Tìm các giá trị của x để các biểu thức sau có nghĩa:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


c
Để biểu thức C có nghĩa thì
\(\sqrt{x\sqrt{2x-1}}>0\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\2x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy để biểu thức C có nghĩa thì \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Giải câu e:
Điều kiện để biểu thức E có nghĩa:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{2}{x}\ge0\\-2x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x^2+2}{x}\ge0\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy không tồn tại x để biểu thức E có nghĩa.


Để biểu thức có nghĩa thì : x2 - 5x + 6 > 0
=> (x - 2)(x - 3) > 0
Xét 2 trường hợp:
+ Với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-2>0\\x-3>0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x>2\\x>3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x>3}\)
+ Với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-2< 0\\x-3< 0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x< 2\\x< 3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x< 2}\)
Vậy x < 2 hoặc x > 3 thì biểu thức có nghĩa

bài 1:
\(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right).\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)>0\)
Để biểu thức \(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\) nhận giá trị dương thì \(-\frac{3}{2}\)và \(\frac{1}{3}-x\)phải cùng âm
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{3}-x< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{1}{3}\)
Vậy \(x>\frac{1}{3}\)thì biểu thức\(\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)\left(\frac{1}{3}-x\right)\) nhận giá trị dương
bài 2:
a)Để \(\frac{x^2-2}{5x}\) nhận giá trị âm thì x2-2<0 hoặc 5x<0
+)Nếu x2-2<0
=>x2<2
=>x<\(\sqrt{2}\)
+)Nếu 5x<0
=>x<0
Vậy x<\(\sqrt{2}\)hoặc x<0 thì biểu thức \(\frac{x^2-2}{5x}\)nhận giá trị âm
b)Để E nhận giá trị âm thì \(\frac{x-2}{x-6}\)nhận giá trị âm
=>x-2<0 hoặc x-6<0
+)Nếu x-2<0
=>x<2
+)Nếu x-6<0
=>x<6
Vậy x<2 hoặc x<6 thì biểu thức E nhận giá trị âm

Bài 1:
a: \(x^2+5x=x\left(x+5\right)\)
Để biểu thức này âm thì \(x\left(x+5\right)< 0\)
hay -5<x<0
b: \(3\left(2x+3\right)\left(3x-5\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{3}{2}< x< \dfrac{5}{3}\)

Lời giải:
a.
\(A=\frac{(x\sqrt{x}-4x)-(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x\geq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-4\neq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-2\neq 0\\ \sqrt{x}-1\neq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\geq 0\\ x\neq 16\\ x\neq 4\\ x\neq 1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\frac{x(\sqrt{x}-4)-(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{2}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}=\frac{(x-1)(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}\)
\(=\frac{(\sqrt{x}-1)(\sqrt{x}+1)(\sqrt{x}-4)}{2(\sqrt{x}-4)(\sqrt{x}-2)(\sqrt{x}-1)}=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{2(\sqrt{x}-2)}\)
b.
Với $x$ nguyên, để $A\in\mathbb{Z}$ thì $\sqrt{x}+1\vdots 2(\sqrt{x}-2)}$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}+1\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x}-2+3\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Leftrightarrow 3\vdots \sqrt{x}-2$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}-2\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 3\right\}$
$\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;9;25\right\}$
Thử lại thấy đều thỏa mãn.
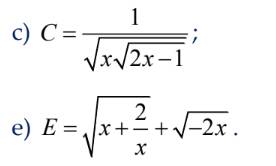

 (Với x > 0; x 1; x4)
(Với x > 0; x 1; x4)