Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Áp dụng vi-et ta suy ra được nghiệm là:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-m-\sqrt{m^2-4n}}{2}\\x=\frac{-m+\sqrt{m^2-4n}}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Ta có:
\(x_1=x_2^2+x_2+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2=\left(x_2+1\right)^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m=\left(x_2+1\right)^2+1\)
Với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_2=\frac{-m-\sqrt{m^2-4n}}{2}\\n=6-m\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m=\frac{\left(m-2\right)\sqrt{m^2+4m-24}+m^2-10}{2}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m-m^2+8=\left(m-2\right)\sqrt{m^2+4m-24}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^3+24m^2-144m+160=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=-10\\m=2\left(l\right)\end{cases}}\)
Tương tự cho trường hợp còn lại.

gọi số vỏ lon bia lớp 8/1 nộp là a ( vỏ ) ( a\(\in\)N*, a< 720 )
=> số vỏ lớp 8 /2 phải nộp là 720 -a ( vỏ)
TĐB ta có (a - 40) / (720- a + 40) = 4/5
=> 5a - 200 = 3040 - 4a
a = 360
số lon của lớp 8/1 là 360 lon. số lon lớp 8/2 là 720 -360 = 360 lon

đk: \(x\ge-3\)
Ta có: \(x^2-x+8=4\sqrt{x+3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)-\left(4\sqrt{x+3}-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-\frac{16\left(x+3\right)-64}{4\sqrt{x+3}+8}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-\frac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt{x+3}+2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-\frac{4}{\sqrt{x+3}+2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\frac{4}{\sqrt{x+3}+2}\end{cases}}\)
Nếu \(x=\frac{4}{\sqrt{x+3}+2}\Leftrightarrow x\sqrt{x+3}+2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\sqrt{x+3}=4-2x\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+3\right)=4x^2-16x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2+16x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+16\right)=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy x = 1

a) * Lớp 10C:

* Lớp 10D:

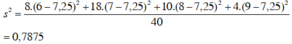
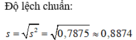
b) Kết quả lớp 10D có độ lệch chuẩn nhỏ hơn kết quả lớp 10C nên kết quả lớp 10D đồng đều hơn.

x 3 – 8 = 0
⇔ (x − 2)( x 2 + 2x + 4) = 0
⇔ x 1 = 2; x 2 = −1 + i 3 ; x 2 = −1 - i 3

x 3 + 8 = 0
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 − 2x + 4) = 0
⇔ x 1 = −2; x 2 = 1 + i 3 ; x 3 = 1 - i 3
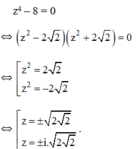
\(a)\dfrac{5}{x+7}=\dfrac{-14}{x-5}\left(x\ne-7;x\ne5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-14\left(x+7\right)=5\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-14x-98=5x-25\\ \Leftrightarrow5x+14x=-98+25\\ \Leftrightarrow19x=-73\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{73}{19}\left(tm\right)\\ b)\dfrac{3}{3x-2}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\left(x\ne\dfrac{2}{3};x\ne-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x+1\right)=3x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x+3=3x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow3=-2\)
=> Pt vô nghiệm
\(c)\dfrac{x}{x-2}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}+1\left(x\ne2;x\ne-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x-2}=\dfrac{x+2}{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x=x^2-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-4\left(tm\right)\)
\(d)\dfrac{x+6}{x+5}+\dfrac{3}{2}=2\left(x\ne-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x+6\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x+6\right)+3\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+12+3x+15=4\left(x+5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow5x+27=4x+20\\ \Leftrightarrow5x-4x=20-27\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-7\left(tm\right)\)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>3
\(\dfrac{x+5}{x-3}+2=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5+2x-6}{x-3}=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)
=>3x-1=2
=>3x=3
=>x=1(nhận)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{3x+5}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{3x+3+2}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x+2x+2}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>4x+2=0
=>4x=-2
=>\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
g: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}+\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)+\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2-9+x^2-4}{x^2-5x+6}=2\)
=>\(2\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=2x^2-13\)
=>-10x+12=-13
=>-10x=-25
=>\(x=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
h: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x-20}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x-3\right)-3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{3x-20}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>\(2x-6-3x+6=3x-20\)
=>3x-20=-x
=>4x=20
=>x=5(nhận)