Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất
a)\(\dfrac{\text{3x^2-2x+3}}{\text{x^2+1}}\)
b)\(\dfrac{\text{3x^2-4x+4}}{\text{x^2+2}}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}-\dfrac{3}{x+2}>0.\left(x\ne-1;-2\right).\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-4-3x-3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Ta có: \(x^2-3x-7=0.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x+1=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-1.\\ x+2=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-2.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
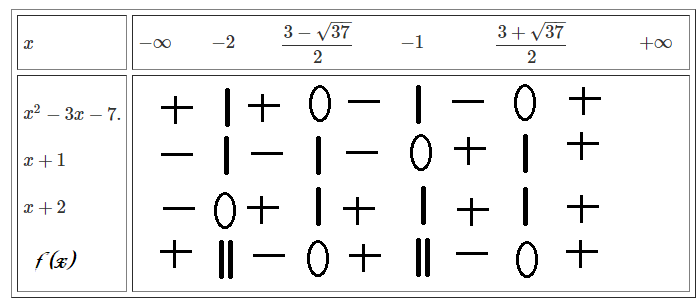
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-\infty-2\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2};-1\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty\right).\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2\ge9.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-7\ge0.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)

Câu 1:
a: Để M là số nguyên thì \(2x^3-6x^2+x-3-5⋮x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{4;2;8;-2\right\}\)
b: Để N là số nguyên thì \(3x^2+2x-3x-2+5⋮3x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+2\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{1}{3};-1;1;-\dfrac{7}{3}\right\}\)

câu c) mang tính mua vui hay gì hả bn
mếu thật thì x=0,x=số nào cx đc(câu trả lời này mang tính mua vui thôi nhé)

a) \(A=2x^2-\dfrac{1}{3}y\)
A= \(\left(2-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)\(x^2y\)
A=\(\dfrac{5}{3}\)\(x^2y\)
Tại \(x=2;y=9\) ta có
A=\(\dfrac{5}{3}\).(2)\(^2\).9 = \(\dfrac{5}{3}\).4 .9 = 60
Vậy tại \(x=2;y=9\) biểu thức A= 60
b) P=\(2x^2+3xy+y^2\) (\(y^2\) là 1\(y^2\) nha bạn)
P=\(\left(2+3+1\right)\left(x^2.x\right)\left(y.y^2\right)\)
P= 6\(x^3y^3\)
Tại \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2};y=\dfrac{2}{3}\) ta có
P= 6.\(\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3.\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right)^3\) = 6.\(\left(-\dfrac{1}{8}\right).\dfrac{8}{27}\) = \(-\dfrac{2}{9}\)
Vậy tại \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2};y=\dfrac{2}{3}\) biểu thức P= \(-\dfrac{2}{9}\)
c)\(\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}xy^2\right).\left(\dfrac{2}{3}x^3\right)\)
=\(\left((-\dfrac{1}{2}).\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\left(x.x^3\right).y^2\)
=\(-\dfrac{1}{3}\)\(x^4y^2\)
Tại \(x=2;y=\dfrac{1}{4}\)ta có
\(-\dfrac{1}{3}\).\(\left(2\right)^4.\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2=-\dfrac{1}{3}.16.\dfrac{1}{16}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\)Vậy \(x=2;y=\dfrac{1}{4}\) biểu thức \(\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}xy^2\right).\left(\dfrac{2}{3}x^3\right)\)= \(-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
CHÚC BẠN HỌC TỐT NHA

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(P=\left[\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x^2\left(x+3\right)+9\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{3}{x^2+9}\right]:\left[\dfrac{1}{x-3}-\dfrac{6x}{x^2\left(x-3\right)+9\left(x-3\right)}\right]\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+9\right)}+\dfrac{3}{x^2+9}\right]:\left[\dfrac{1}{x-3}-\dfrac{6x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+9\right)}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x+3}{x^2+9}:\dfrac{x^2+9-6x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+9\right)}=\dfrac{x+3}{x^2+9}.\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}\)
Ý 2 mình k hiểu ý bạn lắm
\(P=\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}=\dfrac{x-3+6}{x-3}=1+\dfrac{6}{x-3}\in Z\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\inƯ\left(6\right)=\left\{-6;-3;-2;-1;1;2;3;6\right\}\)
Kết hợp vs ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;1;2;4;5;6;9\right\}\)

a: A=[(3x^2+3-x^2+2x-1-x^2-x-1)/(x-1)(x^2+x+1)]*(x-2)/2x^2-5x+5
=(x^2+x+1)/(x-1)(x^2+x+1)*(x-2)/2x^2-5x+5
=(x-2)/(2x^2-5x+5)(x-1)

a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2y=1\\2x+4y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x-4y=2\\2x+4y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8x=5\\3x-2y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{8}\\2y=3x-1=\dfrac{15}{8}-1=\dfrac{7}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{8}\\y=\dfrac{7}{16}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-3y=1\\-x+2y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-3y=1\\-4x+8y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=-1+2y=-1+2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{4}{3}y=1\\\dfrac{1}{2}x-\dfrac{3}{4}y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=3\\2x-3y=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{41}{14}\\y=-\dfrac{5}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a,\) Đặt \(A=\dfrac{3x^2-2x+3}{x^2+1}\Leftrightarrow Ax^2+A=3x^2-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(A-3\right)-2x+A-3=0\)
Coi đây là PT bậc 2 ẩn x, PT có nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4-4\left(A-3\right)^2\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(A-3\right)^2\le1\Leftrightarrow2\le A\le4\)
Vậy \(A_{min}=4\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x^2-2x+3}{x^2+1}=4\Leftrightarrow x=...\)
\(b,\) Đặt \(B=\dfrac{3x^2-4x+4}{x^2+2}\Leftrightarrow Bx^2+2B=3x^2-4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(B-3\right)+4x+2B-4=0\)
Coi đây là PT bậc 2 ẩn x, PT có nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=16-8\left(B-2\right)\left(B-3\right)\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(B-2\right)\left(B-3\right)\le2\\ \Leftrightarrow B^2-5B+4\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(B-1\right)\left(B-4\right)\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow1\le B\le4\)
Vậy\(B_{min}=4\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x^2-4x+4}{x^2+2}=4\Leftrightarrow x=...\)