giải bất phương trình 2x-1/x+2>3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}< \dfrac{1}{3}\left(đk:x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-9< x-1\Leftrightarrow5x< 8\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{8}{5}\) và ĐK \(x\ne1\)
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}>\dfrac{1}{3}\left(đk:x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 6x-9\Leftrightarrow5x>8\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{8}{5}\) và ĐK \(x\ne1\)

a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
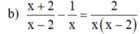
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
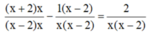
![]()
![]()
![]()
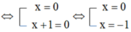
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}

\(\dfrac{x}{2x-6}-\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1,x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\cdot2}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm , trừ x = -1,x = 3
Vậy ...
\(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< \dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\cdot\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< 12\cdot\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-12\cdot\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 4\left(9x+1\right)-3\left(8x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 36x+4-24x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-12x< 1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x< 0\)
Vậy S = {x | x \(\in R\)}

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

a) (x + 2)(x – 1) < (x + 3)2 – 5 ⇔ x2 – x + 2x – 2 < x2 + 6x + 9 – 5
⇔ x – 6x < 2 + 4 ⇔ –5x < 6 ⇔ x > -6/5
Tập nghiệm : S = {x | x > -6/5}
![]()
⇔ 6 + 2(2x + 1) > 2x – 1
⇔ 6 + 4x + 2 > 2x – 1 ⇔ 2x > – 9 ⇔ x > -9/2
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x > -9/2}

\(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\ge\dfrac{5}{2x-1}\)
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 2; \(x\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\ge\dfrac{5}{2x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{x-2}-\dfrac{5}{2x-1}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(2x-1\right)-5\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\ge0\)
*Với: \(\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=0\)
=> x + 7 = 0
<=> x =-7
*Với \(\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}>0\) (1)
Ta lâpj bảng xét dấu:
x |
| -7 |
| 1/2 |
| 2 |
|
X + 7 | - | 0 | + | | | + | | | + |
2x – 1 | - | | | - | 0 | + | | | + |
X - 2 | - | | | - | | | - | 0 | + |
BĐT (1) | - | 0 | + | || | - | || | + |
Từ bảng trên ta có thể thấy: \(\dfrac{x+7}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}>0\) khi -7 < x < 1/2 hoăcj x > 2
Vayj:.............

ĐKXĐ: \(x>3\)
Lấy logarit 2 vế: \(\left(2x^2-7x\right).ln\left(x-3\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-7\right)ln\left(x-3\right)>0\)
Bảng xét dấu:
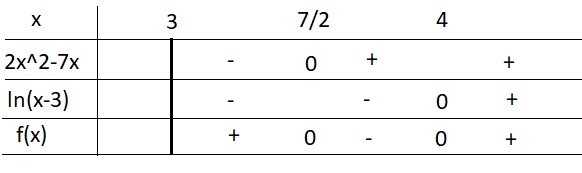
\(\Rightarrow\) Nghiệm của BPT là \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3< x< \dfrac{7}{2}\\x>4\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x-3\ge0\\2x^2-3x+1\ge0\\x^2+2x-3\le2x^2-3x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\x^2-5x+4\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\le-3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge4\\x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x\le-3\\x\ge4\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\frac{2x-1}{x+2}>3\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x-1}{x+2}-3>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x-1}{x+2}-\frac{3x+6}{x+2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{-x-7}{x+2}>0\)
TH1 :\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-7>0\\x+2>0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x< -7\\x>-2\end{cases}}\left(lọai\right)\)
TH2 : \(\hept{\begin{cases}-x-7< 0\\x+2< 0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x>-7\\x< -2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow-7< x< -2\)
Vậy -7 < x < -2