(3x2 -12)(7 - x) = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) (*) m = 0 => x = \(\dfrac{7}{8}\) (loại)
(*) \(m\ne0\) Phương trình có nghiệm
\(\Delta=\left[2\left(m-4\right)\right]^2-4m\left(m+7\right)=-60m+64\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{16}{15}\)
Hệ thức Viet kết hợp 4x1 + 3x2 = 1
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1x_2=\dfrac{m+7}{m}\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{8-2m}{m}\\x_1=2x_2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1x_2=\dfrac{m+7}{m}\\x_1=\dfrac{16-4m}{3m}\\x_2=\dfrac{8-2m}{3m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16-4m}{3m}.\dfrac{8-2m}{3m}=\dfrac{m+7}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(8-2m\right)^2=9m\left(m+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8m^2-64m+128=9m^2+63m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+127m-128=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=128\left(\text{loại}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> m = 1

a: \(x^2+3y^2-4x+6y+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4+3y^2+6y+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2+3\left(y+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)=\left(-2;1\right)\)

a) \(\left(x+5\right).6-7=29\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right).6=29+7\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right).6=36\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)=36:6=6\)
\(\Rightarrow x=6-5=1\)
b) \(5x-3x=12-3.2\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=6\Rightarrow x=6:2=3\)
c) \(\dfrac{1}{4}.3< x< \dfrac{51}{50}.4\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{4}< x< \dfrac{102}{25}\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow2x^2+10x-2x^2=12\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{12}{10}=\dfrac{6}{5}\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(5-2x-4\right)\left(5-2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1-2x\right)\left(9-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x^2+6x=36\Leftrightarrow x=6\\ d,\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2-x\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ e,\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-4x^2+196=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-4x=-197\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{197}{4}\)
\(f,\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x+16-x^2+1=16\Leftrightarrow8x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{8}\\ g,Sửa:\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1-x-1\right)\left(3x+1+x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x\left(4x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ h,\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-x-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\\ i,\Leftrightarrow2x^2-13x+15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x-15x-15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-15\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{15}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Để hàm số nghịch biến với mọi x < 0 thì a > 0
nên m − 7 − 3 > 0
m – 7 < 0 (do −3 < 0) ⇔ m < 7
Vậy m < 7 thỏa mãn điều kiện đề bài
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

