(x2+x)+4(x2+x)-12=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)

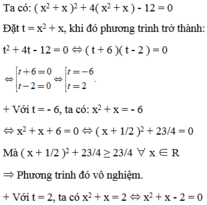
⇔ ( x + 2 )( x - 1 ) = 0 ⇔ 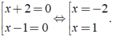
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S = { - 2;1 }.

e, \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-2\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=2\)
f, \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-x\left(x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1;x=-1\)
g, \(x^2\left(x-3\right)+4\left(3-x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=2;x=-2;x=3\)
h, \(\left(2x-1-x-3\right)\left(2x-1+x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(3x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=4;x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

Bài 1
a/ \(x\left(x^2+1\right)+2\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\Rightarrow x=-2\)
b/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+9x+5x^2-30x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)^2+5\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
1.
c/ \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+2x^2+2x+x^2+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+2x+2\right)+x^2+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x^2+2x+2=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3-2x^2-x^3-x^2+2x+4x^2+4x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+x-2\right)-x\left(x^2+x-2\right)+4\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x+4\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x+4=0\left(vn\right)\\x^2+x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow x^3-8-x^3-2x=12\Leftrightarrow-2x=20\Leftrightarrow x=-10\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2+4=16\Leftrightarrow=-6x=3\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ c,\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-6\right)+9\left(x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+9\right)\left(x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=6\left(x^2+9>0\right)\)

Bài 1)1)\(x^2+5x+6=x^2+3x+2x+6\)=0
=x(x+3)+2(x+3)=(x+2)(x+3)=0
Dễ rồi
2)\(x^2-x-6=0=x^2-3x+2x-6=0\)
=x(x-3)+2(x-3)=0
=(x+2)(x-3)=0
Dễ rồi
3)Phương trình tương đương:\(\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
Vì \(x^2+1>0\)
=>\(\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
Dễ rồi
4)Phương trình tương đương\(x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)\)=0
=> \(\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0Vì\) \(x^2+1>0\)
=>x+1=0
=>..................
5)\(x^2-7x+6=x^2-6x-x+6\) =0
=x(x-6)-(x-6)=0
=(x-1)(x-6)=0
=>.....
6)\(2x^2-3x-5=2x^2+2x-5x-5\)=0
=2x(x+1)-5(x+1)=0
=(2x-5)(x+1)=0
7)\(x^2-3x+4x-12\)=x(x-3)+4(x-3)=(x+4)(x-3)=0
Dễ rồi
Nghỉ đã hôm sau làm mệt

Đáp án: B.
Các phương trình còn lại có nhiều hơn một nghiệm:
(x - 5)( x 2 - x - 12) = 0 có các nghiệm x = 5, 4, -3.
sin 2 x - 5sinx + 4 = 0 ⇔ sinx = 1, có vô số nghiệm
sinx - cosx + 1 = 0 có các nghiệm x = 0, x = 3 π /2

Đáp án: B.
Các phương trình còn lại có nhiều hơn một nghiệm:
(x - 5)( x 2 - x - 12) = 0 có các nghiệm x = 5, 4, -3.
sin 2 x - 5sinx + 4 = 0 ⇔ sinx = 1, có vô số nghiệm
sinx - cosx + 1 = 0 có các nghiệm x = 0, x = 3π/2.





(x2 + x) + 4(x2 + x) - 12 = 0
5(x2 + x) = 12
x2 + x = 2,4
x2 + 2.x.0,5 + (0,5)2 = 2,4 + (0,5)2
(x + 0,5)2 = 2,65
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+0,5=\sqrt{2,65}\\x+0,5=-\sqrt{2,65}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{2,65}-0,5\\x=-\sqrt{2,65}-0,5\end{cases}}}\)