M(x) = x^2 -3x + 2
Tìm nghiệm của M(x)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

cho hệ pt 3x-y=2m-1 và x+2y=3m+2
tìm m để hpt có nghiệm ( x;y) thỏa mãn \(^{x^2}\)+\(^{y^2}\)đạt GTNN

Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-y=2m-1\\x+2y=3m+2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-2y=4m-2\\x+2y=3m+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x=7m\\y=3x-2m+1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=m\\y=m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mặt khác: \(x^2+y^2=2m^2+2m+1=2\left(m^2+m+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left(m^2+2\cdot m\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=2\left(m+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow m+\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow m=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy ...

a, \(Chof\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Lập bảng xét dấu :
Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(3;4\right)\\f\left(x\right)< 0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-\infty;3\right)\cup\left(4;+\infty\right)\\f\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{3;4\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+6\right)\)
( Làm tương tự câu a )

b) Thay x=2 vào pt, ta được:
\(4\left(m^2-1\right)-4m+m^2+m+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-4-4m+m^2+m+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5m^2-3m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(5m-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2m}{m^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2+2=0\\x_2+2=\dfrac{6}{5}:\left(\dfrac{36}{25}-1\right)=\dfrac{30}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2=-2\\x_2=\dfrac{8}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Δ=(m+2)^2-4(m^2-1)
=m^2+4m+4-4m^2+4
=-3m^2+4m+8
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì -3m^2+4m+8>=0
=>\(\dfrac{2-2\sqrt{7}}{3}< =m< =\dfrac{2+2\sqrt{7}}{3}\)
x1-x2=2
=>(x1-x2)^2=4
=>(x1+x2)^2-4x1x2=4
=>(m+2)^2-4(m^2-1)=4
=>-3m^2+4m+8=4
=>-3m^2+4m+4=0
=>m=2 hoặc m=-2/3

khi m=2 ta có hệ pt:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=2+1\\2x+y=2.2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=3\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=6\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=2\\x+2y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{3}\\2x+\dfrac{2}{3}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{3}\\2x=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy khi m=2 thì hệ pt có nghiệm duy nhất\(\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{5}{3}\right\}\)
a) Thay m=2 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=3\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=6\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=2\\x+2y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=3-2y=3-2\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Khi m=2 thì hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là \(\left(x,y\right)=\left(\dfrac{5}{3};\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)

a) Thay m=2 vào hệ phương trình, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2y=5\\2x-y=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-4y=10\\2x-y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3y=3\\x-2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x=5+2y=5+2\cdot\left(-1\right)=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Khi m=2 thì hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là (x,y)=(3;-1)

Từ điều kiện đề bài \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b+c=8\\-\dfrac{b}{2a}=2\\\dfrac{4ac-b^2}{4a}=9\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=-x^2+4x+5\)
a. Không tồn tại m để \(3\left|f\left(x\right)\right|+m-5=0\) có 3 nghiệm phân biệt (nếu pt đã cho có 3 nghiệm thì 1 nghiệm trong đó luôn là nghiệm kép). Có 3 nghiệm thì được (khi đó \(\dfrac{5-m}{3}=9\Rightarrow m\))
b. \(2f\left(\left|x\right|\right)-7+5m=0\Leftrightarrow f\left(\left|x\right|\right)=\dfrac{-5m+7}{2}\) (1)
Đồ thì hàm \(y=f\left(\left|x\right|\right)\) (tạo ra bằng cách bỏ phần bên trái trục Oy và lấy đối xứng phần bên phải của đồ thị \(y=f\left(x\right)\) qua):
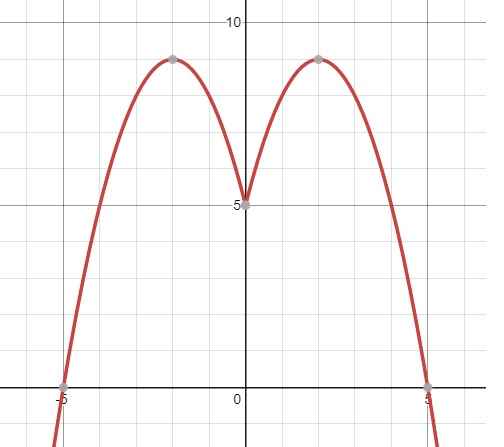
Từ đồ thị ta thấy (1) có 4 nghiệm pb khi:
\(5< \dfrac{-5m+7}{2}< 9\) \(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{11}{5}< m< -\dfrac{3}{5}\)

a, để (d) // (d1) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-m=3\\2m-3\ne-m+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=-3\\m\ne\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=-3\)
b, để (d) ⊥ (d1) thì \(-m.3=-1\Rightarrow-m=-\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{1}{3}\)

\(\left(3x+1\right)^2=9\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9x^2-36x+36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1-9x^2+36x-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x-35=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x=35\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{35}{42}=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{6}\right\}\)
Nghiệm là 2.
Cho \(M\left(x\right)=0\)
hay \(x^2-3x+2=0\)
⇒ \(x^2-2x-x+2=0\)
\(x.x-2x-x+2=0\)
\(x.\left(x-2\right)-\left(x+2\right)=0\)
⇒ \(\left(x-1\right).\left(x-2\right)=0\)
⇒ \(x-1=0\) hoặc \(x-2=0\)
* \(x-1=0\) * \(x-2=0\)
\(x\) \(=0+1\) \(x\) \(=0+2\)
\(x\) \(=1\) \(x\) \(=2\)
Vậy \(x=1\) hoặc \(x=2\) là nghiệm của \(M\left(x\right)\)