Tìm đkxđ của phân thức: \(\dfrac{x^3+1}{x^2-x+1}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) ĐKXĐ `x + 3 ne 0 ` và `x -3 ne 0` và ` 9 -x^2 ne 0`
`<=> x ne -3 ` và `x ne 3` và `(3-x)(3+x) ne 0`
`<=> x ne -3` và `x ne 3`
b) Với `x ne +-3` ta có:
`P= 3/(x+3) + 1/(x-3)- 18/(9-x^2)`
`P= [3(x-3)]/[(x-3)(x+3)] + (x+3)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + 18/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (3x-9)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + (x+3)/[(x-3)(x+3)] + 18/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (3x-9+x+3+18)/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (4x +12)/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= (4(x+3))/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`P= 4/(x-3)`
Vậy `P= 4/(x-3)` khi `x ne +-3`
c) Để `P=4`
`=> 4/(x-3) =4`
`=> 4(x-3) = 4`
`<=> 4x - 12=4`
`<=> 4x = 16
`<=> x= 4` (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Vậy `x=4` thì `P =4`
a) P xác định <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3\ne0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-3\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=>\(x\ne\pm3\)
b)Với \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(P=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}-\dfrac{18}{9-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)+\left(x+3\right)+18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-9+x+3+18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x+12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{4}{x-3}\)
c)Với \(x\ne\pm3\)
P=4 <=>\(\dfrac{4}{x-3}=4\)
<=>\(4x-12=4\)
<=>\(4x=16\)
<=>x=4(tm)
Vậy x=4

a)ĐKXĐ:\(\begin{cases}x\ge0\\2\sqrt{x}-2\ne0\\1-x\ne0\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>` \(\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne1\\\end{cases}\)
`B=1/(2sqrtx-2)-1/(2sqrtx+2)+sqrtx/(1-x)`
`=1/(2(sqrtx-1))-1/(2(sqrtx+1))-sqrtx/(x-1)`
`=(sqrtx+1-(sqrtx-1)-2sqrtx)/(2(sqrtx-1)(sqrtx+1))`
`=(2-2sqrtx)/(2(sqrtx-1)(sqrtx+1))`
`=(2(1-sqrtx))/(2(sqrtx-1)(sqrtx+1))`
`=-1/(sqrtx+1)`
`b)x=3`
`=>B=(-1)/(sqrt3+1)`
`=(-(sqrt3-1))/(3-1)`
`=(1-sqrt3)/2`
`c)|A|=1/2`
`<=>|(-1)/(sqrtx+1)|=1/2`
`<=>|1/(sqrtx+1)|=1/2`
`<=>1/(sqrtx+1)=1/2` do `1>0,sqrtx+1>=1>0`
`<=>sqrtx+1=2`
`<=>sqrtx=1`
`<=>x=1` loại vì `x ne 1`.
a) ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}+2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{1-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{x}+1-2\sqrt{x}}{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
b) Thay x=3 vào B, ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{3}+1}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\)
c) Ta có: \(\left|A\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
nên \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}A=\dfrac{1}{2}\\A=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{-1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x}+1=-2\\\sqrt{x}+1=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=1\)(loại)

a) \(ĐK:x\ge0,x\ne1\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}-3-\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)+\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}-3-x+4+\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}=\dfrac{2x+4\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
b) \(P=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-1< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}< 1\)
Kết hợp với đk:
\(\Rightarrow0\le x< 1\)

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>2; x<>3
\(K=\left(\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^4+2x^2+1-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x^3-3x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x^2+1+x\right)\left(x^2+1-x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3-4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^4+x^2+1}\)
b:
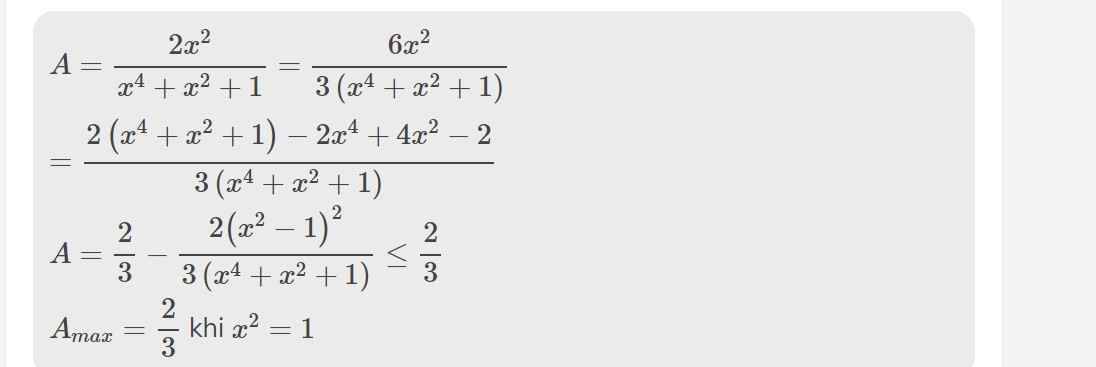

\(a,A=\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2-4}\left(dkxd:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+2+x-2+x^2+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2-4}\)
Vậy \(A=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2-4}\)
\(b,\) Theo đề, ta có : \(-2< x< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2< 0;x+2>0;\left(x+1\right)^2>0\)
\(\Rightarrow A< 0\) hay phân thức luôn có giá trị âm

\(T=\sqrt{\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-6}\cdot\dfrac{x-6\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-6}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-6\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}}\\ =\sqrt{\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\cdot\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{3x}{\sqrt{x}-1}}\\ =\sqrt{\dfrac{3\left(x-1\right)+3}{\sqrt{x}-1}}=\sqrt{3\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}-1}}\\ =\sqrt{3\left(\sqrt{x}-1+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\right)+6}\)
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cosi ta có:
\(\sqrt{x}-1+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow T\ge\sqrt{3\cdot2+6}=2\sqrt{3}\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=4

a: |2x-3|=1
=>2x-3=1 hoặc 2x-3=-1
=>x=1(nhận) hoặc x=2(loại)
KHi x=1 thì \(A=\dfrac{1+1^2}{2-1}=2\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1; x<>2
\(B=\dfrac{2x^2-4x+3x+3-2x^2-1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{x+1}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x^2-x+1\ne0\)
=>\(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\ne0\)
=>\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ne0\)(luôn đúng)
=>\(x\in R\)