cho các số thực a,b thỏa |a|<1, |b|<1. tìm giới hạn I = lim (1+a+a^2+...+a^n)/(1+b+b^2+...+b^n) =
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chọn C.
Ta có 1, a, a2, …, an là một cấp số nhân công bội a nên 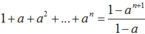
Tương tự 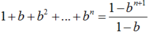
Suy ra 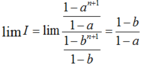
( Vì |a| < 1; |b| < 1). ⇒ liman+1 = limbn+1 = 0.

\(a,lim\left(\sqrt{n^2+n+1}-n\right)\)
\(=lim\dfrac{n^2+n+1-n^2}{\sqrt{n^2+n+1}+n}\)
\(=lim\dfrac{1+\dfrac{1}{n}}{\sqrt{1+\dfrac{1}{n}+\dfrac{1}{n^2}}+1}=\dfrac{1}{1+1}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\lim\dfrac{\sqrt[]{n^3+2n}-2n^2}{3n+1}=\lim\dfrac{\sqrt[]{n+\dfrac{2}{n}}-2n}{3+\dfrac{1}{n}}=\lim\dfrac{n\left(\sqrt[]{\dfrac{1}{n}+\dfrac{2}{n^3}}-2\right)}{3+\dfrac{1}{n}}\)
\(=\dfrac{+\infty\left(0-2\right)}{3}=-\infty\)

\(\lim\dfrac{3+4^n}{1+3.4^{n+1}}=\lim\dfrac{3+4^n}{1+12.4^n}=\lim\dfrac{3\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^n+1}{\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^n+12}=\dfrac{0+1}{0+12}=\dfrac{1}{12}\)
\(\lim\dfrac{\left(-2\right)^n+3^n}{\left(-2\right)^{n+1}+3^{n+1}}=\lim\dfrac{\left(-2\right)^n+3^n}{-2\left(-2\right)^n+3.3^n}=\lim\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{2}{3}\right)^n+1}{-2\left(-\dfrac{2}{3}\right)^n+3}=\dfrac{0+1}{0+3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)

\(\lim\dfrac{n\sqrt{1+2+...+2n}}{3n^2+n-2}=\lim\dfrac{n\sqrt{\dfrac{2n\left(2n+1\right)}{2}}}{3n^2+n-2}=\lim\dfrac{\sqrt{2+\dfrac{1}{n}}}{3+\dfrac{1}{n}-\dfrac{2}{n^2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\)

a. ĐKXĐ: \(n\ge0\)
\(lim_{n\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{2n+1}}{\sqrt{8n}+1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2.0+1}}{\sqrt{8.0}+1}=1\)
\(lim_{n\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{\sqrt{2n+1}}{\sqrt{8n}+1}=lim_{n\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{\sqrt{2+\dfrac{1}{n}}}{\sqrt{8}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{n}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b. ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}n\ne0\\n\le\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{21}}{2}\\n\ge\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(lim_{n\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{3n+\sqrt{n^2+n-5}}{-2n}=\)\(lim_{n\rightarrow+\infty}\dfrac{3+\sqrt{1+\dfrac{1}{n}-\dfrac{5}{n^2}}}{-2}=-2\)
\(lim_{n\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{3n+\sqrt{n^2+n-5}}{-2n}=\)\(lim_{n\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{3+\sqrt{1+\dfrac{1}{n}-\dfrac{5}{n^2}}}{-2}=-1\)

a, \(lim\dfrac{\sqrt{2n+1}}{\sqrt{8n}+1}=lim\dfrac{\sqrt{n}.\sqrt{2+\dfrac{1}{n}}}{\sqrt{n}\left(\sqrt{8}+\dfrac{1}{n}\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{8}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
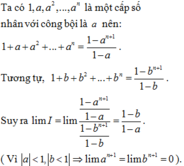

\(I=\lim\limits\dfrac{1+a+a^2+...+a^n}{1+b+b^2+...+b^n}\)
Xet tren tu la 1 csc voi : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u_1=1\\q=a\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow S_a=1.\dfrac{a^{n+1}-1}{a-1}\)
Tuong tu cho mau so: \(S_b=1.\dfrac{b^{n+1}-1}{b-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow.....=\lim\limits\dfrac{\dfrac{a^{n+1}-1}{a-1}}{\dfrac{b^{n+1}-1}{b-1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{a-1}}{\dfrac{1}{b-1}}=\dfrac{1-b}{1-a}\)