 giúp mik với ạ
giúp mik với ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


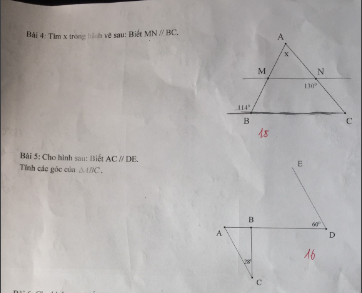
Câu 3:
a: \(BD=\sqrt{BC^2-DC^2}=4\left(cm\right)\)
b: \(\widehat{A}=180^0-2\cdot70^0=40^0< \widehat{B}\)
nên BC<AC=AB
c: Xét ΔEBC vuông tại E và ΔDCB vuông tại D có
BC chung
\(\widehat{EBC}=\widehat{DCB}\)
Do đó:ΔEBC=ΔDCB
d: Xét ΔOBC có \(\widehat{OBC}=\widehat{OCB}\)
nên ΔOBC cân tại O
Câu 2
a) Thay y = -2 vào biểu thức đã cho ta được:
2.(-2) + 3 = -1
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức đã cho tại y = -2 là -1
b) Thay x = -5 vào biểu thức đã cho ta được:
2.[(-5)² - 5] = 2.(25 - 5) = 2.20 = 40
Vậy giá trị của biểu thức đã cho tại x = -5 là 40


1 were - would you play
2 weren't studying - would have
3 had taken - wouldn't have got
4 would you go - could
5 will you give - is
6 recycle - won't be
7 had heard - wouldn't have gone
8 would you buy - had
9 don't hurry - will miss
10 had phoned - would have given
11 were - wouldn't eat
12 will go - rains
13 had known - would have sent
14 won't feel - swims
15 hadn't freezed - would have gone

\(a,=\dfrac{x^3+2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^3+2x+2x-2-\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^3+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^3+3}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)

a: \(=\dfrac{x^3+2x+2x-2-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+3}{x^2+x+1}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{x^2-2x-3+x^2+2x-3+2x-2x^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+3}\)
c: \(=\dfrac{6-7+x}{3\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{3\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
d: \(=\dfrac{x^3+2x+2x-2-x^2-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+3}{x^2+x+1}\)

1 is explained
2 was stolen
3 will be opened
4 is being closed
5 is going to be built

 giúp mik với ạ mik cần gấp. GIẢI CỤ THỂ GIÚP MIK vs ạ
giúp mik với ạ mik cần gấp. GIẢI CỤ THỂ GIÚP MIK vs ạ
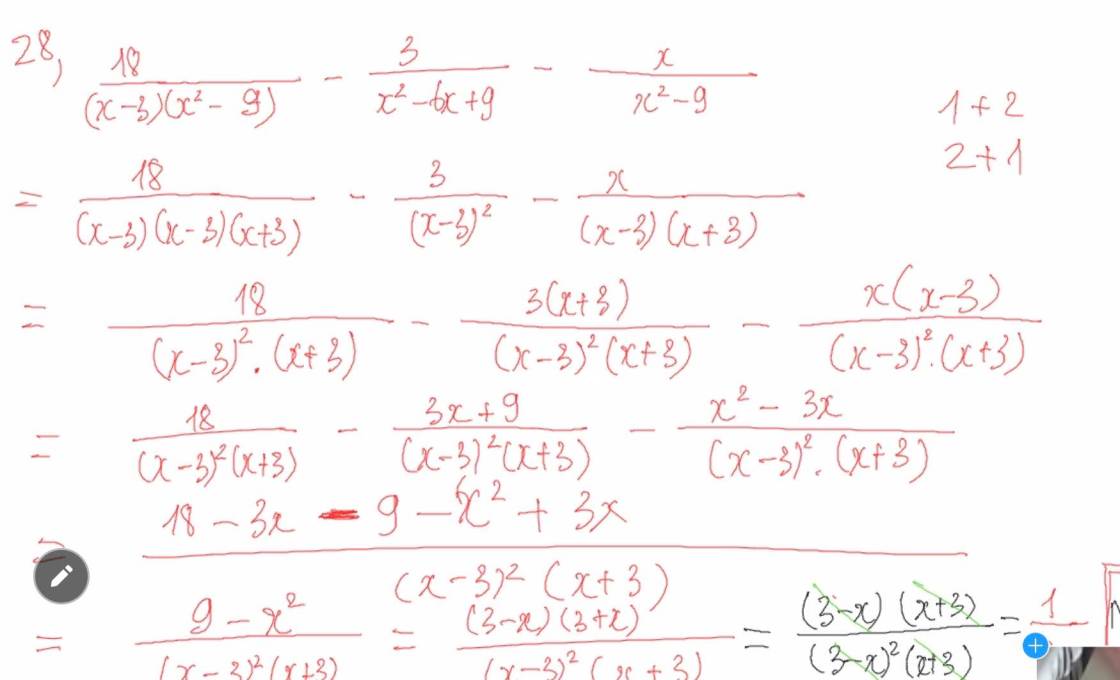
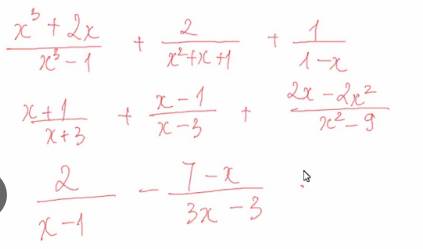

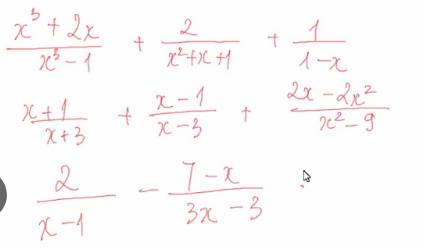
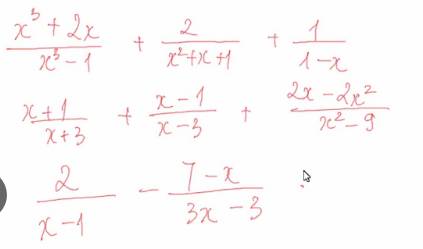


1. Ta nói phân số đó là tối giản khi bội chung nhỏ nhất của tử số và mẫu số chỉ bằng 1.
a) Gọi \(d=BCNN\left(n+1;2n+3\right)\), ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}n+1⋮d\\2n+3⋮d\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2\left(n+1\right)⋮d\\2n+3⋮d\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2n+2⋮d\\2n+3⋮d\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\left(2n+2\right)-\left(2n+3\right)⋮d\)
\(\Rightarrow d=1\)
b) Gọi \(d=BCNN\left(2n+3;4n+8\right)\), ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}2n+3⋮d\\4n+8⋮d\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2n+3⋮d\\\left(4n+8\right):2⋮d\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2n+3⋮d\\2n+4⋮d\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\left(2n+4\right)-\left(2n+3\right)⋮d\)
\(\Rightarrow d=1\)
c) Gọi \(d=BCNN\left(3n+1;4n+1\right)\), ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}3n+1⋮d\\4n+1⋮d\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\left(4n+1\right)-\left(3n+1\right)⋮d\)
\(\Rightarrow d=n\)
Vậy bài toán c) được chứng minh, bài toán xảy ra khi \(n\)là số nguyên tố
Gọi \(d=ƯCNN\left(n+1;2n+3\right)\),\(\left(d\ne1,0\right)\) ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}2n+3⋮d\\6n+4⋮d\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}6n+9⋮d\\6n+4⋮d\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(6n+9\right)-\left(6n+4\right)⋮d\)
\(\Rightarrow n=5\)