giải phương trình này
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


pt: \(\left(1-2x\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}1-2x=0\\x+3=0\\x^2+2=0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=-3\\x^2=-2\left(loại\right)\end{cases}}\)
vậy: \(x=\frac{1}{2}\),\(x=-3\)

\(\dfrac{x+4}{5}-x+4=\dfrac{x}{3}-\dfrac{x-2}{2}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{x+4}{5}-\dfrac{5x}{5}+\dfrac{20}{5}=\dfrac{2x}{6}-\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{-4x+24}{5}=\dfrac{-x+6}{6}\Leftrightarrow6\cdot\left(-4x+24\right)=5\cdot\left(-x+6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-24x+144=-5x+30\(\Leftrightarrow\)-24x+5x=30-144\(\Leftrightarrow\)-19x=-114\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=6

Ta có: I(-1,5; 4,5), J(1; 2)
*x = -1,5 là nghiệm của phương trình 2 x 2 + x – 3 = 0 vì:
2 - 1 , 5 2 + (-1,5) – 3 = 4,5 – 4,5 = 0
*x = 1 là nghiệm của phương trình 2 x 2 + x – 3 = 0 vì:
2. 1 2 + 1 – 3 = 3 – 3 = 0

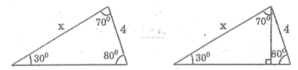
Từ đỉnh của góc 70 ° , kẻ đường cao của tam giác.
Sử dụng tỉ số sin của các góc, ta có phương trình: xsin 30 ° = 4sin 80 °

Đk: \(x\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(4x-5\right)}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+\left(4x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt{x-1}+1}+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)(Dễ thấy ngoặc to lớn hơn 0 với \(x\ge1\))

\(\dfrac{x^2+2}{x^2+4}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+2=0\)
Ta có: \(x^2\ge0;2>0\Rightarrow x^2+2>0\)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x^3-3\left|y+1\right|=18\\2x^3+3\left|y+1\right|=22\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x^3=40\\2x^3+3\left|y+1\right|=22\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3=8\\2x^3+3\left|y+1\right|=22\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3=8\\\left|y+1\right|=2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=5\\\dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{2}{x-y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=5\\\dfrac{2}{x-y}=\dfrac{12}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=5\\6\left(x-y\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=5\\x-y=\dfrac{5}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{35}{6}\\y=x-\dfrac{5}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{35}{12}\\y=\dfrac{25}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
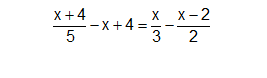
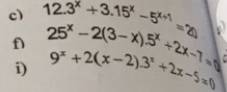
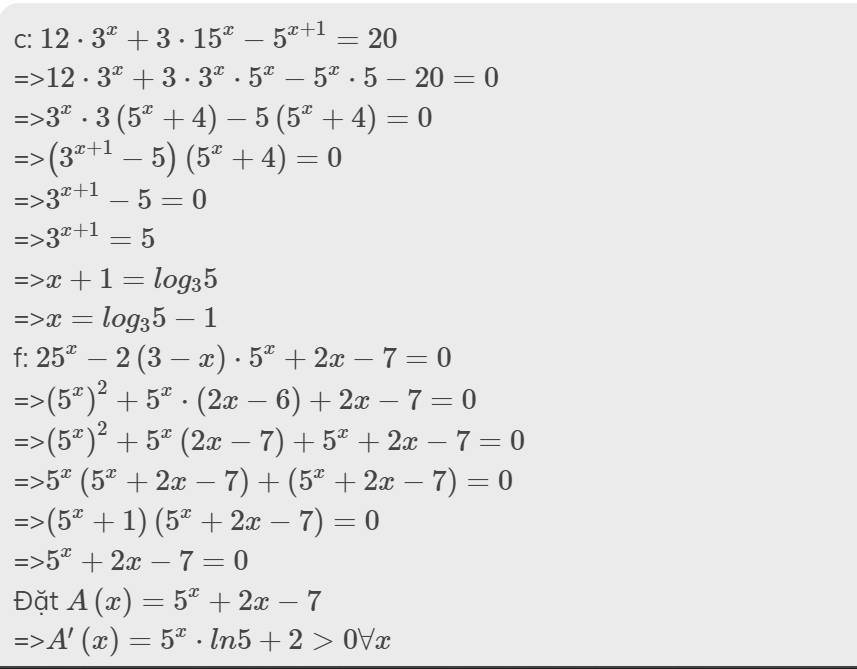

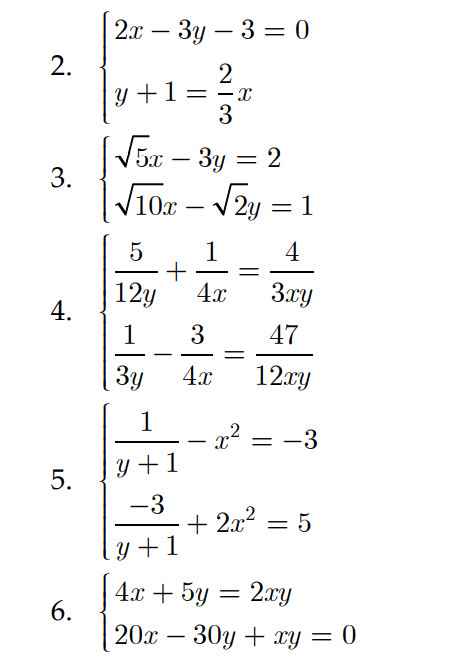
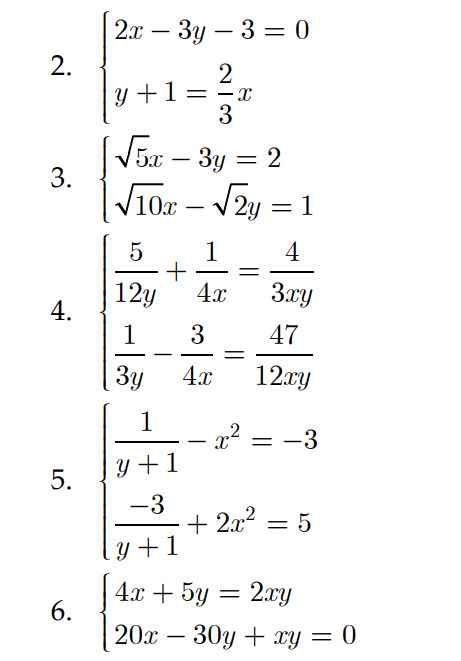
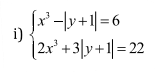
ĐKXĐ: x∉{2;-1;-2}
Ta có: \(\frac{3}{x^2-x-2}+\frac{3}{x^2+3x+2}=\frac{3}{x^2+4}\)
=>\(\frac{1}{x^2-x-2}+\frac{1}{x^2+3x+2}=\frac{1}{x^2+4}\)
=>\(\frac{1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{1}{x^2+4}\)
=>\(\frac{x+2+x-2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{1}{x^2+4}\)
=>\(\frac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{1}{x^2+4}\)
=>\(2x\left(x^2+4\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4\right)\)
=>\(2x^3+8x=x^3-4x-x^2+4\)
=>\(x^3+x^2+12x-4=0\)
=>x≃0,32(nhận)