Ét O Ét, giúp em bài 4 với ạ 🙏🙏🙏🙏🙏. Cần gấp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.
Đường tròn (C): \(x^2+y^2-6x+4y+12=0\) có tâm \(J\left(3;-2\right)\) bán kính \(r=1\)
Tiếp điểm A của 2 đường tròn phải nằm trên đường nối tâm IJ
\(\overrightarrow{JI}=\left(3;4\right)\Rightarrow\) phương trình IJ có dạng:
\(4\left(x-3\right)-3\left(y+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow4x-3y-18=0\)
Tọa độ tiếp điểm A là nghiệm của hệ :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-3y-18=0\\x^2+y^2-6x+4y+12=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{4x-18}{3}\\x^2+y^2-6x+4y+12=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+\left(\dfrac{4x-18}{3}\right)^2-6x+4\left(\dfrac{4x-18}{3}\right)+12=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{25}{9}x^2-\dfrac{50}{3}x+24=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{12}{5}\Rightarrow y=-\dfrac{14}{5}\\x=\dfrac{18}{5}\Rightarrow y=-\dfrac{6}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}A\left(\dfrac{12}{5};-\dfrac{14}{5}\right)\\A\left(\dfrac{18}{5};-\dfrac{6}{5}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AI}=\left(\dfrac{18}{5};\dfrac{24}{5}\right)\\\overrightarrow{AI}=\left(\dfrac{12}{5};\dfrac{16}{5}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}R^2=AI^2=36\\R^2=AI^2=\dfrac{36}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có 2 đường tròn thỏa mãn:
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-6\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2=36\\\left(x-6\right)^2+\left(y-2\right)^2=\dfrac{36}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
Đường tròn (C): \(x^2+y^2=4\) có tâm \(O\left(0;0\right)\) và bán kính \(r=2\)
Gọi \(I\left(a;b\right)\) là tâm của đường tròn (C') cần tìm
Do (C') tiếp xúc Ox \(\Rightarrow d\left(I;Ox\right)=3\Rightarrow\dfrac{\left|b\right|}{1}=3\Rightarrow b=\pm3\)
TH1: \(I\left(a;3\right)\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{OI}=\left(a;3\right)\Rightarrow OI=\sqrt{a^2+9}\)
Do 2 đường tròn tiếp xúc \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}R+r=OI\\R-r=OI\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}OI=5\\OI=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{a^2+9}=5\\\sqrt{a^2+9}=1\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a=\pm4\)
TH2: hoàn toàn tương tự ta có tìm được \(a=\pm4\)
Vậy có 4 đường tròn thỏa mãn: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-4\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2=9\\\left(x+4\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2=9\\\left(x-4\right)^2+\left(y+3\right)^2=9\\\left(x+4\right)^2+\left(y+3\right)^2=9\end{matrix}\right.\)

4b.
\(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< a< \pi\Rightarrow cosa< 0\Rightarrow cosa=-\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow tana=\dfrac{sina}{cosa}=-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(tan\left(a+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{tana+tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)}{1-tana.tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)}=\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{4}+\sqrt{3}}{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{4}\right).\sqrt{3}}=...\)
c.
\(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}< a< 2\pi\Rightarrow cosa>0\Rightarrow cosa=\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-a\right)=cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right).cosa+sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right).sina=\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{5}{13}+\left(-\dfrac{12}{13}\right).\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=...\)

