Giair các phương trình
a) x4 - 4x3 - 19x2 + 106x - 120 = 0
b) 4x4 + 12x3 + 5x2 - 6x - 15 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: =>7x=63
hay x=9
b: =>3x=-15
hay x=-5
d: =>-6x=-16
hay x=8/3
a) \(7x=63\Leftrightarrow x=9\)
b) \(3x=-15\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
c) \(2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow2x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
d) \(-6x=-16\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{3}\)

Lời giải:
a) $0,2x^2+0,4x-7=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+4x-70=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-35=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+7)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=5$ hoặc $x=-7$
b)
$\frac{1}{2}x^2+11x+60,5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+22x+121=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+11)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-11$
c)
$5x^2+\sqrt{3}-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x^2=1-\sqrt{3}< 0$ (vô lý)
Vậy PT vô nghiệm.

a) x 4 – 5 x 2 + 4 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t, điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : t 2 – 5 t + 4 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 1 ; b = -5 ; c = 4 ⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 4
Cả hai giá trị đều thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 = 1 ⇒ x = 1 hoặc x = -1;
+ Với t = 4 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = 2 hoặc x = -2.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-2 ; -1 ; 1 ; 2}.
b) 2 x 4 – 3 x 2 – 2 = 0 ; ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 2 t 2 – 3 t – 2 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 2 ; b = -3 ; c = -2
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 2 . ( - 2 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
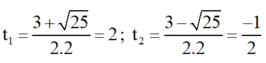
Chỉ có giá trị t 1 = 2 thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2;
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2 ; √2}.
c) 3 x 4 + 10 x 2 + 3 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 + 10 t + 3 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3; b' = 5; c = 3
⇒ Δ ’ = 5 2 – 3 . 3 = 16 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
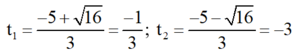
Cả hai giá trị đều không thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy phương trình (1) vô nghiệm.

c) Ta có: \(C=4x^2+y^2-4xy+8x-4y+4\)
\(=\left(2x-y\right)^2+2\cdot\left(2x-y\right)\cdot2+2^2\)
\(=\left(2x-y+2\right)^2\)

11) Ta có: \(a^6+a^4+a^2b^2+b^4-b^6\)
\(=a^6-b^6+a^4+a^2b^2+b^4\)
\(=\left(a^2-b^2\right)\left(a^4+a^2b^2+b^4\right)+\left(a^4+a^2b^2+b^4\right)\)
\(=\left(a^4+a^2b^2+b^4\right)\left(a^2-b^2+1\right)\)
12) Ta có: \(x^3+3xy+y^3-1\)
\(=\left(x^3+3x^2y+3xy^2+y^3-1\right)-3x^2y-3xy^2+3xy\)
\(=\left[\left(x+y\right)^3-1\right]-3xy\left(x+y-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y-1\right)\left[x^2+2xy+y^2+x+y+1\right]-3xy\left(x+y-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2+x+y+1\right)\)
14) Ta có: \(x^8+x+1\)
\(=x^8+x^7-x^7-x^6+x^6+x^5-x^5-x^4+x^4+x^3-x^3+x^2-x^2+x+1\)
\(=x^6\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^5\left(x^2+x+1\right)+x^3\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)+\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^6-x^5+x^3-x^2+1\right)\)
15) Ta có: \(x^8+3x^4+4\)
\(=x^8+4x^4+4-x^4\)
\(=\left(x^4+2\right)^2-\left(x^2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x^4-x^2+2\right)\left(x^4+x^2+2\right)\)

1) \(x^2-7x+6=x^3+1-7x-7=\left(x^3+1\right)-7\left(x+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)\)
2) \(x^3-9x^2+6x+16\)
\(\left(x^3+1\right)-\left[\left(9x^2-6x+1\right)-16\right]\)
\(=\left(x^3+1\right)-\left[\left(3x-1\right)^2-16\right]=\left(x^3+1\right)-\left(3x-1+4\right)\left(3x-1-4\right)\)\(=\left(x^3+1\right)-3\left(3x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)\)\(=\left(x+1\right)\left[x^2-x+1-9x+15\right]=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-10x+16\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left[x\left(x-2\right)-8\left(x-2\right)\right]\)\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-8\right)\)
3) \(x^3-6x^2-x+30\)
\(=x^3-5x^2-x^2+5x-6x+30\)
\(=x^2\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-5\right)-6\left(x-5\right)\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)\left(x^2-x-1\right)\)
4) \(2x^3-x^2+5x+3=\left(2x^3+x^2\right)-\left(2x^2+x\right)+\left(6x+3\right)\)
\(=x^2\left(2x+1\right)-x\left(2x+1\right)+3\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+3\right)\)
5) \(27x^3-27x^2+18x-4=\left(27x^3-1\right)-\left(27x^2-18x+3\right)\)
\(=\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2+3x+1\right)-3\left(9x^2-6x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2+3x+1\right)-3\left(3x-1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2+3x+1-9x+3\right)=\left(3x-1\right)\left(9x^2-6x+4\right)\)
gửi phần này trước còn lại làm sau !!! tk mk nka !!!

1) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=10\\5x-3y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10x+5y=50\\10x-6y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}11y=44\\2x+y=10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=4\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy hpt có nghiệm (x;y) = (3;4)
2)
a) 3x2 - 2x - 1 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x+x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm x = 1 hoặc x = 3
b) Đặt x2 = t (t \(\ge\) 0)
Pt trở thành: t2 - 20t + 4 = 0
\(\Delta\) = (-20)2 - 4.1.4 = 400 - 16 = 384
=> pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt t1 = \(\dfrac{20+8\sqrt{6}}{2}=10+4\sqrt{6}\)
t2 = \(\dfrac{20-8\sqrt{6}}{2}=10-4\sqrt{6}\)
=> x1 = \(\sqrt{10+4\sqrt{6}}=\sqrt{\left(2+\sqrt{6}\right)^2}=2+\sqrt{6}\)
x2 = \(2-\sqrt{6}\)

a,\(x^3-7x+6\)
\(=x^3-2x^2+2x^2-4x-3x+6\)
\(=\left(x^3-2x^2\right)+\left(2x^2-4x\right)-\left(3x-6\right)\)
\(=x^2.\left(x-2\right)+2x.\left(x-2\right)-3.\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).\left(x^2+2x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).\left(x^2-x+3x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).\left[\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(3x-3\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).\left[x.\left(x-1\right)+3.\left(x-1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).\left(x-1\right).\left(x+3\right)\)
b,\(x^3-9x^2+6x+16\)
\(=x^3-8x^2-x^2+8x-2x+16\)
\(=\left(x^3-8x^2\right)-\left(x^2-8x\right)-\left(2x-16\right)\)
\(=x^2.\left(x-8\right)-x.\left(x-8\right)-2.\left(x-8\right)\)
\(=\left(x-8\right).\left(x^2-x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-8\right).\left(x^2+x-2x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x-8\right).\left[\left(x^2+x\right)-\left(2x+2\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-8\right).\left[x.\left(x+1\right)-2.\left(x+1\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-8\right).\left(x+1\right).\left(x-2\right)\)
c,\(x^3-6x^2-x+30\)
\(=x^3-5x^2-x^2+5x-6x+30\)
\(=\left(x^3-5x^2\right)-\left(x^2-5x\right)-\left(6x-30\right)\)
\(=x^2.\left(x-5\right)-x.\left(x-5\right)-6.\left(x-5\right)\)
\(=\left(x-5\right).\left(x^2-x-6\right)\)
\(=\left(x-5\right).\left(x^2+2x-3x-6\right)\)
\(=\left(x-5\right).\left[\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-5\right).\left[x.\left(x+2\right)-3.\left(x+2\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-5\right).\left(x+2\right).\left(x-3\right)\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!!!
d,\(2x^3-x^2+5x+3\)
\(=2x^3+x^2-2x^2-x+6x+3\)
\(=\left(2x^3+x^2\right)-\left(2x^2+x\right)+\left(6x+3\right)\)
\(=x^2.\left(2x+1\right)-x.\left(2x+1\right)+3.\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x+1\right).\left(x^2-x+3\right)\)
e, \(27x^3-27x^2+18x-4\)
\(=27x^3-9x^2-18x^2+6x+12x-4\)
\(=\left(27x^2-9x^2\right)-\left(18x^2-6x\right)+\left(12x-4\right)\)
\(=9x^2.\left(3x-1\right)-6x.\left(3x-1\right)+4.\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(3x-1\right).\left(9x^2-6x+4\right)\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!!!

c) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)=40\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x^2+6x+5\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)-40=0\)
Đặt \(x^2+6x+5=t\) ta có:
\(t\left(t+3\right)-40=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(t^2+3t-40=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(t-5\right)\left(t+8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}t-5=0\\t+8=0\end{cases}}\)
Thay trở lại ta có: \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+6x=0\\x^2+6x+13=0\end{cases}}\)
(*) \(x^2+6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+6=0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-6\end{cases}}\)
(*) \(x^2+6x+13=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(x+3\right)^2+4=0\) (vô lý)
Vậy......
\(a,x^4-4x^3-19x^2+106x-120=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x^3-19x+30\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+5\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-5\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-5;2;3;4\right\}\)
\(b,4x^4+12x^3+5x^2-6x-15=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^3+16x^2+21x+15\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(4x^3+10x^2\right)+\left(6x^2+15x\right)+\left(6x+15\right)\right]=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[2x^2\left(2x+5\right)+3x\left(2x+5\right)+3\left(2x+5\right)\right]=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+5\right)\left(2x^2+3x+3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\\2x^2+3x+3=0\left(vô.lí\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)