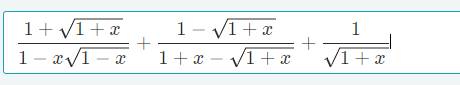
a) rút gọn biểu thức A
b) chứng minh A luôn dương với mọi giá trị của a
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

`#3107.\text {DN}`
a)
\((2x-3)^2-x(3-x)+5x-4x^2+17\)
`= 4x^2 - 12x + 9 - 3x + x^2 + 5x - 4x^2 + 17`
`= x^2 - 10x + 26`
b)
`M = x^2 - 10x + 26`
`= [(x)^2 - 2*x*5 + 5^2] + 1`
`= (x - 5)^2 + 1`
Vì `(x - 5)^2 \ge 0` `AA` `x => (x - 5)^2 + 1 \ge 1` `AA` `x`
Vậy, giá trị biểu thức M luôn có giá trị dương với mọi x.

\(a,B=4x^2+20x+25-9+x^2+14=5x^2+20x+30\\ b,B=5\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+10\\ B=5\left(x+2\right)^2+10\ge10>0,\forall x\)
Do đó B luôn dương với mọi x

a) \(A=\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(A=4x^2+4x+1-x^2+4-2x^2-2x\)
\(A=x^2+2x+5\)
b) Để A = 4
=> \(x^2+2x+5=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
c) Ta có A = x2 + 2x + 5
A = ( x + 1 )2 + 4
=> \(A\ge4>0\left(đpcm\right)\)
a,\(A=\left(2x+1\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^2+4x+1-x^2+4-2x^2-2x\)
\(=x^2+2x+5\)
b,\(A=x^2+2x+5=4\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+2x+5-4=0\)
\(x^2+2x+1=0\)
\(\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(x+1=0\)
\(x=-1\)
c, Ta có: \(A=x^2+2x+5=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+4=\left(x+1\right)^2+4\ge4>0\)
Hay: A > 0 => đpcm
=.= hok tốt!!

a)\(A=x^2+x+1=\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}>0\)
b) \(B=2x^2+2x+1=2\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}=2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\dfrac{1}{2}>0\)

a) \(A= \dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2-4} \\ =\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{x^2+1}{(x-2)(x+2)} \\= \dfrac{x+2+x-2+x^2+1}{(x-2)(x+2)} \\=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{x^2-4} \\ =\dfrac{(x+1)^2}{(x-2)(x+2)}\)
b) Với mọi \(x\) thỏa mãn \(-2<x<2\) và \(x \ne -1\) thì \(x-2\) đều có giá trị âm, mà \(\begin{cases}(x+1)^2≥0\\x+2>0\\\end{cases}\) \( \Rightarrow\) Biểu thức A luôn có giá trị âm.

a: \(A=\dfrac{3\left(1-2x\right)}{2x\left(x^2+1\right)-\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3\left(2x-1\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\dfrac{-3}{x^2+1}\)
b: Khi x=3 thì \(A=\dfrac{-3}{3^2+1}=-\dfrac{3}{10}\)
c: x^2+1>=0
=>3/x^2+1>=0
=>-3/x^2+1<=0
=>A<=0(ĐPCM)

\(Sửa:F=4x^2-12x+11=\left(4x^2-12x+9\right)+2=\left(2x-3\right)^2+2\ge2>0\left(đpcm\right)\)

Điều kiện x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1
Ta có:
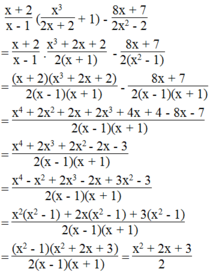
Biểu thức dương khi x 2 + 2 x + 3 > 0
Ta có: x 2 + 2 x + 3 = x 2 + 2 x + 1 + 2 = x + 1 2 + 2 > 0 với mọi giá trị của x.
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức dương với mọi giá trị x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 1