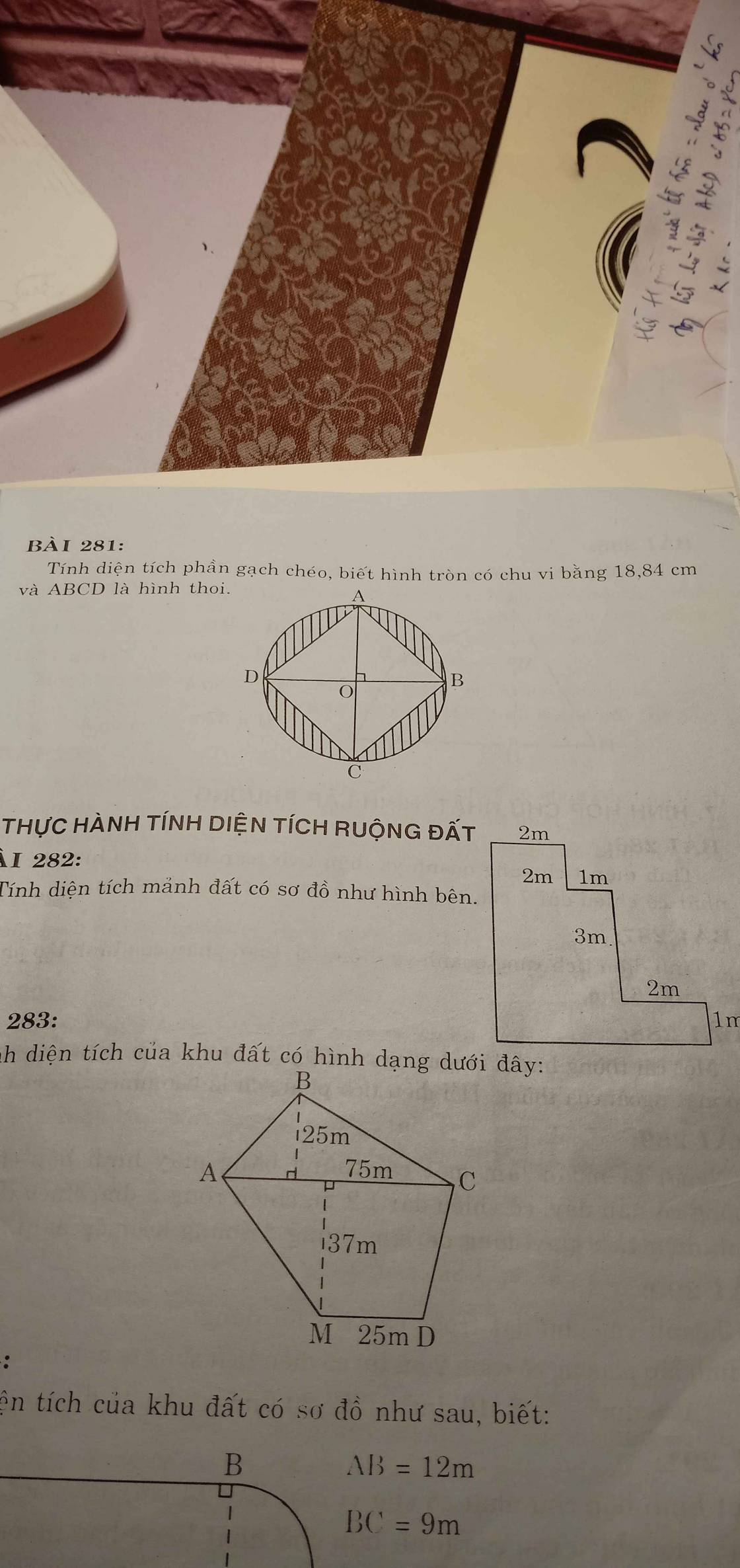
Bán kính hình tròn:
\(18,84:3,14:2=3\left(cm\right)\)
Diện tích hình tròn:
\(3\times3\times3,14=28,26\left(cm^2\right)\)
Đường kính hình tròn:
\(3\times2=6\left(cm\right)\)
Diện tích hình thoi:
\(\dfrac{6\times6}{2}=18\left(cm^2\right)\)
Diện tích phần gạch chéo:
\(28,26-18=10,26\left(cm^2\right)\)

