
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
\(175\cdot19+38\cdot175+43\cdot175\\ =175\cdot19+175\cdot38+175\cdot43\\ =175\cdot\left(19+38+43\right)\\ =175\cdot100\\ =17500\)
b)
\(125\cdot75+125\cdot13-80\cdot125\\ =125\cdot75+125\cdot13-125\cdot80\\ =125\cdot\left(75+13-80\right)\\ =125\cdot10\\ =125\cdot8\\ =1000\)
a, 175. 19 + 38. 175 + 43. 175
= 175. 19 + 175. 38 + 175. 43
= 175.(19 + 38 + 43)
= 175. 100
= 17500

2/
Xét phân số \(\dfrac{2n-3}{n+1}=\dfrac{2n+2-5}{n+1}=\dfrac{2n+2}{n+1}-\dfrac{5}{n+1}=\dfrac{2\left(n+1\right)}{n+1}-\dfrac{5}{n+1}=2-\dfrac{5}{n+1}\)
\(n\in Z\Rightarrow2n-3\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-1;-5;1;5\right\}\)
Ta có bảng:
| 2n - 3 | -1 | -5 | 1 | 5 |
| n | 1 | -1 | 2 | 4 |
Vậy \(n\in\left\{-1;1;2;4\right\}\)
1/
(x + 1) + (x + 3) + (x + 5) + ... + (x + 999) = 500
<=> (x + x + x + ... + x) + (1 + 3 + 5 + ... + 999) = 500
Xét tổng A = 1 + 3 + 5 + ... + 999
Số số hạng của A là: (999 - 1) : 2 + 1 = 500
Tổng A là: (999 + 1) x 500 : 2 = 250 000
Do A có 500 số hạng nên có 500 ẩn x.
Vậy ta có: 500x + 250 000 = 500
=> 500x = -249 500
=> x = 499
Vậy x = 499


\(a,5^x+5^{x+2}=650\\ \Rightarrow5^x+5^x.5^2=650\\ \Rightarrow5^x\left(1+5^2\right)=650\\ \Rightarrow5^x.26=650\\ \Rightarrow5^x=25\\ \Rightarrow5^x=5^2\\ \Rightarrow x=2\)
\(b,\left(4x+1\right)^2=25.9\\\Rightarrow\left(4x+1\right)^2=225\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+1=15\\4x+1=-15\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,2^x+2^{x+3}=144\\ \Rightarrow2^x+2^x.2^3=144\\ \Rightarrow2^x\left(1+2^3\right)=144\\ \Rightarrow2^x=144:\left(1+2^3\right)\\ \Rightarrow2^x=16\\ \Rightarrow2^x=2^4\\ \Rightarrow x=4\)
\(d,3^{x+2}=9^{x+3}\\ \Rightarrow3^{x+2}=\left(3^2\right)^{x+3}\\ \Rightarrow3^{x+2}=3^{2x+6}\\ \Rightarrow x+2=2x+6\\ \Rightarrow x-2x=6-2\\ \Rightarrow-x=4\\ \Rightarrow x=-4\)
