Giải phương trình sau: (x + 1)2 + |x + 10| - x2 - 12 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


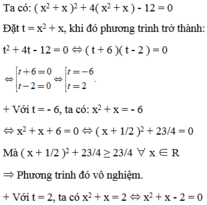
⇔ ( x + 2 )( x - 1 ) = 0 ⇔ 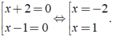
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S = { - 2;1 }.

`a,x^2 +4x-5=0`
`<=> x^2-x+5x-5=0`
`<=> x(x-1)+5(x-1)=0`
`<=>(x-1)(x+5)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
`b, x^2 -x-12=0`
`<=> x^2 +3x-4x-12=0`
`<=>(x^2+3x)-(4x+12)=0`
`<=>x(x+3)-4(x+3)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(x-4)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
`c, (2x-7)^2 - 6(2x-7)(x-3)=0`
`<=>(2x-7)(2x-7 -6x+18)=0`
`<=>(2x-7) ( -4x+11)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\-4x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=7\\-4x=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{11}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: =>(x+5)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-5
b: =>(x-4)(x+3)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-3
c: =>(2x-7)(2x-7-6x+18)=0
=>(2x-7)(-4x+11)=0
=>x=11/4 hoặc x=7/2

b) 2 x 2 + x + 10 = 0
Ta có: a = 2; b = 1; c = 10
Δ = b 2 - 4ac = 1 2 - 4.2.10 = -79 < 0
⇒ Phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.

Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-3)<=0
=>2<=x<=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2< =0\)
=>x=6
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>=0\)
hay \(x\in R\)
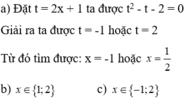
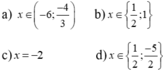
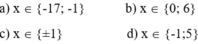
Xét 2 trường hợp
TH1 :
\(x+10\ge0\)
\(x\ge-10\)
\(\left(x+1\right)^2+|x+10|-x^2-12=0\)
\(x^2+2x+1+x+10-x^2-12=0\)
\(3x-1=0\)
\(x=\frac{1}{3}\left(n\right)\)
TH2 :
\(x+10< 0\)
\(x< -10\)
\(\left(x+1\right)^2+|x+10|-x^2-12=0\)
\(x^2+2x+1-\left(x+10\right)-x^2-12=0\)
\(x^2+2x+1-x-10-x^2-12=0\)
\(x-21=0\)
\(x=21\left(l\right)\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{1}{3}\) là nghiệm của phương trình
(x + 1)2 + |x + 10| - x2 - 12 = 0
=> x2 + 2x + 1 + |x + 10| - x2 - 12 = 0
=> |x + 10| = -2x + 11
ĐKXĐ : -2x + 11 \(\ge0\Rightarrow x\le5\)
Khi đó |x + 10| = -2x + 11
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+10=-2x+11\\x+10=2x-11\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=1\\x=21\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\left(\text{loại}\right)\\x=21\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\Rightarrow x=21\)
Vậy x = 21 là giá trị cần tìm