x,y thuộc N
(2x+1).(3y-2)=12
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1)
xy + x - 4y = 12
x + y(x - 4) = 12
y(x - 4) = 12 - x
\(y=\dfrac{-x+12}{x-4}\)
Vì \(x,y\inℕ\) nên
\(\left(-x+12\right)⋮\left(x-4\right)\)
\(\left(-x+12\right)-\left(x-4\right)⋮\left(x-4\right)\)
\(16⋮\left(x-4\right)\)
\(\left(x-4\right)\inƯ\left(16\right)\)
\(\left(x-4\right)\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4;8;-8;16;-16\right\}\)
\(x\in\left\{5;3;6;2;8;0;12;-4;20;-12\right\}\)
\(y\in\left\{\dfrac{-5+12}{5-4};\dfrac{-3+12}{3-4};\dfrac{-6+12}{6-4};\dfrac{-2+12}{2-4};\dfrac{-8+12}{8-4};\dfrac{-0+12}{0-4};\dfrac{-12+12}{12-4};\dfrac{4+12}{-4-4};\dfrac{-20+12}{20-4};\dfrac{12+12}{-12-4}\right\}\)
\(y\in\left\{7;-9;3;-5;1;-3;0;-2;-\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{7}{5}\right\}\)
\(\left(x;y\right)\in\left\{\left(5;7\right);\left(3;-9\right);\left(6;3\right);\left(2;-5\right);\left(8;1\right);\left(0;-3\right);\left(12;0\right);\left(-4;-2\right);\left(20;-\dfrac{1}{2}\right);\left(-12;-\dfrac{7}{5}\right)\right\}\)
Mà \(x,y\inℕ\) nên các giá trị cần tìm là \(\left(x;y\right)\in\left\{\left(5;7\right);\left(6;3\right);\left(8;1\right);\left(12;0\right)\right\}\)
2)
(2x + 3)(y - 2) = 15
\(\left(2x+3\right)\inƯ\left(15\right)\)
\(\left(2x+3\right)\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3;5;-5;15;-15\right\}\)
Ta lập bảng
| 2x + 3 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 | 5 | -5 | 15 | -15 |
| y - 2 | 15 | -15 | 5 | -5 | 3 | -3 | 1 | -1 |
| (x; y) | (-1; 17) | (-2; -13) | (0; 7) | (-3; -3) | (1; 5) | (-4; -1) | (6; 3) | (-9; 1) |
Mà \(x,y\inℕ\) nên các giá trị cần tìm là \(\left(x;y\right)\in\left\{\left(0;7\right);\left(1;5\right);\left(6;3\right)\right\}\)

a) ( 2 x + 1 ) ( 3 y − 2 ) = − 55
Suy ra ( 2 x + 1 ) v à ( 3 y − 2 ) ∈ Ư ( - 55 ) = 1 ; − 1 ; 5 ; − 5 ; 11 ; − 11 ; 55 ; − 55
Khi đó ta có bảng sau:
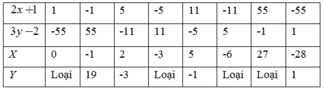
b) ( x − 3 ) ( 2 y + 1 ) = 7
Suy ra ( x − 3 ) và ( 2 y + 1 ) ∈ Ư ( 7 ) = 1 ; − 1 ; 7 ; − 7
Khi đó ta có bảng sau
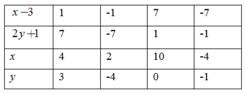
c) y ( y 4 + 12 ) = − 5
Suy ra ( y 4 + 12 ) ∈ Ư ( - 5 ) = 1 ; − 1 ; 5 ; − 5
Vì y 4 ≥ 0 ⇒ y 4 + 12 ≥ 12 ⇒ không có giá trị của y thỏa mãn ycbt.

