Cho x+1/x=3. Tính:
a) x4+1/x4
b)x5+1/x5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


c. Thay x = -1 vào A(x) và B(x) ta có:
A(-1) = 0, B(-1) = 2
Vậy x = -1 là nghiệm của A(x) nhưng không là nghiệm của B(x) (1 điểm)

Thu gọn, sắp xếp đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm của biến:
* Ta có: f(x) = x7 – 3x2 – x5 + x4 – x2 + 2x – 7
= x7 - (3x2+ x2) – x5+ x4 + 2x – 7
= x7 – 4x2 – x5+ x4 + 2x – 7
= x7 – x5 + x4 – 4x2 + 2x - 7
g(x) = x – 2x2 + x4 – x5 – x7 – 4x2 – 1
= x – ( 2x2 + 4x2) + x4 – x5 –x7 – 1
= x – 6x2 + x4 – x5 – x7 – 1
= -x7 – x5 + x4 – 6x2 + x – 1
* f(x) – g(x)
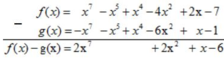
Vậy f(x) – g(x) = 2x7 + 2x2 + x - 6

Vì P(x) có hệ số bậc cao nhất là 1
Nên P(x) có thể được viết dưới dạng: \(P\left(x\right)=\left(x-x_1\right)\left(x-x_2\right)\left(x-x_3\right)\left(x-x_4\right)\left(x-x_5\right)\)
Và \(P\left(-1\right)=\left(-1\right)^5-5\left(-1\right)^3+4\left(-1\right)+1=1\)
\(P\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=\frac{77}{32}\)
Ta có: \(Q\left(x\right)=2x^2+x-1=2x^2+2x-x-1=2x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
=> \(Q\left(x_1\right).\text{}\text{}Q\left(x_2\right).\text{}\text{}Q\left(x_3\right).\text{}\text{}Q\left(x_4\right).\text{}\text{}Q\left(x_5\right)\text{}\text{}\)
\(=\left(x_1+1\right)\left(2x_1-1\right)\left(x_2+1\right)\left(2x_2-1\right)\left(x_3+1\right)\left(2x_3-1\right)\left(x_4+1\right)\left(2x_4-1\right)\left(x_5+1\right)\left(2x_5-1\right)\)
\(=32\left(-1-x_1\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_1\right)\left(-1-x_2\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_2\right)\left(-1-x_3\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_3\right)\left(-1-x_4\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_4\right)\left(-1-x_5\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_5\right)\)\(=32.P\left(-1\right).P\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=32.1.\frac{77}{32}=77\)
\(p\left(x\right)=x^5-5x^3+4x+1=\left(x-x_1\right)\left(x-x_2\right)\left(x-x_3\right)\left(x-x_4\right)\left(x-x_5\right)\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=2\left(\frac{1}{2}-x\right)\left(-1-x\right)\)
Do đó \(Q\left(x_1\right)\cdot Q\left(x_2\right)\cdot Q\left(x_3\right)\cdot Q\left(x_4\right)\cdot Q\left(x_5\right)\)
\(=2^5\left[\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_1\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_2\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_3\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_4\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}-x_5\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(-1-x_1\right)\left(-1-x_2\right)\left(-1-x_3\right)\left(-1-x_4\right)\left(-1-x_5\right)\)
\(=32P\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\cdot\left[P\left(-1\right)\right]\)
\(=32\cdot\left(\frac{1}{32}-\frac{5}{8}+\frac{4}{2}+1\right)\left(-1+5-4+1\right)\)
\(=4300\)
*Mình không chắc*

Ta có: f(x) + g(x) – h(x)
= (x5 – 4x3 + x2 – 2x + 1) + (x5 – 2x4 + x2 – 5x + 3) – (x4 – 3x2 + 2x – 5)
= x5 – 4x3 + x2 – 2x + 1 + x5 – 2x4 + x2 – 5x + 3 – x4 + 3x2 - 2x + 5
= (x5 +x5) – (2x4 + x4) – 4x3 + (x2 + x2 + 3x2)- (2x + 5x + 2x) + (1 + 3 + 5)
= (1 + 1)x5 – (2 + 1)x4 – 4x3 + (1 + 1 + 3)x2 - (2 + 5 + 2)x + (1 + 3 + 5)
= 2x5 – 3x4 – 4x3 + 5x2 – 9x + 9

x1;x2;x3;x4;x5=-1 hoặc 1
=>x1.x2;x2.x3;x3.x4;x4.x5;x5.x1 bằng 1 hoặc -1
giả sử x1.x2+x2.x3+x3.x4+x4.x5+x5.x1=0
=>số các số hạng 1 và -1 bằng nhau
=>số các số hạng chia hết cho 2
=>5 chia hết cho 2(có 5 số hạng) Vô lí
=>x1.x2+x2.x3+x3.x4+x4.x5+x5.x1\(\ne0\)
=>đpcm

Thu gọn, sắp xếp đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm của biến:
* Ta có: f(x) = x5 – 3x2 + x3 – x2 – 2x + 5
= x5 – (3x2 + x2 ) + x3 - 2x + 5
= x5 – 4x2 + x3 – 2x + 5
= x5 + x3 – 4x2 – 2x + 5
Và g(x) = x2 – 3x + 1 + x2 – x4 + x5
= (x2 + x2 ) – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= 2x2 – 3x + 1 – x4 + x5
= x5 – x4 + 2x2 – 3x + 1
* f(x) + g(x):
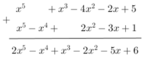

\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=\left(x^5-3x^2+x^3-x^2-2x+5\right)-\left(x^2-3x+1+x^2-x^4+x^5\right)\)
\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=x^5-3x^2+x^3-x^2-2x+5-x^2+3x-1-x^2+x^4-x^5\)
\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=\left(x^5-x^5\right)+\left(-3x^2-x^2-x^2-x^2\right)+x^3+\left(-2x+3x\right)+\left(5-1\right)+x^4\)
\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=-6x^2+x^3+x+4+x^4\)
\(f\left(x\right)-g\left(x\right)=x^4+x^3-6x^2+x+4\)