1, Tìm x :a,2x2+x=0
b, x2+4x+3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
3 · x 2 + x 2 - 2 x 2 + x - 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt t = x 2 + x ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 – 2 t – 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3 ; b = -2 ; c = -1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = - 1 / 3 .
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 + x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + x – 1 = 0 ( * )
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -1 ⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
(*) có hai nghiệm
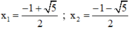
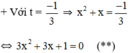
Có a = 3; b = 3; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = 3 2 – 4 . 3 . 1 = - 3 < 0
⇒ (**) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm 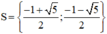
b)
x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 ⇔ x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x + 2 − 6 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 4 x + 2 = t ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 + t – 6 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -6
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 6 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm
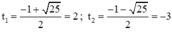
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = 2
⇔ x 2 – 4 x = 0
⇔ x(x – 4) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x = 4.
+ Với t = -3 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = - 3
⇔ x2 – 4x + 5 = 0 (*)
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 5 ⇒ Δ ’ = ( - 2 ) 2 – 1 . 5 = - 1 < 0
⇒ (*) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình ban đầu có tập nghiệm S = {0; 4}.
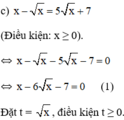
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 – 6 t – 7 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -6; c = -7
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = 7 .
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có nghiệm t = 7 thỏa mãn.
+ Với t = 7 ⇒ √x = 7 ⇔ x = 49 (thỏa mãn).
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x = 49.
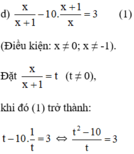
⇔ t 2 – 10 = 3 t ⇔ t 2 – 3 t – 10 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -3; c = -10
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 1 . ( - 10 ) = 49 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
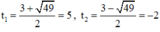
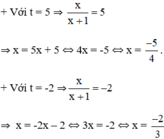
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm 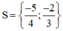


a) Ta có: \(x^2\left(x+1\right)+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\)
hay x=-1
b) Ta có: \(x^2-x=-2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(2x^2\left(x-1\right)+x^2=x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-1\right)+x^2-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\cdot\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)=x^2-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)-x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2

Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4

1.
a) \(2x^4-4x^3+2x^2\)
\(=2x^2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=2x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\)
b) \(2x^2-2xy+5x-5y\)
\(=\left(2x^2-2xy\right)+\left(5x-5y\right)\)
\(=2x\left(x-y\right)+5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\cdot\left(2x+5\right)\)
2 .
a,
\(4x\left(x-3\right)-x+3=0\)
⇒\(4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left(x-3\right)\left(4x-1\right)=0\)
⇒\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\4x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\4x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
b,
\(\)\(\left(2x-3\right)^2-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
⇒\(\left(2x-3-x-1\right)\left(2x-3+x+1\right)\) = 0
⇒\(\left(x-4\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\3x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\3x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{4;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)

Câu 2:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-4x-x^3-8=4\)
hay x=-3

a) Ta có: \(\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-6x^2+12x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)^2-6\left(x^2-2x\right)+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-1}
b) Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right)=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+x\right)+2-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)^2+5\left(x^2+x\right)-2\left(x^2+x\right)-10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x\right)\left(x^2+x+5\right)-2\left(x^2+x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+5\right)\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0\)(Vì \(x^2+x+5>0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-2;1}
2 ý a và b anh CTV nãy đã làm rồi nha, còn câu c này thì làm dài dòng+không chắc :VVV
c)\(\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)\left(2x^2+5x+1\right)-9x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)\left(2x^2-3x+1+8x\right)-9x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)^2+8x\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)+16x^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-3x+1+4x\right)^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+x+1\right)^2-25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+x+1-5x\right)\left(2x^2+x+1+5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-4x+1\right)\left(2x^2+6x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x^2-4x+1\right)=0\\\left(2x^2+6x+1\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Rồi đến đây tự giải nhé, không phân tích được thì bấm máy tính là ra nha:vv

a) \(2x^2-4x=0\)
\(2x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
TH1:2x=0⇒x=0
TH2:x-2=0⇒x=2
\(a,\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-4\right)-\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
2x2 + x = 0
<=> x( 2x + 1 ) = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc 2x + 1 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = -1/2
b) x2 + 4x + 3 = 0
<=> ( x2 + 4x + 4 ) - 1 = 0
<=> ( x + 2 )2 - 12 = 0
<=> ( x + 2 - 1 )( x + 2 + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 1 )( x + 3 ) = 0
<=> x + 1 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
<=> x = -1 hoặc x = -3