tính nhanh:
(2/3x4/5)x5/6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Cách 1:
\(\left(\frac{2}{3}\times\frac{4}{5}\right)\times\frac{5}{6}\)
\(=\frac{8}{15}\times\frac{5}{6}\)
\(=\frac{4}{9}\)
Cách 2:
\(\left(\frac{2}{3}\times\frac{4}{5}\right)\times\frac{5}{6}\)
\(=\frac{2}{3}\times\left(\frac{4}{5}\times\frac{5}{6}\right)\)
\(=\frac{2}{3}\times\frac{2}{3}\)
\(=\frac{4}{9}\)

\(a.=\left(\dfrac{4}{5}.\dfrac{5}{6}\right).\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{4}{6}.\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
\(b.\dfrac{4}{5}.\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{5}{4}.\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{5}+\dfrac{15}{16}=\dfrac{123}{80}\)
\(c.\left(\dfrac{11}{23}+\dfrac{9}{23}\right)+\left(\dfrac{2}{23}+\dfrac{18}{23}\right)=\dfrac{20}{23}+\dfrac{20}{23}=\dfrac{40}{23}\)
\(d.\left(\dfrac{27}{12}-\dfrac{25}{36}\right)+\left(\dfrac{17}{6}-\dfrac{15}{6}\right)=\dfrac{14}{9}+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{17}{9}\)

a, = 8/15 x 5/6 = 40/90 = 4/9
b, = 5/6 x 1/5 = 5/30 = 1/6
a, \(= 8/15 x 5/6 = 40/90 = 4/9\)
b, \(= 5/6 x 1/5 = 5/30 = 1/6\)

Đặt f(x) = x5 – 3x4 + 5x – 2
f(x) là hàm đa thức nên liên tục trên R.
Ta có: f(0) = –2 < 0
f(1) = 1 > 0
f(2) = -8 < 0
f(3) = 13 > 0
⇒ f(0).f(1) < 0; f(1).f(2) < 0; f(2).f(3) < 0
⇒ Phương trình f(x) = 0 có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc khoảng (0; 1); 1 nghiệm thuộc khoảng (1; 2); 1 nghiệm thuộc khoảng (2; 3)
⇒ f(x) = 0 có ít nhất 3 nghiệm thuộc (0; 3) hay f(x) = 0 có ít nhất 3 nghiệm thuộc (-2; 5).

Chọn A
Ta có: P(x) = -x5 + 3x4+ 2x5 - x3+ x4 - 3x4 - 5 = x5 + x4 - x3 - 5
Nên hệ số cao nhất là 1 và hệ số tự do là -5.


Ta có
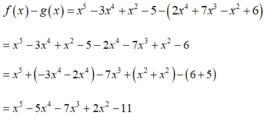
Sắp xếp theo lũy thừa tăng dần của biến ta được
- 11 + 2 x 2 - 7 x 3 - 5 x 4 + x 5
Chọn đáp án B

26 x 56 = ( 2 x 5 )6 = 106 = 1 000 000
43 x 53 = ( 4 x 5 )3 = 203 = 8 000
63 x 53 = ( 6 x 5 )3 = 303 = 27 000
82 x 52 = ( 8 x 5 ) 2 = 402 = 160
\(2^6.5^6=10^6=100000\)
\(4^3.5^3=20^3=8000\)
\(6^3.5^3=30^3=27000\)
\(8^2.5^2=40^2=1600\)
4/9 nha
\(\dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}\times\dfrac{5}{6}=\dfrac{2\times4}{3\times6}=\dfrac{8}{18}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)