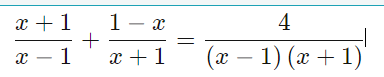
tìm đkxd và giải pt .hứa vote nhanh ạ.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
$2x^4-3x^2-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x^4+2x^2)-(5x^2+5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2(x^2+1)-5(x^2+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+1)(2x^2-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2-5=0$ (do $x^2+1\geq 1>0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$)
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=\frac{5}{2}$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}$
Bài 2:
a. Khi $m=1$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-6x+5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2-x)-(5x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-1)-5(x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x-5)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$ hoặc $x-5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=5$
b.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta=(m+5)^2-4(-m+6)\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+14m+1\geq 0(*)$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=m+5$
$x_1x_2=-m+6$
Khi đó:
$x_1^2x_2+x_1x_2^2=18$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2(x_1+x_2)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+5)(-m+6)=18$
$\Leftrightarrow -m^2+m+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2-m-12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m+3)(m-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-3$ hoặc $m=4$
Thử lại vào $(*)$ thấy $m=4$ thỏa mãn.

4.3:
a: Xét ΔCED vuông tại E và ΔCAB vuông tại A có
góc C chung
=>ΔCED đồng dạng với ΔCAB
b: ΔCED đồng dạng với ΔCAB
=>ED/AB=EC/AC
=>ED*AC=EC*AB
c: BC=căn 9^2+12^2=15cm
AD là phân giác
=>DB/AB=DC/AC
=>DB/3=DC/4=(DB+DC)/(3+4)=15/7
=>DC=60/7cm

ĐKXĐ: x^2-5x+6>=0 và x^2-2<>0
=>(x>=3 hoặc x<=2) và (x<>căn 2 và x<>-căn 2)
=>x>=3 hoặc \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =2\\x\notin\left\{\sqrt{2};-\sqrt{2}\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)

1. \(S=1+3+3^2+3^3+........+3^{2019}+3^{2020}\)
\(\Rightarrow3S=3+3^2+3^3+3^4+........+3^{2020}+3^{2021}\)
\(\Rightarrow3S-S=3^{2021}-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2S=3^{2021}-1\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\frac{3^{2021}-1}{2}\)
2. \(\left(3x-2\right)^3=64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)^3=4^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(x=2\)
[3x-2]^3=64
Ta có:64=4^3
Suy ra:3x-2=4
3x =4+2
3x=6
x=6:3
x=2

a) Xác định bài toán
-Input: Dãy n số
-Output: Các số nguyên khác 0
b) Biểu diễn thuật toán
-Bước 1: Nhập n và nhập dãy số
-Bước 2: i←1;
-Bước 3: Nếu a[i]<>0 thì xuất a[i]
-Bước 4: i←i+1;
-Bước 5: Nếu i<=n thì quay lại bước 3
-Bước 6: Kết thúc


Tham khảo
+ HAVE TO diễn tả nghĩa “phải” do xuất phát từ chủ quan người nói. Ví dụ: I have to brush my teeth twice a day.
+ MUST chỉ dùng được cho thì hiện tại hoặc tương lai, nhưng nếu muốn diễn tả ý nghĩa “phải” trong quá khứ, ta phải sử dụng
Have To. Ví dụ: I had to go to the dentist yesterday.

Bài 7:
Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{x\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}-x-1}\right):\left(1+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\left(x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{x\sqrt{x}-1}\)

Bài 2:
a: \(6.25\cdot1.34=8.375\)
b: \(48.6\cdot2.5=121.5\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{1-x}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne1;x\ne-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)+\left(1-x\right)\left(x-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+x+1+x-1-x^2+x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x^2+x+x+x+x-4+1-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{1-x}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(1-x\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{\left(x+1+x-1\right)\left(x+1-x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{2x.2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
⇒ \(4x=4\)
⇔ \(x=1\) (ko thỏa mãn dktc)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm