tìm điệu kiện xác định của phân thức a)5x/2x+4? b)5x/3x+9
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


`a,x^3-8 ne 0`
`=>x^3 ne 8`
`=>x ne 2`
`b,2x^2+5x+3 ne 0`
`=>2x^2+2x+3x+3 ne 0`
`=>2x(x+1)+3(x+1) ne 0`
`=>(x+1)(2x+3) ne 0`
`=>x ne -1,-3/2`
`c,x^2-4 ne 0`
`=>x^2 ne 4`
`=>x ne 2,-2`
a) ĐK:
\(x^3-8\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne2\)
b) ĐK:
\(2x^2+5x+3\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-1\\x\ne-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) ĐK:
\(x^2-4\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm2\)

a)ĐK:`3x-6>=0`
`<=>3x>=6<=>x>=2`
b)ĐK:`-3x+9>=0`
`<=>-3x>=-9`
`<=>x<=3`
c)ĐK:`(-5)/(-3x+2)>=0(x ne -2/3)`
Vì `-5<0`
`<=>-3x+2<0`
`<=>-3x<-2`
`<=>x>2/3`
e)ĐK:`(5x-3)/(-4)>=0`
MÀ `-4<0`
`<=>5x-3<=0`
`<=>5x<=3`
`<=>x<=3/5`

a) ĐK: x ≥ 2
\(\sqrt{3x-6}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-6=9\)
<=> 3x = 15
<=> x = 5
Vậy:....
b) ĐK: 5x - 16 ≥ 0
<=> 5x ≥ 16
<=> x ≥ 16/5
\(\sqrt{5x-16}=2\)
<=> 5x - 16 = 4
<=> 5x = 20
<=> x = 4
c) ĐK: \(x^2-4x+3\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
bình phương hai vế ta được:
a)điều kiện của x:x≥2
3x-6=9 <=> x=5(nhận)
b)ĐK: x≥16/5
5x-16=4 <=>x=4(nhận)
c) ta có: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{\left(x-2\right)^2-1}\)= \(\dfrac{2x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: x≠3 ;x≠1

a) \(\dfrac{5x}{10}=\dfrac{x}{2}\)
b) \(\dfrac{4xy}{2y}=2x\left(y\ne0\right)\)
c) \(\dfrac{5x-5y}{3x-3y}=\dfrac{5}{3}\left(x\ne y\right)\)
d) \(\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{x+y}=x-y\left(đk:x\ne-y\right)\)
e) \(\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x-1}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x+1}\left(đk:x\ne\pm1\right)\)
f) \(\dfrac{x^2+4x+4}{2x+4}=\dfrac{x+2}{2}\left(đk:x\ne-2\right)\)

a) Phân thức xác định \(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x\ne0\\x+1\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}\)
b) Để phân thức bằng 1 thì :
\(5x+5=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy.......
Phân thức xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+2\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+1\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy với \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}\) thì phân thức xác định

Đặt \(\frac{5x+5}{2x^2+2x}=A\)
a/ Để A xác định\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
TXĐ:\(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
b/ Với \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)ta có \(A=\frac{5x+5}{2x^2+2x}\)
Để A=1\(\Leftrightarrow5x+5=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=2x\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{2}{5}\)( TM )

a. \(x^2-5x\ne0\)
=> ĐKXĐ: \(x\left(x-5\right)\ne0\) => \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x\ne5\end{matrix}\right.\)
b. \(\dfrac{x^2-10x+25}{x^2-5x}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{x\left(x-5\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{x-5}{x}\)
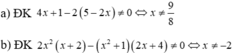

\(a,\dfrac{5x}{2x+4}\\ ĐK:2x+4\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x\ne-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne-2\\ b,\dfrac{5x}{3x+9}\\ ĐK:3x+9\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x\ne-9\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne-3\)