tìm x (x+7)-25=13
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{y+5}{y\left(y-5\right)}-\dfrac{y-5}{2y\left(y+5\right)}=\dfrac{y+25}{2\left(y-5\right)\left(y+5\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(y+5\right)^2-\left(y-5\right)^2=y^2+25y\)
=>\(2y^2+20y+50-y^2+10y-25=y^2+25y\)
=>30y+25=25y
=>5y=-25
=>y=-5(loại)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
=>x^2+x+x^2-3x-4x=0
=>2x^2-6x=0
=>2x(x-3)=0
=>x=0(nhận) hoặc x=3(loại)
c: =>x^2-9-6(2x+7)=-13(x+3)
=>x^2-9-12x-42+13x+39=0
=>x^2+x-6=0
=>(x+3)(x-2)=0
=>x=2(nhận) hoặc x=-3(loại)

a) Sai lầm là coi -2 là hạng từ và chuyển vế hạng tử này trong khi -2 là một nhân tử.
Lời giải đúng:
-2x > 23
⇔ x < 23 : (-2) (chia cho số âm nên đổi chiều)
⇔ x < -11,5
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là x < -11,5
b) Sai lầm là nhân hai vế của bất phương trình với 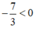 mà không đổi chiều bất phương trình.
mà không đổi chiều bất phương trình.
Lời giải đúng:
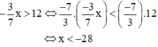
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là x < -28

\(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\Rightarrow x^2-36\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-6\\x\ge6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bất phương trình đó tương đương với:
\(\left(\dfrac{x^2-26}{10}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-25}{11}-1\right)\ge\left(\dfrac{x^2-24}{12}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x^2-23}{13}-1\right)\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}\ge\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{x^2-36}{10}+\dfrac{x^2-36}{11}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{12}-\dfrac{x^2-36}{13}\ge0\)
⇔ \(\left(x^2-36\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)\ge0\)
+)Vì \(\dfrac{1}{10}>\dfrac{1}{11}>\dfrac{1}{12}>\dfrac{1}{13}\) nên \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}>0\)
⇔ \(x^2-36\ge0\)
⇔ \(x^2\ge36\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x^2}\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left|x\right|\ge6\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
➤ Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge6\\x\le-6\end{matrix}\right.\)



\(3x-7=13-x\)
\(\Rightarrow3x+x=13+7\)
\(\Rightarrow4x=20\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5\)

\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+13-\sqrt{x^2-4x+13}-6=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2-4x+13}=t>0\)
\(\Rightarrow t^2-t-6=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=3\\t=-2< 0\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-4x+13}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+13=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4=0\Rightarrow x=2\)

Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: $x\geq -3,5$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow (\sqrt{2x+7}-1)+(\sqrt[3]{x+4}-1)+(x^2+8x+15)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{2(x+3)}{\sqrt{2x+7}+1}+\frac{x+3}{\sqrt[3]{(x+4)^2}+\sqrt[3]{x+4}+1}+(x+3)(x+5)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+3)\left[\frac{2}{\sqrt{2x+7}+1}+\frac{1}{\sqrt[3]{(x+4)^2}+\sqrt[3]{x+4}+1}+(x+5)\right]=0\)
Với $x\geq -3,5$ dễ thấy biểu thức trong ngoặc vuông $>0$
Do đó: $x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-3$ (thỏa mãn)
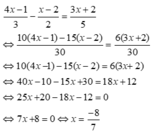
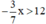 . Ta có:
. Ta có: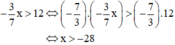
`(x + 7) - 25 = 13`
`=> x +7 = 13 + 25`
`=> x+ 7 = 38`
`=> x = 38 - 7`
`=> x = 31`
Vậy `x=31`
\(\left(x+7\right)-25=13\)
\(x+7=13+25\)
\(x+7=38\)
\(x=38-7\)
\(x=31\)
vậy x = 31