a) Ta có bảng sau:
| x-1 | -5 | 5 | 1 | -1 |
| y+4 | -1 | 1 | 5 | -5 |
| x | -4 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| y | -5 | -3 | 1 | -9 |
Vậy:
b) Ta có bảng sau:
| 2x+3 | 11 | -11 | 1 | -1 |
| y-2 | 1 | -1 | 11 | -11 |
| x | 4 | -7 | -1 | -2 |
| y | 3 | 1 | 13 | -9 |
Vậy: ...
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`a)`
`(x-1)(y+4) = 5`
`=> (x-1)(y+4) \in \text {Ư(5)} = +-1; +-5`
Ta có bảng sau:
| \(x-1\) | \(1\) | \(5\) | \(-1\) | \(-5\) |
| \(y+4\) | \(-5\) | \(-1\) | \(5\) | \(1\) |
| \(x\) | `2` | `6` | `0` | `-4` |
| `y` | `-9` | `-5` | `1` | `-8` |
Vậy, ta có các cặp `x,y` thỏa mãn `{2; -9}; {6; -5}; {0; 1}; {-4; -8}`


a, y2 = 3 - |2x - 3|
=> y2 + |2x - 3| = 3
Mà y2 > hoặc = 0
|2x - 3| > hoặc = 0
Do đó: {y2; |2x - 3|} thuộc {(1; 2); (2; 1); (0; 3); (3; 0)}
Mà x thuộc Z => 2x - 3 là số lẻ => |2x - 3| là số lẻ
=> |2x - 3| thuộc {1; 3}
+ |2x - 3| = 1
=> y2 = 2 (vô lí vì y thuộc Z)
+ |2x - 3| = 3
=> y2 = 1`
=> 2x - 3 thuộc {3; -3}
và y thuộc {1; -1}
=> x thuộc {3; 0}
và y thuộc {1; -1}
b, Phần b tương tự mà làm thôi

1)(x-3)(y+2)=-6
Ta xét bảng sau:
| x-3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | -1 | -2 | -3 | -6 |
| x | 4 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -3 |
| y+2 | -6 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| y | -8 | -5 | -4 | -3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
2)(5-x)(4-y)=-5
Ta xét bảng sau:
| 5-x | 1 | 5 | -1 | -5 |
| x | 4 | 0 | 6 | 10 |
| 4-y | -5 | -1 | 5 | 1 |
| y | 9 | 5 | -1 | 3 |
3)4) tương tự

Bài 1:
a,x + ( x + 1) + (x + 2) + (x + 3) +....+ (x + 30) = 1240
x + x +x +.... + x + (1 + 2+ 3+ ....+ 30) = 1240
31x + 465 =1240
31x = 1240 - 465
31x = 775
x = 775 : 31
x = 25
b, Đề sai, bạn xem lại đề nhé.
bài 1 câu b
1+2+3+...+x=40
\(\frac{x.\left(x+1\right)}{2}\)=40
x.(x+1)=40.2
x.(x+1)=80
x.(x+1)=?
cậu viết đề sai thì phải

\(a,3x^2-6x\)
\(=3x\left(x-2\right)\)
\(b,18x^2-4x+12\)
\(=2\left(9x^2-2x+6\right)\)
\(c,4x^2\left(2x-y\right)-12x\left(2x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-y\right)\left(4x^2-12x\right)\)
\(=4x\left(2x-y\right)\left(x-3\right)\)
\(d,7\left(x-3y\right)-2y\left(3y-x\right)\)
\(=7\left(x-3y\right)+2y\left(x-3y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-3y\right)\left(2y+7\right)\)
\(f,6\left(x-2y\right)-3\left(2y-x\right)\)
\(=6\left(x-2y\right)+3\left(x-2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2y\right)\left(6+3\right)=9\left(x-2y\right)\)

a) giải:
2x(3y-2) + (3y-2) = -55
=>(2x+1)(3y-2) =-55
=>3y-2 E Ư(-55) = {-1;-5;-11;-55;1;5;11;55}
Mà 3y -2 chia cho 3 dư 1
=> 3y - 2 E {-1;-5;-11;-55}
Vậy:(x,y) E {(5;-1) ; (2;-3) ; (-28 - 1) ; (-1;19)}