X x 9 - X x 2 = 41 + 22
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


X + 6 = 33
X = 33 − 6
X = 27
9 + x = 22
X = 22 − 9
X = 13
X − 41 = 41
X = 41 + 41
X = 82

X x 9 - X x 2 = 41 + 22
X x 9 - X x 2 = 63
X x ( 9 - 2 ) = 63
X x 7 = 63
X = 63 : 7
X = 9
Vậy : X = 9

\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}-\dfrac{41}{x+3}+\dfrac{x^2+22}{9-x^2}=0\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne3;x\ne-3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}-\dfrac{41}{x+3}-\dfrac{x^2+22}{x^2-9}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)-41\left(x-3\right)-x^2-22}{x^2-9}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+3-41x+123-x^2-22=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-37x+104=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-37x=-104\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{104}{37}\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{104}{37}\) là nghiệm của pt.

Bài 3:
\(a,\dfrac{x-1}{10}+\dfrac{x-1}{11}=\dfrac{x-1}{12}+\dfrac{x-1}{13}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{10}+\dfrac{x-1}{11}-\dfrac{x-1}{12}-\dfrac{x-1}{13}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\right)=0\)
Mà \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{11}-\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{13}\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
Vậy x = 1
b, \(\dfrac{x-2000}{10}+\dfrac{x-1999}{9}=\dfrac{x-1998}{8}+\dfrac{x-1997}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-2000}{10}+1+\dfrac{x-1999}{9}+1=\dfrac{x-1998}{8}+\dfrac{x-1997}{7}+1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-1990}{10}+\dfrac{x-1990}{9}-\dfrac{x-1990}{8}-\dfrac{x-1990}{7}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1990\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{9}-\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{7}\right)=0\)
Mà \(\dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{9}-\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{7}\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1990=0\Rightarrow x=1990\)

Đáp án D.
Phương trình tương đương với

Đặt 2 x - 1 2 x = t → 4 x + 1 4 x = t 2 + 2 . Xét hàm số t ( x ) = 2 x - 1 2 x trên 0 ; 1 .
Đạo hàm t ' ( x ) = 2 x . ln 2 + ln 2 2 x > 0 , ∀ x ∈ 0 ; 1 ⇒ Hàm số t ( x ) luôn đồng biến trên 0 ; 1 . Suy ra min x ∈ 0 ; 1 t ( x ) = t ( 0 ) = 0 và max x ∈ 0 ; 1 t ( x ) = t ( 1 ) = 3 2 . Như vậy t ∈ 0 ; 3 2 .
Phương trình (1) có dạng:
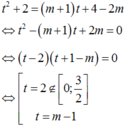
Phương trình (1) có nghiệm t ∈ 0 ; 1 ⇔ phương trình ẩn t có nghiệm t ∈ 0 ; 3 2 ⇔ 0 ≤ m - 1 ≤ 3 2 ⇔ 1 ≤ m ≤ 5 2 . Mà m ∈ ℤ nên m ∈ 1 ; 2 . Tổng tất cả các giá trị nguyên của m bằng 3.

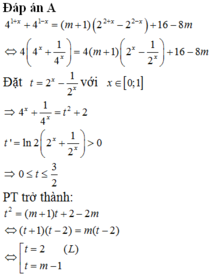
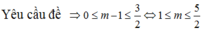
\(Xx\left(9-2\right)=63\)
\(Xx7=63\)
\(X=63:7=9\)
x(9-2)=63
x . 7= 63
x=63:7
x=9