16x + 40 = 120
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Không biết em có làm sai không:
ĐKXĐ: \(x,y\ge0\).
Đặt 2x = a; 3y = b.
HPT trở thành:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^a-\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^b+\left(a-b\right)\left(ab+12\right)=0\\a^2+b^2=16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a^2+b^2=16\\\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^a-\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^b+\left(b-a\right)\left(a^2+b^2\right)+a^3-b^3+12\left(a-b\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a^2+b^2=16\\\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^a+a^3-4a=\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^b+b^3-4b=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\).
Giả sử \(a\ge b\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^a\ge\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^b\). Mà \(\left(a^3-4a\right)-\left(b^3-4b\right)=\left(a-b\right)\left(a^2+ab+b^2-4\right)\ge0\) nên VT(1) \(\ge\) VP(1).
Do đẳng thức xảy ra nên ta có a = b. Thay vào ta tìm được a = b = \(2\sqrt{2}\) nên \(x=\sqrt{2};y=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\).
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{2x}-\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{3y}=\left(3y-2x\right)\left(6xy+12\right)\left(1\right)\\4x^2+9y^2=16\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(2\right)\Rightarrow4x^2+9y^2-4=12\) the vo (1)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{2x}-\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{3y}=\left(3y-2x\right)\left(6xy+4x^2+9y^2-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{2x}-\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{3y}=27y^3-8x^3-12y+8x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{2x}+\left(2x\right)^3-4.\left(2x\right)=\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{3y}+\left(3y\right)^3-4.\left(3y\right)\left(3\right)\)
Xét hàm số \(f\left(t\right)=\left(\sqrt{5}\right)^{2t}+\left(2t\right)^3-4.2t\) đồng biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow\left(3\right):f\left(2x\right)=f\left(3y\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=3y\\4x^2+9y^2=16\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{2}\\y=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Tham khảo bài này :
(3x+1)(7x+3)=(5x-7)(3x+1)
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3)-(5x-7)(3x+1)=0
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3-5x+7)=0
<=> (3x+1)(2x+10)=0
<=> 2(3x+1)(x+5)=0
=> 3x+1=0 hoặc x+5=0
=> x= -1/3 hoặc x=-5
Vậy x = -1/3 hoặc x = -5
\(a,x^2+10x+25-4x\left(x+5\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2-4x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(5-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\5-3x=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(b,\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(16x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(4x+5\right)\left(4x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(4x-5\right)\left(4x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}4x-5=0\\4x+15=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{4}\\x=-\frac{15}{4}\end{cases}}}\)

Đặt ![]() ta có phương trình 6u – 8 = 3u + 7.
ta có phương trình 6u – 8 = 3u + 7.
Giải phương trình này:
6u – 8 = 3u + 7
⇔ 6u – 3u = 7 + 8
⇔ 3u = 15 ⇔ u = 5
Vậy (16x + 3)/7 = 5 ⇔ 16x + 3 = 35
⇔ 16x = 32 ⇔ x = 2
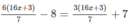
⇔ (16x + 3)/7 = 5 ⇔ 16x + 3 = 35
⇔ 16x = 32 ⇔ x = 2

Xem video này nhé:
https://www.facebook.com/BBCnewsVietnamese/videos/408386896476118

\(\dfrac{48}{120}=\dfrac{48:24}{120:24}=\dfrac{2}{5}\\ \dfrac{-60}{108}=\dfrac{-60:12}{108:12}=-\dfrac{5}{9}\)

Nhúng một thanh sắt vào dung dịch và để một thời gian cho phản ứng xảy ra hoàn toàn.
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
Cu2+ +Fe→ Fe2+ + Cu
(Fe đứng trước Cu trong dãy hoạt động hóa học nên đẩy Cu ra khỏi dung dịch muối)
Toàn bộ Cu thoát ra bám trên bề mặt thanh sắt, lấy thanh sắt ra ta còn lại dung dịch chỉ có FeSO4

\(16x^4-8x^2+1=\left(4x^2\right)^2-2.4x^2.1+1=\left(4x^2-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow16x^4+1\ge8x^2\)(1)
\(y^4-2y^2+1=\left(y^2-1\right)^2\ge0\forall y\)
\(\Rightarrow y^4+1\ge2y^2\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow\left(16x^4+1\right)\left(y^4+1\right)\ge8x^2.2y^2=16x^2y^2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi: \(\hept{\begin{cases}4x^2-1=0\\y^2-1=0\end{cases}}\)
Từ đó tìm được \(x=\pm\frac{1}{2},y=\pm1\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)\in\left\{\left(\frac{1}{2};1\right),\left(\frac{1}{2};-1\right),\left(-\frac{1}{2};1\right),\left(-\frac{1}{2};-1\right)\right\}\)

\(4x^3-16x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\cdot\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\cdot\left(x-2\right)\cdot\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=0\\x-2=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Ta có: \(\sqrt{16x}=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x=64\)
hay x=4
16x+40=120
=>16x=120-40=80
=>\(x=\dfrac{80}{16}=5\)
\(16x+40=120\)
\(16x=120-40\)
\(16x=80\)
\(x=80:16\)
\(x=5\)
Vậy...