x+1=2
tìm x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(3x+1\right)^2=9\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9x^2-36x+36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1-9x^2+36x-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x-35=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x=35\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{35}{42}=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{6}\right\}\)

\(\)áp dụng BĐT AM-GM(BÀi này ko có Max chỉ có Min)
\(=>\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{xy}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{xy}}\)
\(=>\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{xy}}=>\sqrt{xy}\ge4\)
\(=>S=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\ge2\sqrt{4}=4\)
dấu"=" xảy ra<=>x=y=4

Lời giải:
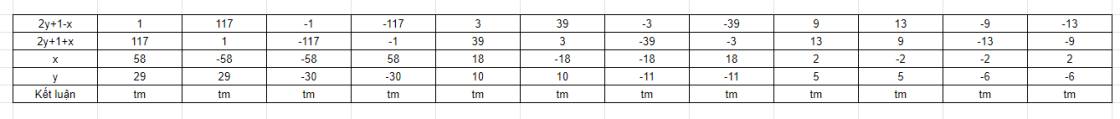
$117=(2y+1)^2-x^2=(2y+1-x)(2y+1+x)$
Vì $x,y$ nguyên nên $2y+1-x, 2y+1+x$ nguyên. Do đó ta có bảng sau:

\(\Leftrightarrow a\cdot\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{28}{13}:2=\dfrac{14}{13}\)
=>\(a=\dfrac{14}{13}:\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{210}{169}\)

Để A là số nguyên thì \(2x-1\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;0;3;-2\right\}\)

ĐK: x≥2
\(\sqrt{x^2-4}=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4=x^2-4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)

P>1/3
=>P-1/3>0
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}-\dfrac{1}{3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-3-\sqrt{x}-2}{3\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}>0\)
=>2 căn x-5>0
=>x>25/4
x + 1 = 2
x = 2 - 1
x = 1
x+1=2
x=2-1
x=1