Tìm các giá trị của m để hàm số y=1/3(m-1) x^3-(m-1)x^2 + x + 2 đồng biến trên R
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
Để hàm số y=(2-m)x-2 là hàm số bậc nhất thì 2-m<>0
=>m<>2
a=2-m
b=-2
Bài 2:
a: Để hàm số y=(m-5)x+1 đồng biến trên R thì m-5>0
=>m>5
b: Để hàm số y=(m-5)x+1 nghịch biến trên R thì m-5<0
=>m<5
Bài 3:
a: Để (d1)//(d2) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-m=2\\2\ne m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=1\)
b: Để (d1) cắt (d2) thì \(3-m\ne2\)
=>\(m\ne1\)
c: Để (d1) cắt (d2) tại một điểm trên trục tung thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-m\ne2\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne1\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m=2

a: \(y=-x^3+\left(m+2\right)x^2-3x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+2\left(m+2\right)x-3\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+\left(2m+4\right)\cdot x-3\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2m+4\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(-3\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+16m+16-4\cdot9< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+16m-20< =0\)
=>\(m^2+4m-5< =0\)
=>\(\left(m+5\right)\left(m-1\right)< =0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+5>=0\\m-1< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=-5\\m< =1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-5<=m<=1
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+5< =0\\m-1>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=1\\m< =-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
b: \(y=x^3-3x^2+\left(1-m\right)x\)
=>\(y'=3x^2-3\cdot2x+1-m\)
=>\(y'=3x^2-6x+1-m\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì \(y'>=0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3>0\\\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot3\left(1-m\right)>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(36-12\left(1-m\right)>=0\)
=>\(36-12+12m>=0\)
=>12m+24>=0
=>m+2>=0
=>m>=-2

a: \(y=-x^3-\left(m+1\right)x^2+3\left(m+1\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-\left(m+1\right)\cdot2x+3\left(m+1\right)\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+x\cdot\left(-2m-2\right)+\left(3m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-2m-2\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(3m+3\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+12\left(3m+3\right)< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+36m+36< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+44m+40< =0\)
=>\(m^2+11m+10< =0\)
=>\(\left(m+1\right)\left(m+10\right)< =0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1>=0\\m+10< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=-1\\m< =-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1< =0\\m+10>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =-1\\m>=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-10<=m<=-1
b: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3+mx^2-\left(2m+3\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2+m\cdot2x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
=>\(y'=-x^2+2m\cdot x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< 0\\\left(2m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+4\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\)
=>\(m^2-2m-3< =0\)
=>(m-3)(m+1)<=0
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3>=0\\m+1< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=3\\m< =-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3< =0\\m+1>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =3\\m>=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-1<=m<=3

\(y'=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-m\cdot2x+2m+3=x^2-2m\cdot x+2m+3\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì y'>=0 với mọi x thuộc R
=>Δ=(-2m)^2-4(2m+3)<=0 và 1>0
=>4m^2-8m-12<=0
=>m^2-2m-3<=0
=>(m-3)(m+1)<=0
=>-1<=m<=3
mà m nguyên
nên \(m\in\left\{-1;0;1;2;3\right\}\)

a: \(y=-x^3-3x^2+\left(5-m\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-3\cdot2x+5-m\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-6x+5-m\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(5-m\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(36+12\left(5-m\right)< =0\)
=>\(36+60-12m< =0\)
=>\(-12m+96< =0\)
=>-12m<=-96
=>m>=8
b: \(y=x^3+\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x^2+mx\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+2\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x+m\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+\left(4m-4\right)x+m\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì y'>=0 với mọi x
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3>0\\\left(4m-4\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot m< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(16m^2-32m+16-12m< =0\)
=>\(16m^2-44m+16< =0\)
=>\(4m^2-11m+4< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{11-\sqrt{57}}{8}< =m< =\dfrac{11+\sqrt{57}}{8}\)

a: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-mx^2+4x+2021m\)
=>\(y'=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-m\cdot2x+4\)
=>\(y'=-x^2-2m\cdot x+4\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-2m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot4< =0\\-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+16< =0\)
mà \(4m^2+16>=16>0\forall m\)
nên \(m\in\varnothing\)
b: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot x^3-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot m\cdot x^2+x+20\)
=>\(y'=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot m\cdot2x+1\)
=>\(y'=-x^2-m\cdot x+1\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot1< =0\\-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m^2+4< =0\)
mà \(m^2+4>=4>0\forall m\)
nên \(m\in\varnothing\)

\(y=\dfrac{x^2-m^2+2m+1}{x-m}\) đúng không nhỉ?
\(y'=\dfrac{x^2-2mx+m^2-2m-1}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
Hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng xác định khi và chỉ khi:
\(x^2-2mx+m^2-2m-1\ge0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=m^2-\left(m^2-2m-1\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\)