\(e,x^{15}=x^2\\ \Rightarrow x^{15}-x^2=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2\left(x^{13}-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\x^{13}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: =>5^x+5^x*25=650
=>5^x*26=650
=>5^x=25
=>x=2
b: =>4x+1=15 hoặc 4x+1=-15
=>4x=-16 hoặc 4x=14
=>x=7/2 hoặc x=-8
c: =>2^x*9=144
=>2^x=16
=>x=4
d: =>2x+2=2x+6
=>2=6(loại)
e: =>x^2(x^13-1)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=1

f)
`(2x+1)^3=343`
`(2x+1)^3=7^3`
`=>2x+1=7`
`2x=7-1`
`2x=6`
`x=6:2`
`x=3`
g)
`(x-1)^3 =125`
`(x-1)^3 =5^3`
`=>x-1=5`
`x=6`
h)
`2^(x+2)-2^x=96`
`2^x *2^2 -2^x =96`
`2^x (2^2 -1)=96`
`2^x *3=96`
`2^x =32`
`2^x =2^5`
`=>x=5`
i)
`(x-5)^4 =(x-5)^6` (`x>=5`)
`(x-5)^6 -(x-5)^4 =0`
`(x-5)^4 [(x-5)^2 -1]=0`
`=>x-5=0` hoặc `(x-5)^2 -1=0`
`<=>x=5` hoặc `(x-5)^2 =1`
`<=>x=5` hoặc `x-5=1` hoặc `x-5=-1`
`<=>x=5` hoặc `x=6` hoặc `x=4`
j)
`720:[41-(2x-5)]=2^3 *5`
`720:[41-(2x-5)]=8*5`
`720:[41-(2x-5)]=40`
`41-(2x-5)=720:40`
`41-(2x-5)=18`
`2x-5=41-18`
`2x-5=23`
`2x=28`
`x=14`

1: 2⋮x
mà x là số tự nhiên
nên x∈{1;2}
2: 2⋮x+1
=>x+1∈{1;-1;2;-2}
=>x∈{0;-2;1;-3}
mà x>=0
nên x∈{0;1}
3: 2⋮x+2
mà x+2>=2(Do x là số tự nhiên)
nên x+2=2
=>x=0
4: 2⋮x-1
=>x-1∈{1;-1;2;-2}
=>x∈{2;0;3;-1}
mà x>=0
nên x∈{0;2;3}
5: 2⋮x-2
=>x-2∈{1;-1;2;-2}
=>x∈{3;1;4;0}
6: 2⋮2-x
=>2⋮x-2
=>x-2∈{1;-1;2;-2}
=>x∈{3;1;4;0}
Bài 1:
2 ⋮ \(x\)(\(x\) ∈ N*)
2 ⋮ \(x\)
⇒ \(x\) ∈ Ư(2) = {-2; -1; 1; 2}
Vì \(x\) ∈ N* nên \(x\) ∈ {1; 2}
Vậy \(x\) ∈ {1; 2}

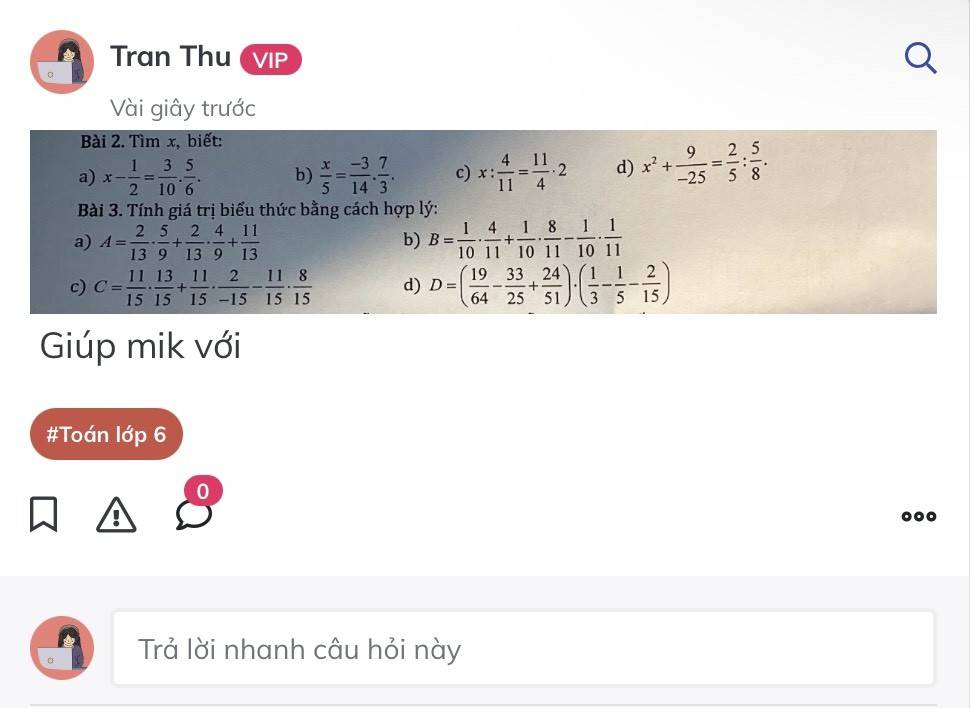
Bài 2:
a; \(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{10}\).\(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(x\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
b; \(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{14}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) \(\times\) 5