5:
a: sin x=2*cosx
\(A=\dfrac{6cosx+2cosx-4\cdot8\cdot cos^3x}{cos^3x-2cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{8-32cos^2x}{cos^2x-2}\)
b: VT=sin^4(pi/2-x)+cos^4(x+pi/2)+6*1/2*sin^22x+1/2*cos4x
=cos^4x+sin^4x+3*sin^2(2x)+1/2*(1-2*sin^2(2x))
=1-2*sin^2x*cos^2x+3*sin^2(2x)+1/2-sin^2(2x)
==3/2=VP

a.
Trong tam giác A'BC ta có: I là trung điểm BA', M là trung điểm BC
\(\Rightarrow IM\) là đường trung bình tam giác A'BC
\(\Rightarrow IM||A'C\)
\(\Rightarrow IM||\left(ACC'A'\right)\)
Do \(A\in\left(AB'M\right)\cap\left(ACC'A'\right)\) và \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}IM\in\left(AB'M\right)\\A'C\in\left(ACC'A'\right)\\IM||A'C\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Giao tuyến của (AB'M) và (ACC'A') là đường thẳng qua A và song song A'C
Qua A kẻ đường thẳng d song song A'C
\(\Rightarrow d=\left(AB'M\right)\cap\left(ACC'A'\right)\)
b.
I là trung điểm AB', E là trung điểm AM
\(\Rightarrow IE\) là đường trung bình tam giác AB'M \(\Rightarrow IE||B'M\) (1)
Tương tự ta có IN là đường trung bình tam giác AA'B' \(\Rightarrow IN||A'B'\) (2)
(1);(2) \(\Rightarrow\left(EIN\right)||\left(A'B'M\right)\)
c.
Trong mp (BCC'B'), qua K kẻ đường thẳng song song B'M lần lượt cắt BC và B'C' tại D và F
\(DF||B'M\Rightarrow DF||IE\Rightarrow DF\subset\left(EIK\right)\)
Trong mp (ABC), nối DE kéo dài cắt AB tại G
\(\Rightarrow G\in\left(EIK\right)\)
Trong mp (A'B'C'), qua F kẻ đường thẳng song song A'C' cắt A'B' tại H
Do IK là đường trung bình tam giác A'BC' \(\Rightarrow IK||A'B'\)
\(\Rightarrow FH||IK\Rightarrow H\in\left(EIK\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tứ giác DFHG là thiết diện (EIK) và lăng trụ
Gọi J là giao điểm BK và B'M \(\Rightarrow J\) là trọng tâm tam giác B'BC
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{BJ}{BK}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Áp dụng talet: \(\dfrac{BM}{BD}=\dfrac{BJ}{BK}=\dfrac{2}{3}\Rightarrow BD=\dfrac{3}{2}BM=\dfrac{3}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}BC=\dfrac{3}{4}BC\)
\(\Rightarrow MD=\dfrac{1}{4}BC=\dfrac{1}{2}CM\Rightarrow D\) là trung điểm CM
\(\Rightarrow DE\) là đường trung bình tam giác ACM
\(\Rightarrow DE||AC\Rightarrow DE||FH\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Thiết diện là hình thang











4:
a: -90<a<0
=>cos a>0
cos^2a=1-(-4/5)^2=9/25
=>cosa=3/5
\(sin\left(45-a\right)=sin45\cdot cosa-cos45\cdot sina=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(cosa-sina\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{4}{5}\right)=\dfrac{-\sqrt{2}}{10}\)
b: pi/2<a<pi
=>cosa<0
cos^2a+sin^2a=0
=>cos^2a=16/25
=>cosa=-4/5
tan a=3/5:(-4/5)=-3/4
\(tan\left(a+\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{tana+\dfrac{tanpi}{3}}{1-tana\cdot tan\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{4}+\sqrt{3}}{1-\dfrac{-3}{4}\cdot\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{48-25\sqrt{3}}{11}\)
c: 3/2pi<a<pi
=>cosa>0
cos^2a+sin^2a=1
=>cos^2a=25/169
=>cosa=5/13
cos(pi/3-a)
\(=cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\cdot cosa+sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\cdot sina\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{13}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{-12}{13}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{5-12\sqrt{3}}{26}\)