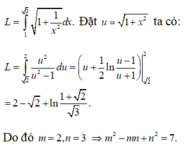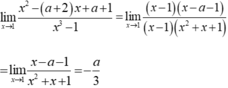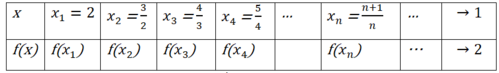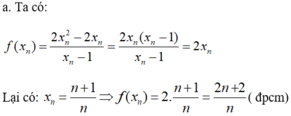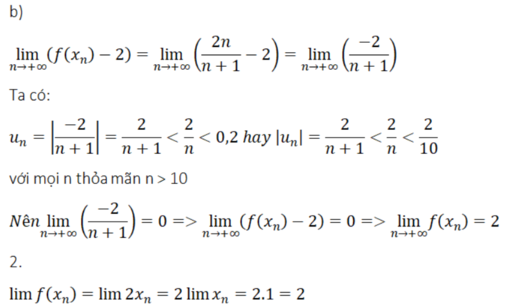Gọi `bb A` là giới hạn của hàm số `f(x)=[x+x^2+x^3+...+x^50 -50]/[x-1]` khi `x -> 1.` Tính giá trị của `bb A.`
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


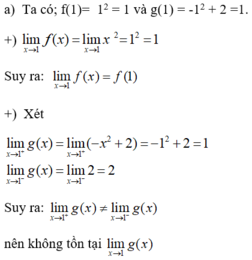
b)
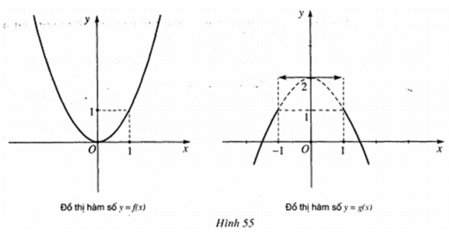
+ Đồ thị của hàm số y = f(x) là đường liền nét tại điểm có hoành độ x= 1.
+ Đồ thị hàm số y = g(x) là đường không liền nét tại điểm có hoành độ x= 1.

a: \(A=5\sqrt{2}-6\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}-1=-1\)
\(B=\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}+1-\left(x-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}+1-x\sqrt{x}+x+\sqrt{x}-1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}}{x-1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
b: A=B
=>căn x=-căn x+1
=>căn x=1/2
=>x=1/4

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}x^2-x+3=1^2-1+3=3\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}\dfrac{x+m}{x}=\dfrac{1+m}{1}=m+1\)
Để tồn tại \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}f\left(x\right)\) thì \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+1=3\Leftrightarrow m=2\)
Vậy ...

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{x^3-1}{x-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{x-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}x^2+x+1=1^2+1+1=3\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}mx+2=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}m+2\)
Để tồn tại \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}f\left(x\right)\) thì \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+2=3\\ \Leftrightarrow m=1\)
Vậy ...

a, \(B=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{2x-\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}}\)ĐK : \(x>0;x\ne1\)
\(=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\sqrt{x}-1\)
b,Ta có \(x=3+2\sqrt{2}=\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}=\sqrt{2}+1\)
Vậy \(B=\sqrt{2}+1-1=\sqrt{2}\)
a) Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{2x-\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\sqrt{x}-1\)
b) Thay \(x=3+2\sqrt{2}\) vào B, ta được:
\(B=\sqrt{2}+1-1=\sqrt{2}\)