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\);
c; \(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) \(\times\) 2
\(x\) : \(\dfrac{4}{11}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{11}{2}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{4}{11}\)
\(x\) = 2
Vậy \(x\) = 2
d; \(x^2\) + \(\dfrac{9}{-25}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\) : \(\dfrac{5}{8}\)
\(x^2\) - \(\dfrac{9}{25}\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{16}{25}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = \(\dfrac{25}{25}\)
\(x^2\) = 1
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\)\(\in\) {-1; 1}
Bài 3:
a; A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\) \(\dfrac{5}{9}\)+ \(\dfrac{2}{13}\)\(\times\)\(\dfrac{4}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\)(\(\dfrac{5}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) \(\times\) \(\dfrac{9}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = \(\dfrac{2}{13}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
A = 1
b; B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{10}\).\(\dfrac{1}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{4}{11}\) + \(\dfrac{8}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x (\(\dfrac{12}{11}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{11}\))
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) x \(\dfrac{11}{11}\)
B = \(\dfrac{1}{10}\)

a) \(\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\dfrac{5}{7}+\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\dfrac{2}{7}+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot\left(\dfrac{5}{7}+\dfrac{2}{7}\right)+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}\cdot1+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{5}{11}+\dfrac{6}{11}=\dfrac{11}{11}=1\)
