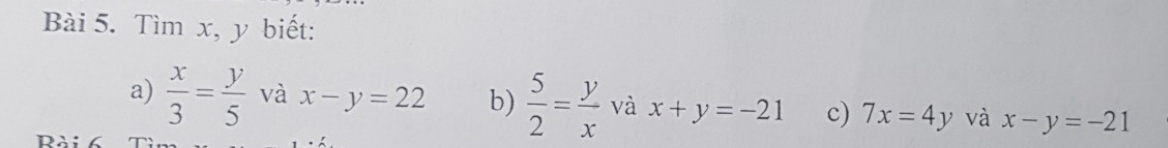 giúp e ạ
giúp e ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Đề : Một hình chữ nhật có chu vi bằng 80 cm. Tăng chiều rộng lên 3cm; tăng chiều dài lên 5 cm thì diện tích tăng thêm 195 cm^2.
Tìm chiều dài và chiều rộng ban đầu.

Bài 1 : x² + x² -12 = 0
a = 1 , b = 1 , c = -12
∆ = 1 -4 × 1 × (-12)
∆ = 49 > 0 .✓49 =7
Vậy pt có 2 ng⁰ pb ( tự viết nhé ) !

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{2+5\sqrt{x}}{4-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\cdot\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}-\dfrac{2+5\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+3\sqrt{x}+2+2x-4\sqrt{x}-2-5\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-6\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
b)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x\ne4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để P=2 thì \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}=2\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}=2\sqrt{x}+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=4\)
hay x=16(nhận)
Vậy: Để P=2 thì x=16
2.
a, \(m=3\), hệ phương trình trở thành:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3y=9\\3x-3y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x=13\\y=\dfrac{3x-4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{13}{4}\\y=\dfrac{23}{12}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-1;3\right)\) là nghiệm của hệ, suy ra:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1+3m=9\\-m-9=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{10}{3}\\m=-13\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Không tồn tại giá trị m thỏa mãn

a) Thay m=3 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3y=1\\x+y=9\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-4y=-8\\x+y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=9-y\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Khi m=3 thì hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Để hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\dfrac{1}{1}\ne\dfrac{-m}{1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m\ne1\)
hay \(m\ne-1\)
Vậy: Để hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất thì \(m\ne-1\)
c) Để hệ phương trình có vô số nghiệm thì \(\dfrac{1}{1}=\dfrac{-m}{1}=\dfrac{1}{m^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-m=1\\m^2=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=-1\\m\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=-1\)
Vậy: Để hệ phương trình có vô số nghiệm thì m=-1


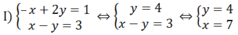
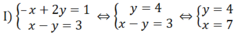
a, Theo tc dãy tỉ số bằng nhau
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{x-y}{3-5}=\dfrac{22}{-2}=-11\Rightarrow x=-33;y=-55\)
b, \(\dfrac{5}{2}=\dfrac{y}{x}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}\)Theo tc dãy tỉ số bằng nhau
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{x+y}{2+5}=-\dfrac{21}{7}=-3\Rightarrow x=-6;y=-15\)
c, \(7x=4y\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{7}\)Theo tc dãy tỉ số bằng nhau
\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{7}=\dfrac{x-y}{3-7}=-\dfrac{21}{-4}=7\Rightarrow x=28;y=49\)