Cho hàm số y= -2 + 1 có đồ thị là đường thẳng (d)
a) Xác định hệ số góc của đường thẳng (d). Góc tạo bởi đường thẳng (d) và trục Ox là góc nhọn hay góc tù?
b) Vẽ đồ thị hàm số y = -2 + 1(d)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

d: Cặp đường song song là y=x-3 và y=x+4 vì a=1=a'=1
Cặp đường cắt nhau là y=x-3 và y=-2x+5 vì a=1<>a'=-2

\(a,\Leftrightarrow3m-1=-2\Leftrightarrow m=-\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow\left(d\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{3}x-1\\ c,\text{Hs góc: }-\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \text{Gọi góc cần tìm là }\alpha>90^0\\ \Leftrightarrow\tan\left(180^0-\alpha\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\approx\tan18^0\\ \Leftrightarrow\alpha\approx180^0-18^0=162^0\)

a: Vì (d)//y=1/2x+1 nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+b\)
Thay x=2 và y=2 vào (d), ta được:
\(b+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2=2\)
=>b+1=2
=>b=1
vậy: (d): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\)
b: 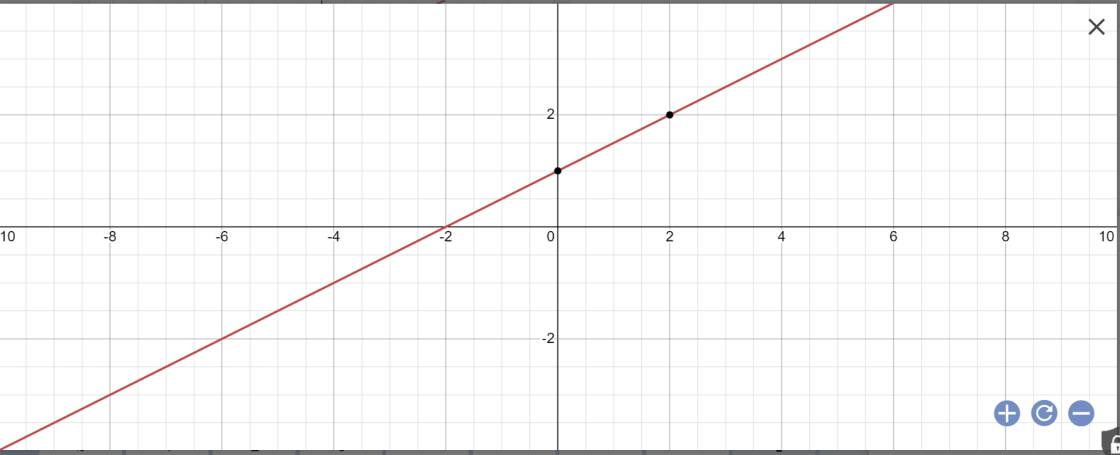
c: Gọi \(\alpha\) là góc tạo bởi (d) với trục Ox
Ta có: (d): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\)
=>a=1/2
=>\(tan\alpha=a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\alpha\simeq26^034'\)
d: tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{1}{2}x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{1}{2}x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là;
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+1=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot0+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: B(-2;0); C(1;0)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(-2-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{2^2+0^2}=2\)
\(OC=\sqrt{\left(1-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{1^2+0^2}=1\)
Vì Ox\(\perp\)Oy nên OB\(\perp\)OC
=>ΔBOC vuông tại O
=>\(S_{BOC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OB\cdot OC=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot1=1\)

a: Hệ số góc là a=2
Tung độ góc là b=2
c: Thay x=3 vào y=2x+2, ta được:
y=2x3+2=8
Vậy: A(3;8) có thuộc (d)

1: Khi m=2 thì y=(2-1)x+2=x+2
Vẽ đồ thị:
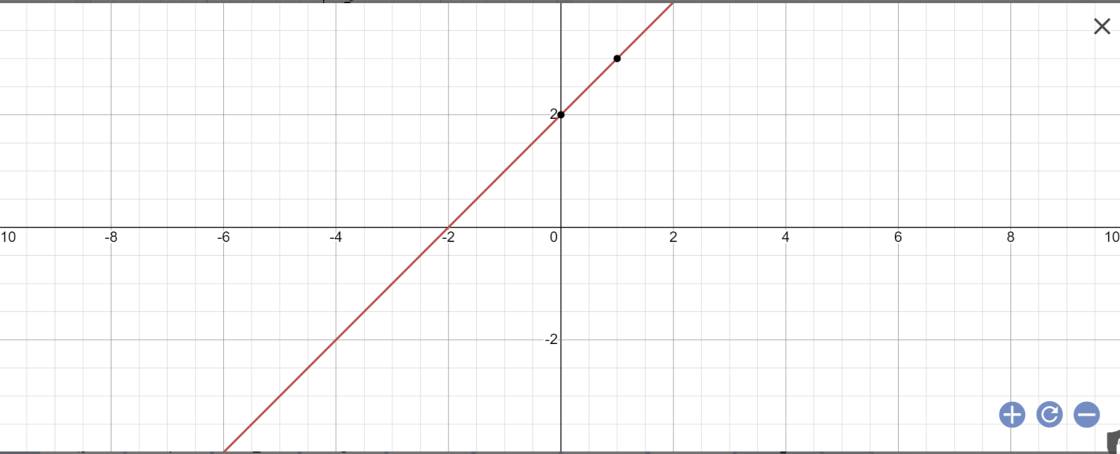
\(tan\alpha=a=1\)
=>\(\alpha=45^0\)
2: Thay x=1 và y=0 vào (d), ta được:
\(1\left(m-1\right)+m=0\)
=>2m-1=0
=>m=1/2
3:
y=(m-1)x+m
=mx-x+m
=m(x+1)-x
Điểm mà (d) luôn đi qua có tọa độ là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 2:
c: Vì (d')//(d) nên a=-1
Vậy: (d'): y=-x+b
Thay x=4 và y=2 vào (d'), ta được:
b-4=2
hay b=6

a) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\\\left(d'\right):y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
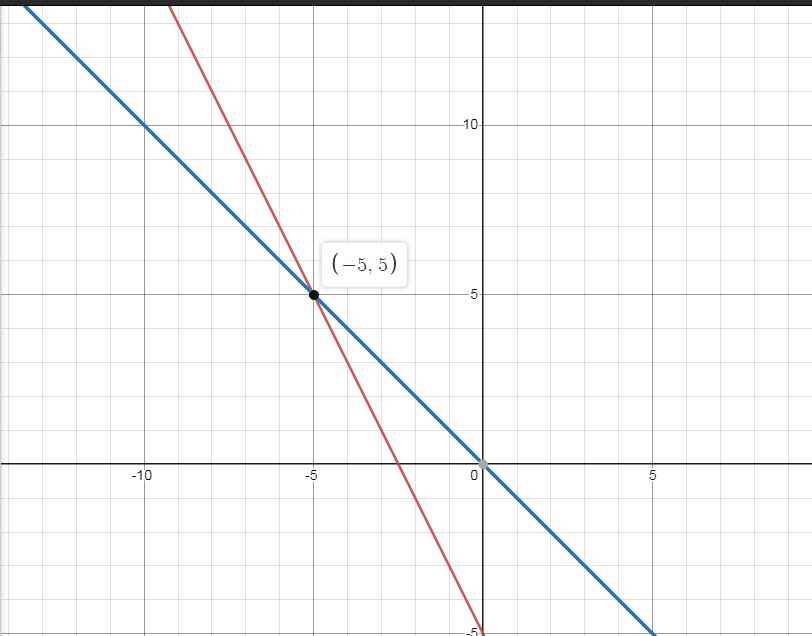
b) \(\left(d\right)\cap\left(d'\right)=M\left(x;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=-2x-5\\y=-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow M\left(-5;5\right)\)
c) Gọi \(\widehat{M}=sđ\left(d;d'\right)\)
\(\left(d\right):y=-2x-5\Rightarrow k_1-2\)
\(\left(d'\right):y=-x\Rightarrow k_1-1\)
\(tan\widehat{M}=\left|\dfrac{k_1-k_2}{1+k_1.k_2}\right|=\left|\dfrac{-2+1}{1+\left(-2\right).\left(-1\right)}\right|=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{M}\sim18^o\)
d) \(\left(d\right)\cap Oy=A\left(0;y\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y=-2.0-5=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow A\left(0;-5\right)\)
\(OA=\sqrt[]{0^2+\left(-5\right)^2}=5\left(cm\right)\)
\(OM=\sqrt[]{5^2+5^2}=5\sqrt[]{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(MA=\sqrt[]{5^2+10^2}=5\sqrt[]{5}\left(cm\right)\)
Chu vi \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(C=OA+OB+MA=5+5\sqrt[]{2}+5\sqrt[]{5}=5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow p=\dfrac{C}{2}=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}p-OA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}-1\right)}{2}\\p-OB=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{2}=\dfrac{5\left(-\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\\p-MA=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}-5\sqrt[]{5}=\dfrac{5\left(\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}+\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}.\dfrac{5\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}-\sqrt[]{5}\right)}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow p\left(p-MA\right)=\dfrac{25\left[\left(1+\sqrt[]{2}\right)^2-5\right]}{4}=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}\)
\(\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25\left[5-\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)^2\right]}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)=\dfrac{25.2\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}=\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{4}\)
Diện tích \(\Delta MOA:\)
\(S=\sqrt[]{p\left(p-OA\right)\left(p-OB\right)\left(p-MA\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}-1\right)}{2}.\dfrac{25\left(\sqrt[]{2}+1\right)}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S=\sqrt[]{\dfrac{25^2}{2^2}}=\dfrac{25}{2}=12,5\left(cm^2\right)\)

1: Thay x=3 và y=6 vào (d), ta được:
3a+2=6
hay \(a=\dfrac{4}{3}\)