b) \(\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{6}{11}+\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{9}{11}-\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{4}{11}=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\left(\dfrac{6}{11}+\dfrac{9}{11}-\dfrac{4}{11}\right)=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot\dfrac{11}{11}=\dfrac{3}{13}\cdot1=\dfrac{3}{13}\)
c) \(\dfrac{-5}{6}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}+\dfrac{7}{12}\cdot\dfrac{4}{-19}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{-5}{6}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}+\dfrac{-7}{12}\cdot\dfrac{4}{19}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{4}{19}\cdot\left(\dfrac{-5}{6}+\dfrac{-7}{12}\right)-\dfrac{40}{57}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{19}\cdot\dfrac{-17}{12}-\dfrac{40}{47}=\dfrac{-17}{57}-\dfrac{40}{57}=\dfrac{-57}{57}=-1\)
d) \(\left(\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{4}{9}\cdot\dfrac{11}{-4}\right)\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}=\left(\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{-4}{9}\cdot\dfrac{11}{4}\right)\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}=\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}\cdot\left(\dfrac{-5}{9}+\dfrac{-4}{9}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{11}{4}\cdot\dfrac{8}{33}\cdot1=\dfrac{11\cdot8}{4\cdot33}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
e) \(\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{12}{61}-\dfrac{31}{22}+\dfrac{14}{91}\right)\cdot0=0\)
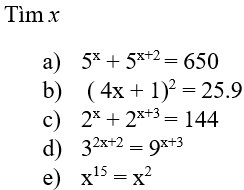
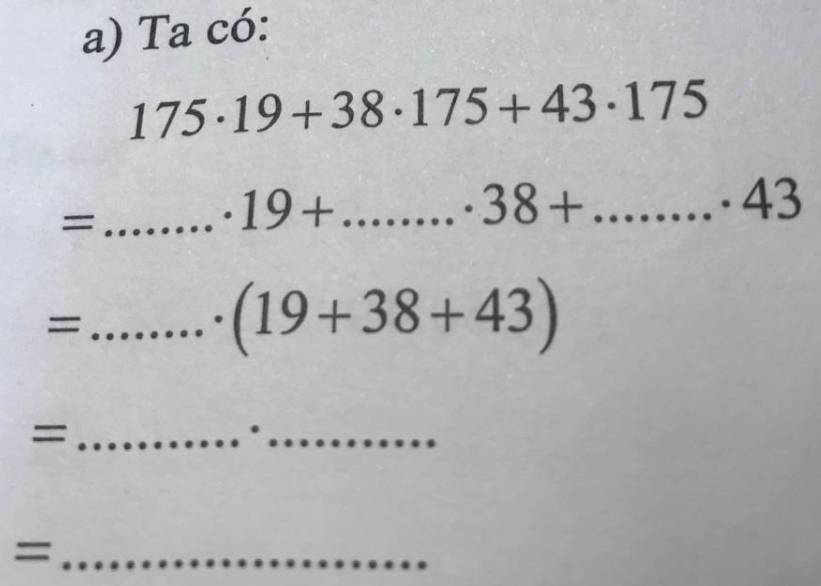
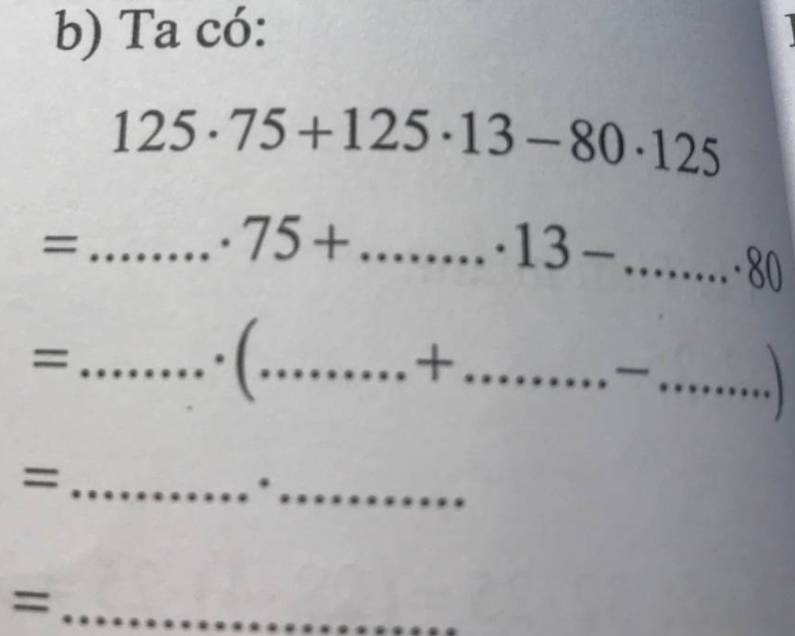
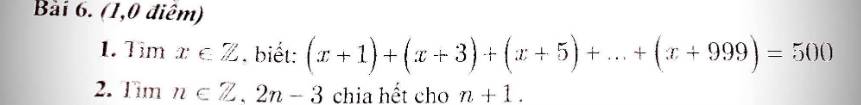