tròi oi a viết chữ xấu wá đi à, đọc bài của a mà đau mắt wá

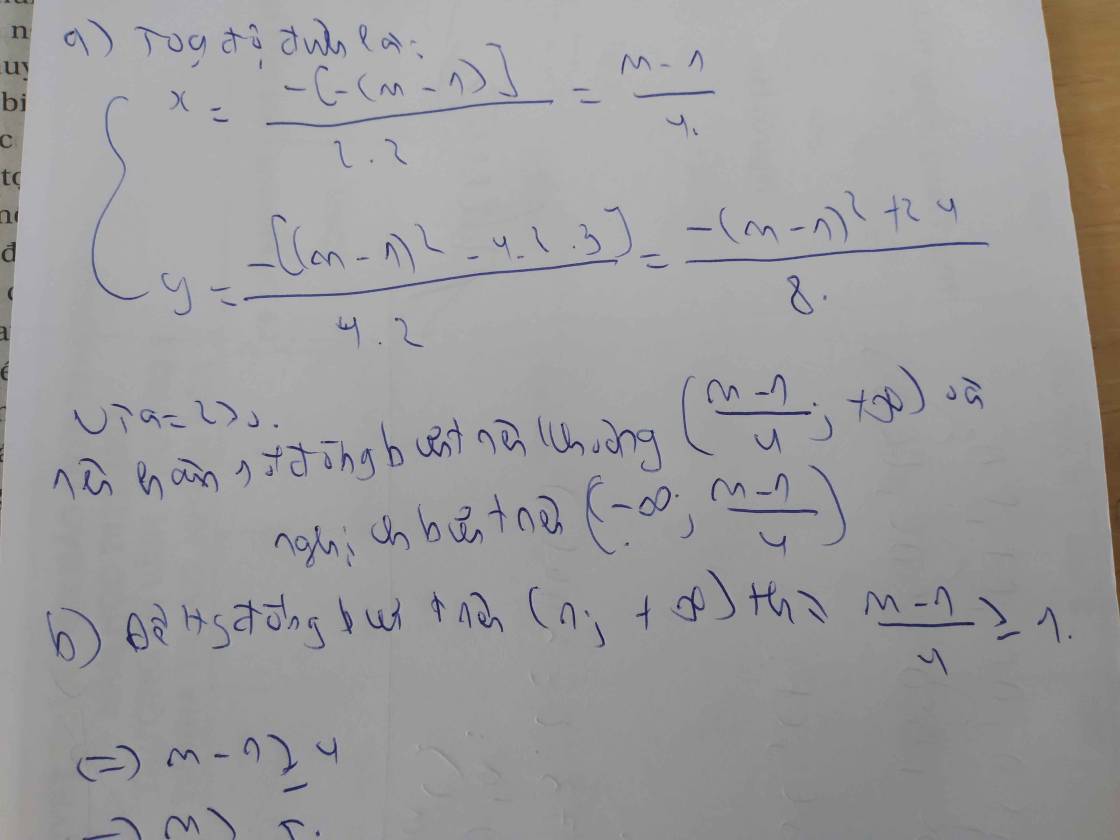

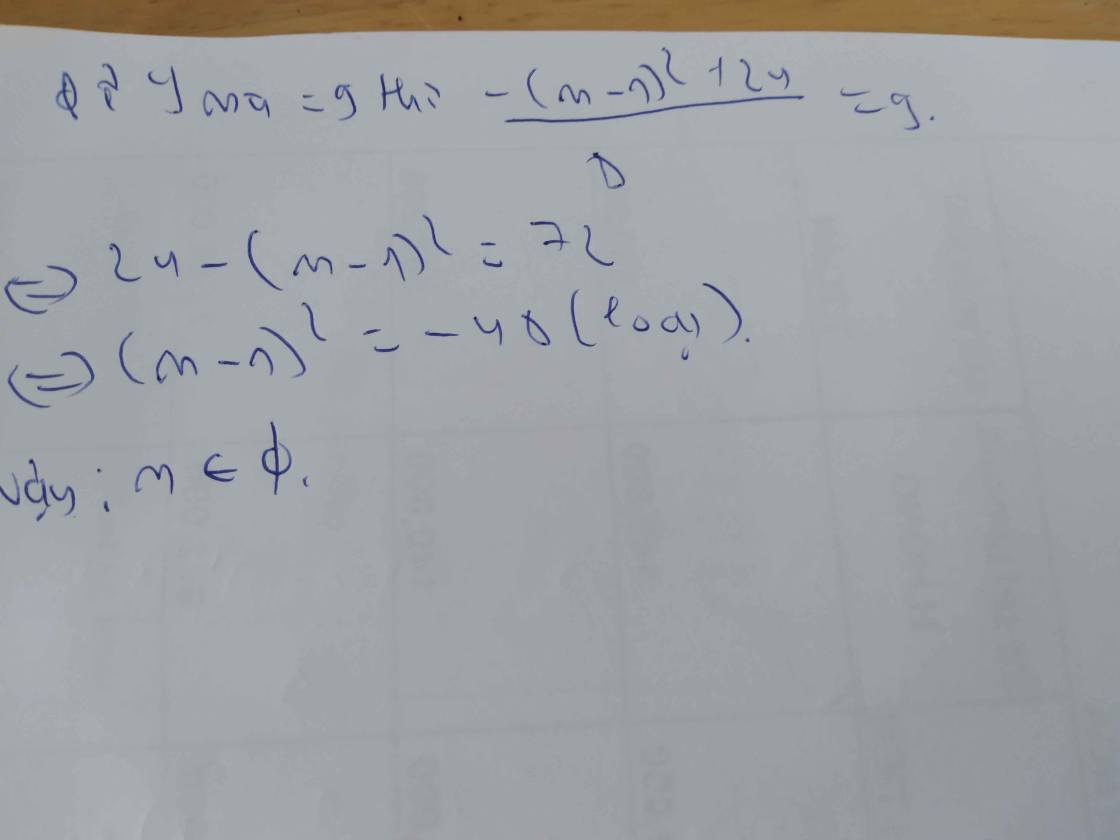
y'=1/3*3x^2(m-1)-(m-1)2x+1
=x^2(m-1)-x(2m-2)+1
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì y'>0 với mọi x
=>m-1<>0 và (2m-2)^2-4(m-1)>0
=>m<>1 và 4m^2-8m+4-4m+4>0
=>4m^2-12m+8>0 và m<>1
=>m^2-3m+2>0 và m<>1
=>m>2 hoặc m<1