Nếu r(x^2 - 1) - (x^2 - s) = 5x +6 thì r - s = ?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
\(\begin{array}{l}R(x) + S(x) = - 8{x^4} + 6{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 5x + 1 + {x^4} - 8{x^3} + 2x + 3\\ = ( - 8 + 1){x^4} + (6 - 8){x^3} + 2{x^2} + ( - 5 + 2)x + (1 + 3)\\ = - 7{x^4} - 2{x^3} + 2x - 3x + 4\end{array}\)
b)
\(\begin{array}{l}R(x) - S(x) = - 8{x^4} + 6{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 5x + 1 - ({x^4} - 8{x^3} + 2x + 3)\\ = - 8{x^4} + 6{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 5x + 1 - {x^4} + 8{x^3} - 2x - 3\\ = ( - 8 - 1){x^4} + (6 + 8){x^3} + 2{x^2} + ( - 5 - 2)x + (1 - 3)\\ = - 9{x^4} + 14{x^3} + 2x - 7x - 2\end{array}\)

\(S=\dfrac{3x+6}{x^2-4x+4}-\dfrac{5x-16}{x^2+4x+4}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x+6}{\left(x-2\right)^2}-\dfrac{5x-16}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x+6}{\left(x-2\right)^2}-\dfrac{5x-16}{-\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x+6}{\left(x-2\right)^2}-\dfrac{-(5x-16)}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x+6}{\left(x-2\right)^2}-\dfrac{-5x+16}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x+6-\left(-5x\right)+16}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{3x-\left(-5x\right)+6+16}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)
\(S=\dfrac{8x+22}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)

Bài 1.
a) Do hai phân thức bằng nhau , ta có :
( x +2)P( x2 - 22) = ( x - 1)Q( x -2)
=( x + 2)P( x - 2)( x + 2) = ( x - 1)Q( x - 2)
Suy ra : P = x - 1 ; Q = ( x + 2)2
b) Do hai phân thức bằng nhau , ta có :
( x + 2)P(x2 - 2x + 1) = ( x - 2)Q( x2 - 1)
= ( x + 2)P( x - 1)2 = ( x - 2)Q( x - 1)( x + 1)
Suy ra : P = ( x - 2)( x + 1) = x2 - x - 2
Q = ( x + 2)( x - 1) = x2 + x + 2
Bài 2. a) Do : \(\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}=>PS=QR\)
Xét : ( P + Q)S= PS + QS = QR + QS = Q( R + S)
-> \(\dfrac{P+Q}{Q}=\dfrac{R+S}{S}\)
b) Do : \(\dfrac{P}{Q}=\dfrac{R}{S}=>PS=QR\)
Xét : ( S - R)P = PS - PR = QR - PR = R( Q - P)
-> \(\dfrac{R-S}{R}=\dfrac{Q-P}{P}\)
- > \(\dfrac{R}{R-S}=\dfrac{P}{Q-P}\)

a)S=\(\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-36}-\dfrac{x-6}{x^2+6x}\right):\dfrac{2x-6}{x^2+6x}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
=\(\left(\dfrac{x}{\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}-\dfrac{x-6}{x\left(x+6\right)}\right):\dfrac{2x-6}{x\left(x+6\right)}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
\(\left(\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-6\right)^2}{x\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}\right):\dfrac{2x-6}{x\left(x+6\right)}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
=\(\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-6\right)^2}{x\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)}:\dfrac{2\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+6\right)}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
=\(\dfrac{6\left(2x-6\right)x\left(x+6\right)}{x\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)\left(2x-6\right)}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
=\(\dfrac{6}{x-6}+\dfrac{x}{6-x}\)
=\(\dfrac{6}{x-6}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}=\dfrac{6-x}{x-6}=-1\)
b ) S khi rút gọn=-1 => mọi giá trị của x đều thỏa mãn S=-1

Đường tròn : C): (x-1)2+ (y-3) 2 = R2 có tâm I( 1;3) bán kính R.
Để đường thẳng d tiếp xúc với đường tròn (C) khi
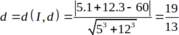
Chọn B.


r(x2-1)-(x2-s)=5x+6
=>rx2-r-x2+s=5x+6
=>x2(r-1)-r+s
- Áp dụng phương pháp hệ số bất định ta có:
-r+s=6 =>r-s=-6