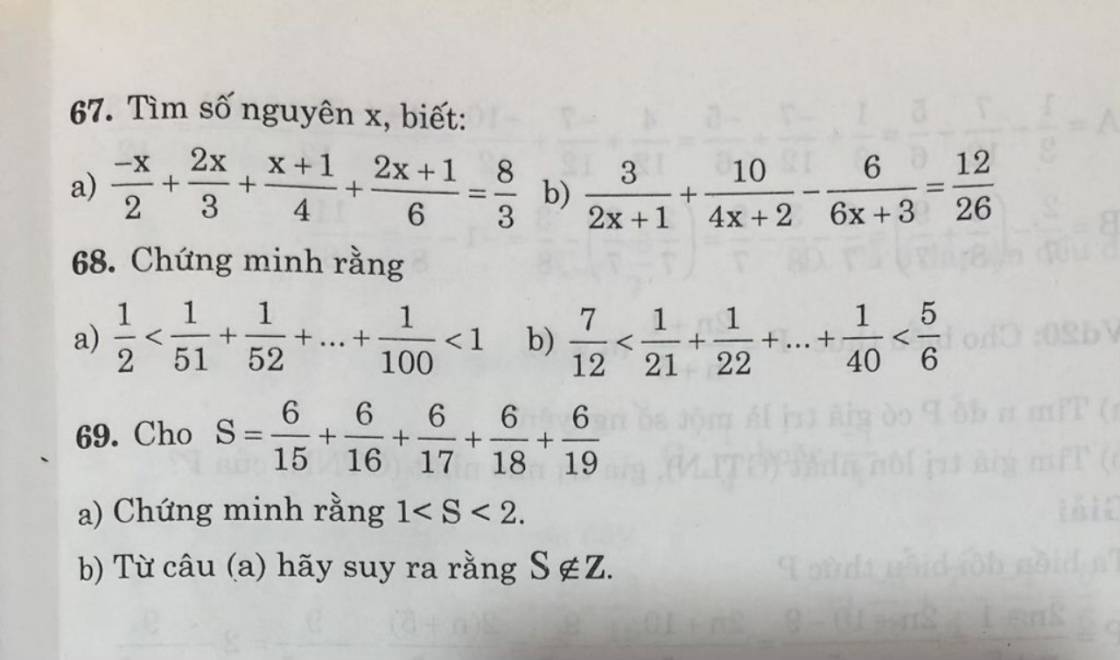
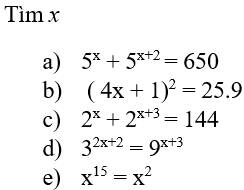
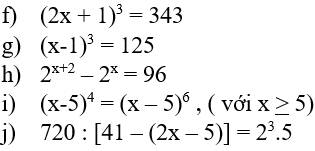

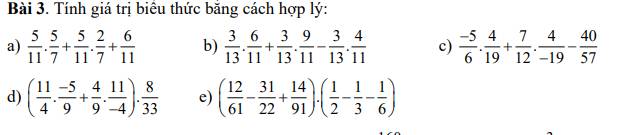
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`a)`
\(5^x+5^{x+2}=650\)
`\Rightarrow 5^x + 5^x . 5^2 = 650`
`\Rightarrow 5^x . (1 + 5^2) = 650`
`\Rightarrow 5^x . 26 = 650`
`\Rightarrow 5^x = 650 \div 26`
`\Rightarrow 5^x = 25`
`\Rightarrow 5^x = 5^2`
`\Rightarrow x = 2`
Vậy, `x = 2`
`b)`
`(4x + 1)^2 = 25.9`
`\Rightarrow (4x + 1)^2 = 225`
`\Rightarrow (4x + 1)^2 = (+-15^2)`
`\Rightarrow`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x-1=15\\4x-1=-15\end{matrix}\right.\)
`\Rightarrow `\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=16\\4x=-14\end{matrix}\right.\)
`\Rightarrow `\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy, `x \in`\(\left\{-\dfrac{7}{2};4\right\}\)
`c)`
\(2^x+2^{x+3}=144\)
`\Rightarrow 2^x + 2^x . 2^3 = 144`
`\Rightarrow 2^x . (1 + 2^3) = 144`
`\Rightarrow 2^x . 9 = 144`
`\Rightarrow 2^x = 144 \div 9`
`\Rightarrow 2^x = 16`
`\Rightarrow 2^x = 2^4`
`\Rightarrow x = 4`
Vậy, `x = 4`
`d)`
\(3^{2x+2}=9^{x+3}\)
`\Rightarrow `\(3^{2x+2}=\left(3^2\right)^{x+3}\)
`\Rightarrow `\(3^{2x+2}=3^{2x+6}\)
`\Rightarrow 2x + 2 = 2x + 6`
`\Rightarrow 2x - 2x = 6 - 2`
`\Rightarrow 0 = 4 (\text {vô lý})`
Vậy, `x` không có giá trị nào thỏa mãn.
`e)`
\(x^{15}=x^2\)
`\Rightarrow `\(x^{15}-x^2=0\)
`\Rightarrow `\(x^2\cdot\left(x^{13}-1\right)=0\)
`\Rightarrow `\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\x^{13}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
`\Rightarrow `\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^{13}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
`\Rightarrow `\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy, `x \in`\(\left\{0;1\right\}.\)