giải phương trình: 6x - 6 = 2x+ 10
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-8x+16\right)+\left(2x+1-6\sqrt{2x+1}+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{2x+1}-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\\sqrt{2x+1}-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)

a:=>3x=15
=>x=5
b: =>8-11x<52
=>-11x<44
=>x>-4
c: \(VT=\left(\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-6\right)^2}{x\left(x+6\right)\left(x-6\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x+6\right)}{2x-6}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{12x-36}{2x-6}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x-6}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}=\dfrac{6}{x-6}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}=-1\)

\(\dfrac{15-2x}{4}-\dfrac{x+1}{3}+\dfrac{6x-1}{2}=\dfrac{x-3}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow45-6x-4x-4+36x-6=2x-12\) (quy đồng và khử mẫu)
\(\Leftrightarrow24x=23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{23}{24}\)

a) \(\dfrac{15-6x}{3}>5\Leftrightarrow15-6x>15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x>0\Leftrightarrow x< 0\) (vì \(-6< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x< 0\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{8-11x}{4}< 13\Leftrightarrow8-11x< 52\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-11x< -44\Leftrightarrow x>4\) (vì \(-11< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x>4\right\}\)
c) \(8x+3\left(x+1\right)>5x-\left(2x-6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x+3x+1>5x-2x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x+3x-5x+2x>6-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x>5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{5}{8}\) (vì \(8>0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x>\dfrac{5}{8}\right\}\)
d) \(2x\left(6x-1\right)>\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x>12x^2+9x-8x-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x-12x^2-9x+8x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 2\) (vì \(-3< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x< 2\right\}\)
a) \(\dfrac{15-6x}{3}>5\) <=> \(15-6x>15\) <=> \(6x< 0\) <=> \(x< 0\)
b) \(\dfrac{8-11x}{4}< 13\) <=> \(8-11x< 52\) <=> \(11x>-44\)<=> \(x>-4\)
c) \(8x+3\left(x+1\right)>5x-\left(2x-6\right)\)
<=> 8x + 3x + 3 - 5x + 2x - 6 > 0
<=> 8x > 3
<=> x > 3/8
d) 2x(6x - 1) > (3x - 2)(4x + 3)
<=> 12x2 - 2x > 12x2 + x - 6
<=> 12x2 - 2x - 12x2 - x > -6
<=> -3x > -6
<=> x < 2

Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^4+2x^3y+x^2y^2=2x+9\\x^2+2xy=6x+6\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x^2+xy\right)^2=2x+9\\x^2+2xy=6x+6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x^2+xy\right)^2=2x+9\\xy=3x+3-\dfrac{x^2}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{x^2}{2}+3x+3\right)^2=2x+9\)( đến đây là phương trình 1 ẩn rồi, tự giải tiếp)

\(\sqrt{x^2-6x+6}=2x-1\) (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}2x-1\ge0\\x^2-6x+6=\left(2x-1\right)^2\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}x\ge\frac{1}{2}\\3x^2+2x-5=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x\ge\frac{1}{2}\\x=1;x=-\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=1\)

a: \(\sqrt{x^2+6x+9}=\sqrt{11+6\sqrt{2}}\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}\)
=>\(\left|x+3\right|=\left|3+\sqrt{2}\right|=3+\sqrt{2}\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=3+\sqrt{2}\\x+3=-3-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{2}\\x=-6-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=4\\x+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y=8\\x+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y+x+2y=8-3\\2x-y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x=5\\y=2x-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\cdot1-4=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)


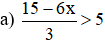
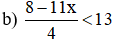
6x - 6 = 2x + 10
6x - 2x = 10 + 6
4x = 16
x = 16 : 4
x = 4
Vậy S = {4}