Cho hỏi ạ
tìm x :
căn (x-2) + căn (4-x) =2x^2-5x-1 ( đk: 2<=x<=4)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) \(\sqrt[]{x^2-4x+4}=x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[]{\left(x-2\right)^2}=x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=x+3\\x-2=-\left(x+3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}0x=5\left(loại\right)\\x-2=-x-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b) \(2x^2-\sqrt[]{9x^2-6x+1}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-\sqrt[]{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-\left|3x-1\right|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=2x^2-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=2x^2-5\\3x-1=-2x^2+5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-3x-4=0\left(1\right)\\2x^2+3x-6=0\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải pt (1)
\(\Delta=9+32=41>0\)
Pt \(\left(1\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt[]{41}}{4}\)
Giải pt (2)
\(\Delta=9+48=57>0\)
Pt \(\left(2\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-3\pm\sqrt[]{57}}{4}\)
Vậy nghiệm pt là \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt[]{41}}{4}\\x=\dfrac{-3\pm\sqrt[]{57}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) ( x - 3)4 + ( x - 5)4 = 82
Đặt : x - 4 = a , ta có :
( a + 1)4 + ( a - 1)4 = 82
⇔ a4 + 4a3 + 6a2 + 4a + 1 + a4 - 4a3 + 6a2 - 4a + 1 = 82
⇔ 2a4 + 12a2 - 80 = 0
⇔ 2( a4 + 6a2 - 40) = 0
⇔ a4 - 4a2 + 10a2 - 40 = 0
⇔ a2( a2 - 4) + 10( a2 - 4) = 0
⇔ ( a2 - 4)( a2 + 10) = 0
Do : a2 + 10 > 0
⇒ a2 - 4 = 0
⇔ a = + - 2
+) Với : a = 2 , ta có :
x - 4 = 2
⇔ x = 6
+) Với : a = -2 , ta có :
x - 4 = -2
⇔ x = 2
KL.....
b) ( n - 6)( n - 5)( n - 4)( n - 3) = 5.6.7.8
⇔ ( n - 6)( n - 3)( n - 5)( n - 4) = 1680
⇔ ( n2 - 9n + 18)( n2 - 9n + 20) = 1680
Đặt : n2 - 9n + 19 = t , ta có :
( t - 1)( t + 1) = 1680
⇔ t2 - 1 = 1680
⇔ t2 - 412 = 0
⇔ ( t - 41)( t + 41) = 0
⇔ t = 41 hoặc t = - 41
+) Với : t = 41 , ta có :
n2 - 9n + 19 = 41
⇔ n2 - 9n - 22 = 0
⇔ n2 + 2n - 11n - 22 = 0
⇔ n( n + 2) - 11( n + 2) = 0
⇔ ( n + 2)( n - 11) = 0
⇔ n = - 2 hoặc n = 11
+) Với : t = -41 ( giải tương tự )
@Giáo Viên Hoc24.vn
@Giáo Viên Hoc24h
@Giáo Viên
@giáo viên chuyên
@Akai Haruma

Pt xác định khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x-4\ge0\\2-x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{4}{5}\\x\le2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{5}\le x\le2\)
Nhưng trong TH này cậu phải làm cả hai nhé !
\(\sqrt[]{5x-4}=2-x\)
Phải lấy điều kiện \(2-x\ge0\) vì phương trình trên có dạng :
\(\sqrt[]{A}=B\) nên khi đặt điều kiện \(B\ge0\) thì chắc chắn \(\sqrt[]{A}\ge0\)
Nên không cần điều kiện \(A\ge0\) mà chỉ cần điều kiện \(B\ge0\) hay \(2-x\ge0\) là đủ.

điều kiện của x để căn thức xác định
\(x^2+2x+1\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow x+1\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne-1\)
tick mik nha



1) Ta có: \(\frac{x+6\sqrt{x}+9}{x-9}=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
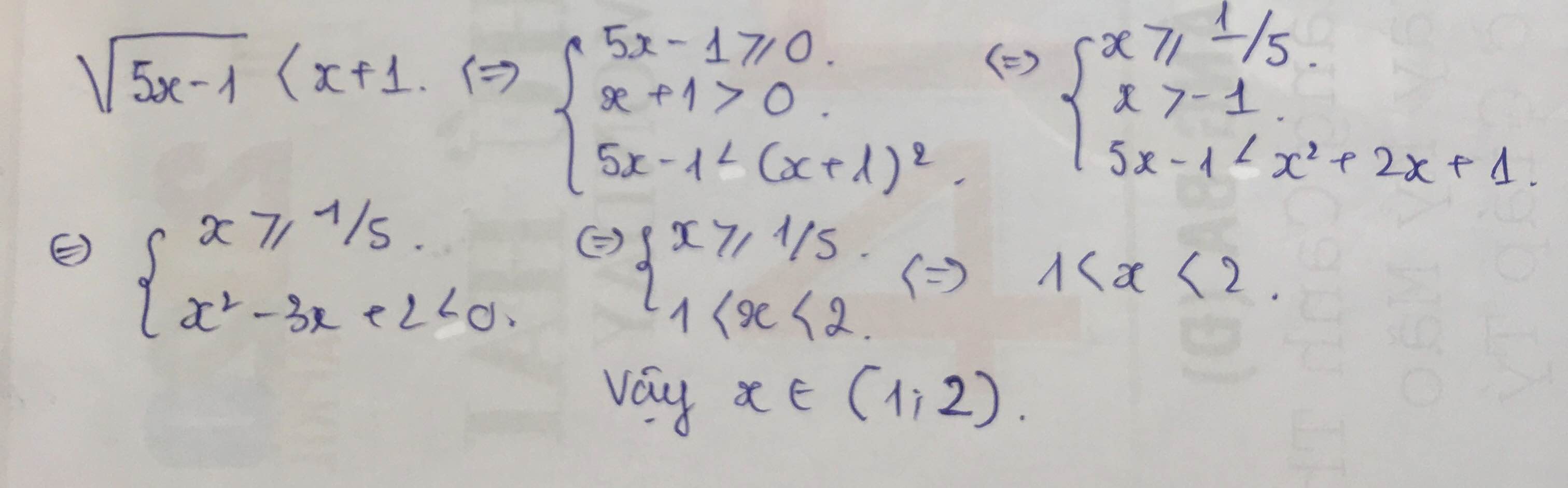

\(\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x}=2x^2-5x-1\)
Ta có : \(VT=\sqrt{x-2}+\sqrt{4-x}\Rightarrow VT^2=x-2+4-x+2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(4-x\right)}\)
\(=2+2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(4-x\right)}\)
Theo Cauchy ta có : \(2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(4-x\right)}\le x-2+4-x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow VT^2\le2+2=4\Rightarrow VT\le2\)
Ta lại có : \(VP=2x^2-5x-1=\left(2x^2-5x-3\right)+2=\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)+2\)
Mà \(2\le x\le4\Rightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\ge0\Rightarrow VT\ge2\)
Ta thấy : \(VT\le2\le VP\) nên dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(x=3\)
cảm ơn nhiều ạ mà vì sao nghĩ ra cách đó ạ có thể diễn giải giúp mình không ạ