2x+1/x + x/2x+1=2 giải phương trình trên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x-5=\frac{1}{3\left(x+2\right)}\left(đkxđ:x\ne-2\right)\)
\(< =>3\left(x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=1\)
\(< =>3\left(x^2-3x-10\right)=1\)
\(< =>x^2-3x-10=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(< =>x^2-3x-\frac{31}{3}=0\)
giải pt bậc 2 dễ r
\(\frac{x}{3}+\frac{x}{4}=\frac{x}{5}-\frac{x}{6}\)
\(< =>\frac{4x+3x}{12}=\frac{6x-5x}{30}\)
\(< =>\frac{7x}{12}=\frac{x}{30}< =>12x=210x\)
\(< =>x\left(210-12\right)=0< =>x=0\)

Ta có:\(\left(2x-5\right)\left(\sqrt{x+3}-1\right)=2x^2-x-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(\sqrt{x+3}-1\right)-\left(2x^2-x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right).\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)}{\sqrt{x+3}+1}-\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+3}+1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=0\\x+2=0\\\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+3}+1}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-2\\\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+3}+1}=1\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải (1) ta có:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow1=\sqrt{x+3}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Vậy,phương trình có 3 nghiệm là.....

Bài này có trong báo THTT và đang trong thời hạn giải nên mình nghĩ bạn không nên đăng hỏi.
Với lại bài này có số mũ thực nên không thể là bài lớp 9.
Với lớp 12 thì đây là 1 bài toán rất dễ
Nhưng lớp 9 thì nan giải :D

a, 3x - 2x < 6 <=> x < 6
b, đk : x khác -1 ; 3
=> x^2 - 3x = x^2 - x - 2
<=> -2x = -2 <=> x = 1 (tm)

a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
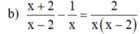
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
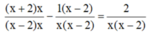
![]()
![]()
![]()
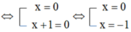
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}

\(\dfrac{x}{2x-6}-\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1,x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\cdot2}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm , trừ x = -1,x = 3
Vậy ...
\(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< \dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\cdot\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< 12\cdot\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-12\cdot\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 4\left(9x+1\right)-3\left(8x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 36x+4-24x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-12x< 1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x< 0\)
Vậy S = {x | x \(\in R\)}

\(2x+\left|3-x\right|=x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+\left[-\left(3-x\right)\right]=x+1\\2x+\left(3-x\right)=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3+x=x+1\\2x+3-x=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\0x=-2\left(vô.lí\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm của pt là \(S=\left\{2\right\}\)


Điều kiện: \(x\ne0;x\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{x}+\dfrac{x}{2x+1}=2\)
\(\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}{x\left(2x+1\right)}+\dfrac{x\cdot x}{x\left(2x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x+1\right)+x^2}{x\left(2x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\dfrac{4x^2+4x+1+x^2}{x\left(2x+1\right)}=2\)
\(\dfrac{5x^2+4x+1}{x\left(2x+1\right)}=2\\ 5x^2+4x+1=2x\left(2x+1\right)\\ 5x^2+4x+1=4x^2+2x\\ x^2+2x+1=0\\ \left(x+1\right)^2=0\\ x+1=0\)
`x = 0 - 1 = -1 (` Thỏa mãn điều kiện `)`