a, 12 - (2\(x^2\) - 3) = 7
2\(x^2\) - 3 = 12 - 7
2\(x^2\) - 3 = 5
2\(x^2\) = 8
\(x^2\) = 4
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,x^2=5\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{5}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{5}\right\}\)
\(b,3x^2-12=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2=12\Leftrightarrow x^2=4\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm2\right\}\)
\(c,4x^2-3=-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) (loại)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm.
\(d,5x^2-3=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{0\right\}\)
a)
`x^2 =5`
`=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{5}\\x=-\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)
`3x^2 -12=0`
`<=>3x^2 =12`
`<=>x^2 =4`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)
`4x^2 -3=-9`
`<=>4x^2 =-6`
`<=>x^2 =-3/2` (vô lí vì `x>=0AA x` )
d)
`5x^2 -3=3`
`<=>5x^2 =0`
`<=>x^2 =0`
`<=>x=0`
 Bài 1.
Bài 1.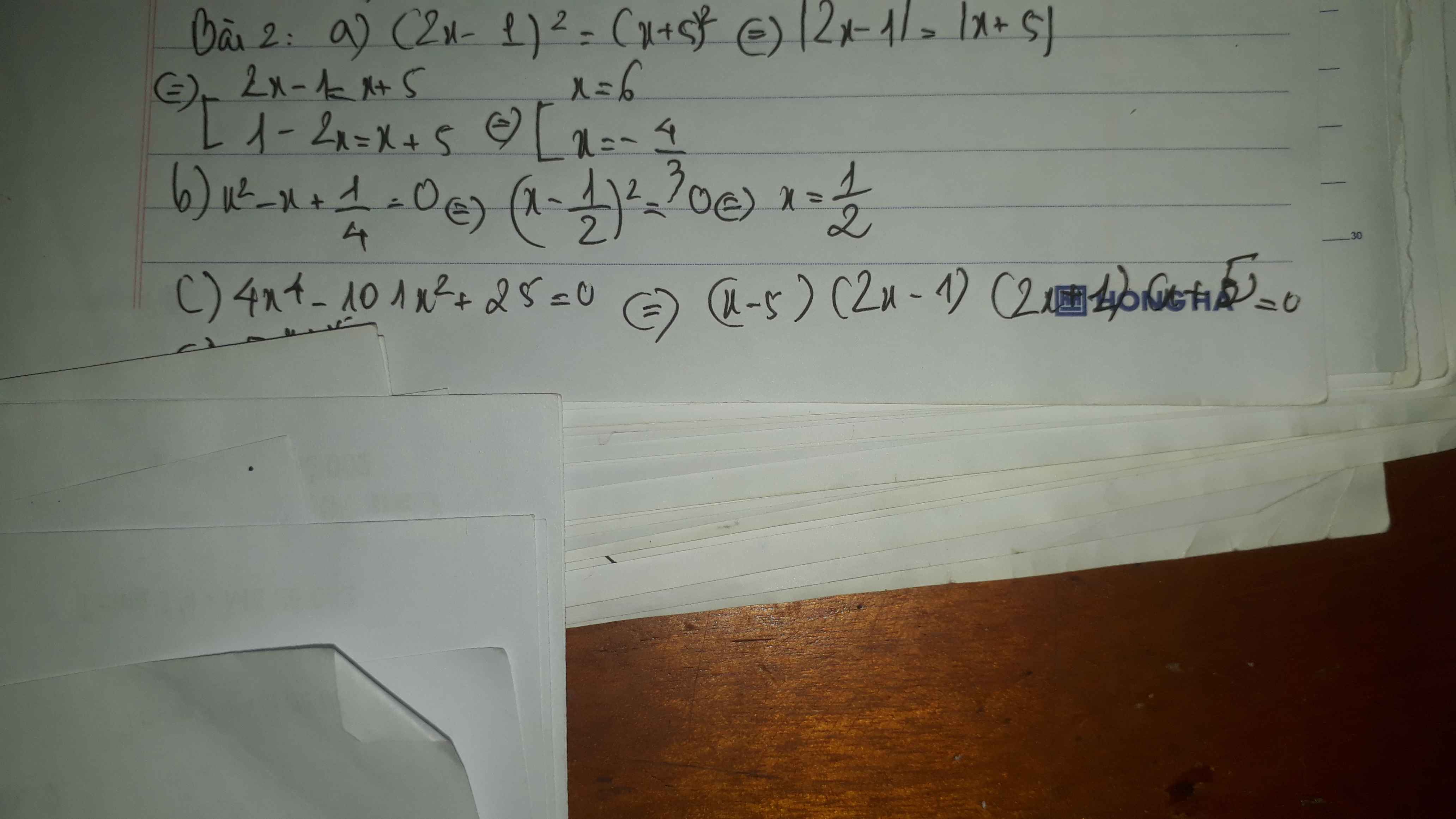
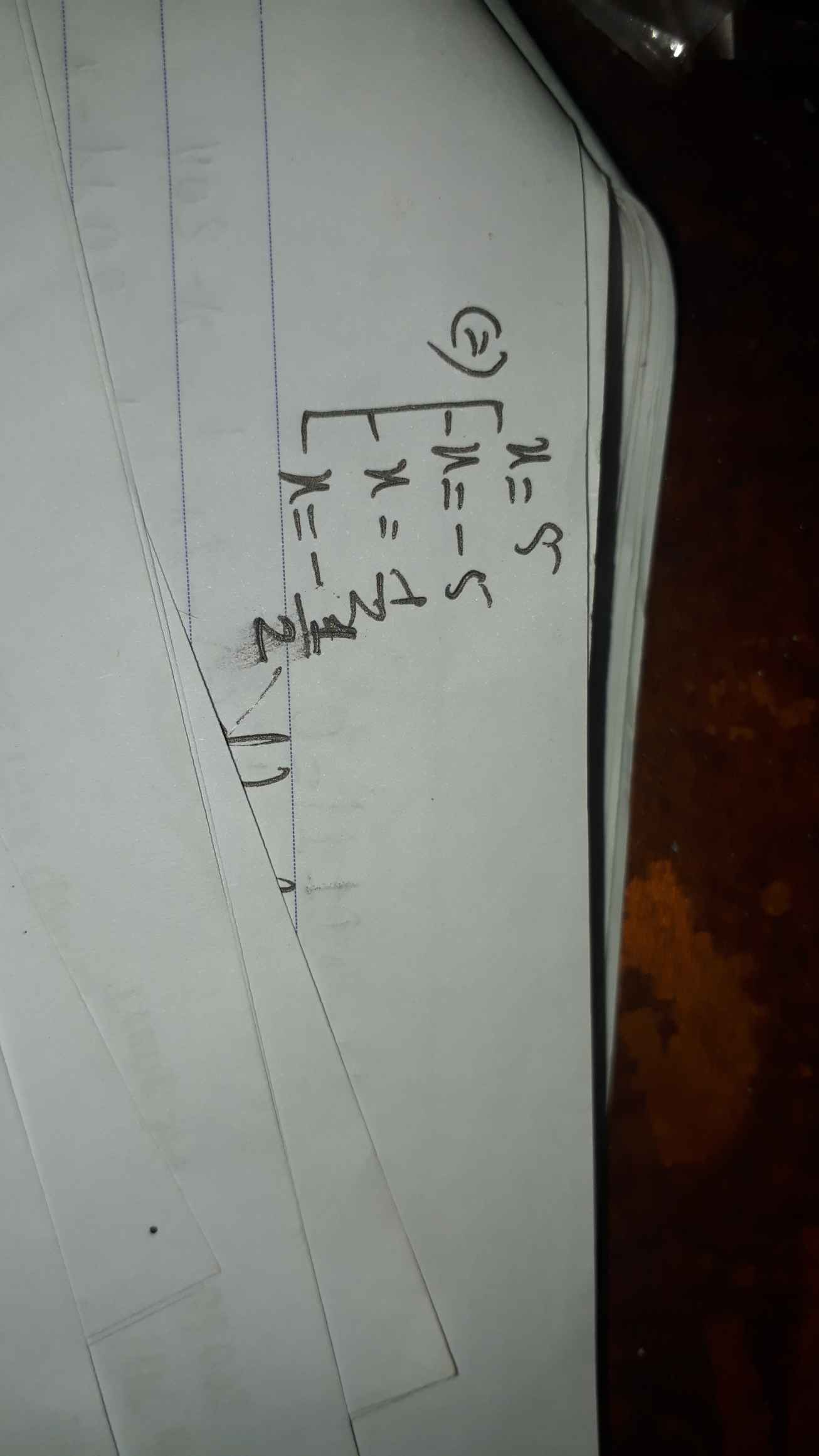
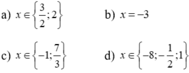
Ta có: \(\left(3x^2-12\right)\left(7-x\right)=0\)
=>\(3\left(x^2-4\right)\left(7-x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-4\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)
=>(x-2)(x+2)(x-7)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+2=0\\x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
(3\(x^2\) - 12).(7 - \(x\)) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x^2-12=0\\7-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=4\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=2\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\){-2; 2; 7}