Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.
tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất và giá trị lớn nhất của các hàm số sau:
a/ y =
#Hỏi cộng đồng OLM
#Toán lớp 11
Bài 1. Trong các dãy số sau đây, dãy số nào là cấp số cộng? Tính số hạng đầu và công sai của nó:
a) un = 5 - 2n; b) un =
#Hỏi cộng đồng OLM
#Toán lớp 11

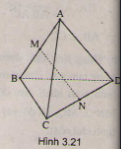
Cho tứ diện ABCD có AB = AC = AD và
#Hỏi cộng đồng OLM
#Toán lớp 11

a) Hàm số f(x) = xác định trên R\{
} và ta có x = 4 ∈ (
;+∞).
Giả sử (xn) là dãy số bất kì và xn ∈ (;+∞); xn ≠ 4 và xn → 4 khi n → +∞.
Ta có lim f(xn) = lim =
=
.
Vậy
=
.
b) Hàm số f(x) = xác định trên R.
Giả sử (xn) là dãy số bất kì và xn → +∞ khi n → +∞.
Ta có lim f(xn) = lim = lim
= -5.
Vậy
= -5.

\(lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{x^3+2x-3}{x^2-x}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+3\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{x^2+x+3}{x}\)
\(=\frac{1^2+1+3}{1}\)
\(=5\)
\(lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\sqrt{2x+2}-\sqrt{3x+1}}{x-1}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\left(2x+2\right)-\left(3x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}\right)}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{2x+2-3x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}\right)}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}\right)}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{-1\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}\right)}\)
\(=lim_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{-1}{\left(\sqrt{2x+2}+\sqrt{3x+1}\right)}\)
\(=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2\cdot1+2}+\sqrt{3\cdot1+1}}\)
\(=\frac{-1}{2+2}=\frac{-1}{4}\)

a) Học sinh tự vẽ hình. Đồ thị hàm số y = f(x) là một đường không liền nét mà bị đứt quãng tại x0 = -1. Vậy hàm số đã cho liên tục trên khoảng (-∞; -1) và (- 1; +∞).
b) +) Nếu x < -1: f(x) = 3x + 2 liên tục trên (-∞; -1) (vì đây là hàm đa thức).
+) Nếu x> -1: f(x) = x2 - 1 liên tục trên (-1; +∞) (vì đây là hàm đa thức).
+) Tại x = -1;
Ta có f(x) =
(3x + 2) = 3(-1) +2 = -1.
f(x) =
(x2 - 1) = (-1)2 - 1 = 0.
Vì f(x) ≠
f(x) nên không tồn tại
f(x). Vậy hàm số gián đoạn tại
x0 = -1.

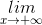 (x4 – x2 + x - 1) =
(x4 – x2 + x - 1) =  ) = +∞.
) = +∞.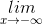 (-2x3 + 3x2 -5 ) =
(-2x3 + 3x2 -5 ) = 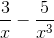 ) = +∞.
) = +∞.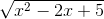 =
= 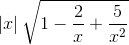 = +∞.
= +∞. =
= 
 =
= 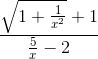 = -1.
= -1.
Mình đăng nhầm