒ C(1; 0)
c) Gọi (t): y = ax + b (a 0)
Do (t) // (d) nên a = -2
⇒ (t): y = -2x + b
Thay y = -3 vào (d') ta có:
x - 1 = -3
⇔ x = -3 + 1
⇔ x = -2
Thay x = -2; y = -3 vào (t) ta có:
-2.(-2) + b = -3
⇔ 4 + b = -3
⇔ b = -3 - 4
⇔ b = -7
Vậy (t): y = -2x - 7

a, Thay x = -2 => y = -2 + 4 = 2 => A(-2;2)
(d) cắt y = x + 4 tại A(-2;2) <=> 2 = -2 ( m + 1 ) - 2
<=> -2m - 2 - 2 = 2 <=> -2m = 6 <=> m = -3
Vậy (d) : y = -2x - 2
b, bạn tự vẽ nhé
c, Cho x = 0 => y = -2
=> (d) cắt trục Oy tại A(0;-2) => OA = | -2 | = 2
Cho y = 0 => x = -1
=> (d) cắt trục Ox tại B(-1;0) => OB = | -1 | = 1
Ta có : \(S_{OAB}=\frac{1}{2}.OA.OB=\frac{1}{2}.2.1=1\)( dvdt )
Đặt: (d): y = (m+5)x + 2m - 10
Để y là hàm số bậc nhất thì: m + 5 # 0 <=> m # -5
Để y là hàm số đồng biến thì: m + 5 > 0 <=> m > -5
(d) đi qua A(2,3) nên ta có:
3 = (m+5).2 + 2m - 10
<=> 2m + 10 + 2m - 10 = 3
<=> 4m = 3
<=> m = 3/4
(d) cắt trục tung tại điểm có tung độ bằng 9 nên ta có:
9 = (m+5).0 + 2m - 10
<=> 2m - 10 = 9
<=> 2m = 19
<=> m = 19/2
(d) đi qua điểm 10 trên trục hoành nên ta có:
0 = (m+5).10 + 2m - 10
<=> 10m + 50 + 2m - 10 = 0
<=> 12m = -40
<=> m = -10/3
(d) // y = 2x - 1 nên ta có:
\hept{m+5=22m−10≠−1\hept{m+5=22m−10≠−1 <=> \hept{m=−3m≠92\hept{m=−3m≠92 <=> m=−3
Giả sử (d) luôn đi qua điểm cố định M(x0; y0)
Ta có: y0=(m+5)x0+2m−10y0=(m+5)x0+2m−10
<=> mx0+5x0+2m−10−y0=0mx0+5x0+2m−10−y0=0
<=> m(xo+2)+5x0−y0−10=0m(xo+2)+5x0−y0−10=0
Để M cố định thì: \hept{x0+2=05x0−y0−10=0\hept{x0+2=05x0−y0−10=0 <=> \hept{x0=−2y0=−20\hept{x0=−2y0=−20
Vậy...

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\\\left(d'\right):y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
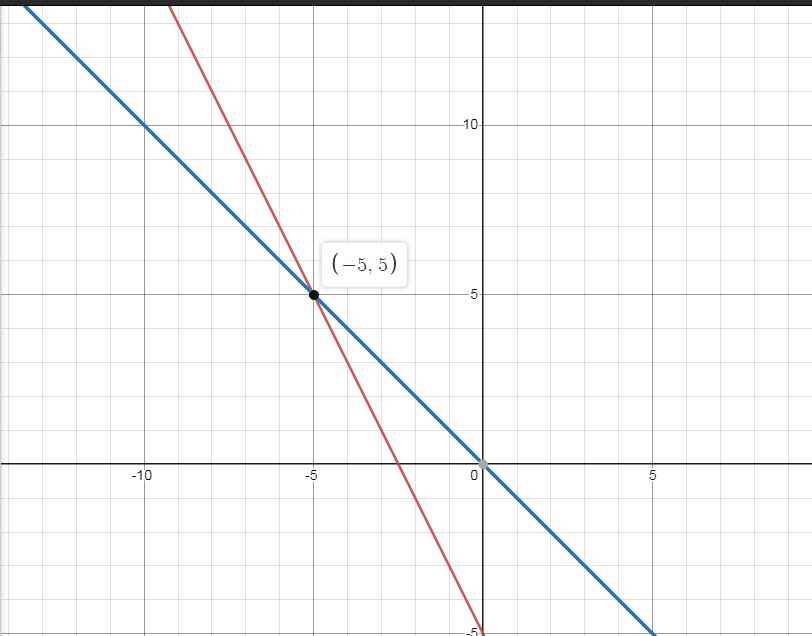
b) \(\left(d\right)\cap\left(d'\right)=M\left(x;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow M\left(-5;5\right)\)
c) Gọi \(\widehat{M}=sđ\left(d;d'\right)\)
\(\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\Rightarrow k_1-2\)
\(\left(d'\right):y=-x\Rightarrow k_1-1\)
\(tan\widehat{M}=\left|\dfrac{k_1-k_2}{1+k_1.k_2}\right|=\left|\dfrac{-2+1}{1+\left(-2\right).\left(-1\right)}\right|=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{M}\sim18^o\)
d) \(\left(d\right)\cap Oy=A\left(0;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=-2.0-5=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow A\left(0;-5\right)\)
\(OA=\sqrt[]{0^2+\left(-5\right)^2}=5\left(cm\right)\)
\(OM=\sqrt[]{5^2+5^2}=5\sqrt[]{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(MA=\sqrt[]{5^2+10^2}=5\sqrt[]{5}\left(cm\right)\)
Chu vi \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(C=OA+OB+MA=5+5\sqrt[]{2}+5\sqrt[]{5}=5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow p=\dfrac{C}{2}=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}p-OA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}-1\right)}{2}\\p-OB=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{2}=\dfrac{5\left(-\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\\p-MA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{5}=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}.\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{25\left[\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}\right)^2-5\right]}{4}=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}\)
\(\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25\left[5-\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)^2\right]}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}\)
Diện tích \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(S=\sqrt[]{p\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)\left(p-MA\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}.\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25^2}{2^2}}=\dfrac{25}{2}=12,5\left(cm^2\right)\)
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
2x-1=x+2 và y=x+2
=>3x=3 và y=x+2
=>x=1 và y=3
a: