2x +3x+1-4x+2=36
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a) (x + 6)(3x + 1) + x2 - 36 = 0
<=> 3x2 + x + 18x + 6 + x2 - 36 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 19x - 30 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 24x - 5x - 30 = 0
<=> 4x(x + 6) - 5(x + 6) = 0
<=> (x + 6)(4x - 5) = 0
<=> x + 6 = 0 hoặc 4x - 5 = 0
<=> x = -6 hoặc x = 5/4
Bài 1 mình đã làm xong rồi, anh em nào giúp mình bài 2 với!

\(a,2x\left(x-5\right)+4\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;-2\right\}\)
\(b,3x-15=2x\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x-5\right)-2x\left(x-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(-2x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\-2x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{5;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
\(c,\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)=\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(5x-8\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x-2-5x+8\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(-2x+6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\-2x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};3\right\}\)
Câu d xem lại đề

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

2x(6x – 1) > (3x – 2)(4x + 3)
⇔ 12x2 – 2x > 12x2 – 8x + 9x – 6
⇔ 12x2 – 2x – 12x2 + 8x – 9x > -6 (Chuyển vế, đổi dấu)
⇔ -3x > -6
⇔ x < 2 (Chia cả hai vế cho -3 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm x < 2.

ĐKXĐ: x∈{0;−1;−2;−3}. Ta biến đổi phương trình như sau:
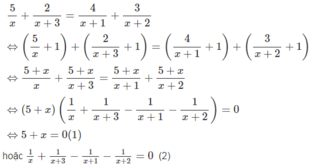
Ta có:
(1) ⇔x = −5
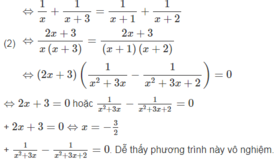
Tóm lại, phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm là S = {−5;−3/2}

<=> (3x+2)(1-2x)=(2x+1)(2x-1)
<=> (3x+2)(1-2X)+(1-2x)(1+2x)=0
<=> (1-2x)(3x+2+1+2x)=0
<=> (1-2x)(5x+3)=0
<=> 1-2x=0 hoặc 5x+3=0
<=> x=1/2 hoặc x=-3/5
Vậy PT có 2 nghiệm x=1/2 và x=-3/5 ( câu kết luận là và nha bạn ^^! ) chúc bạn học tốt :v
<=> (3x+2)(1-2x)=(2x+1)(2x-1)
<=> (3x+2)(1-2X)+(1-2x)(1+2x)=0
<=> (1-2x)(3x+2+1+2x)=0
<=> (1-2x)(5x+3)=0
<=> 1-2x=0 hoặc 5x+3=0
<=> x=1/2 hoặc x=-3/5
Vậy PT có 2 nghiệm x=1/2 và x=-3/5


`2x + 3x + 1 - 4x + 2 = 36`
`=> (2+3-4) x + 3 = 36`
`=> x + 3 = 36`
`=> x = 36-3`
`=> x = 33`
Tìm x biết. 180-(x_45):2=120