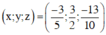Giải hệ phương trình 2 x - 3 y + z = - 7 - 4 x + 5 y + 3 z = 6 x + 2 y - 2 z = 5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-5\right)\left(y-2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\\\left(x-4\right)\left(y+7\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(y+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2x-5y+10=xy-x+2y-2\\xy+7x-4y-28=xy+4x-3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+7y=12\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+21y=36\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}22y=20\\x+7y=12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{62}{11}\\y=\dfrac{10}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(1+y\right)=2\\3\left(x-2\right)-2\left(1+y\right)=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6\left(x-2\right)+9\left(1+y\right)=6\\6\left(x-2\right)-4\left(1+y\right)=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}13\left(1+y\right)=12\\2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(1+y\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{21}{13}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{13}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-5\right)\left(y-2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\\\left(x-4\right)\left(y+7\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(y+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2x-5y+10=xy-x+2y-2\\xy+7x-4y-28=xy+4x-3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-7y=-12\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-7y=-12\\21x-7y=112\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}22x=124\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{62}{11}\\y=\dfrac{10}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y-z=7\\x^2+y^2-z^2=37\\x^3+y^3-z^3=1\end{cases}}\)<=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=7+z\\x^2+y^2=37+z^2\\x^3+y^3=1+z^3\end{cases}}\)
Ta có: \(x^2+y^2=37+z^2\)
<=> \(\left(x+y\right)^2-2xy=37+z^2\)
<=> \(2xy=\left(7+z\right)^2-37-z^2\)
<=> \(xy=6+7z\)
Ta có: \(x^3+y^3=1+z^3\)
<=> \(\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2-xy\right)=1+z^3\)
<=> \(\left(7+z\right)\left(37+z^2-6-7z\right)=1+z^3\)đây là phương trình bậc 2. Em giải ra tìm z => x; y

e: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{3}{y}=3\\\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-7}{y}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{x}=1+\dfrac{2}{7}=\dfrac{9}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{7}{9}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Ta có hệ \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(4x^2+1\right)x+\left(y-3\right)\sqrt{5-2y}=0\left(1\right)\\4x^2+y^2+2\sqrt{3-4x}=7\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
ĐK \(\hept{\begin{cases}y\ge\frac{5}{2}\\x\le\frac{3}{4}\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}2x=a\\\sqrt{5-2y}=b\ge0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}4x^2=a^2\\5-2y=b^2\end{cases}}}\)\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}4x^2=a^2\\y-3=\frac{5-b^2}{2}-3=\frac{-1-b^2}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Thế vào (1) ta có \(\left(a^2+1\right)\frac{a}{2}+\frac{-1-b^2}{2}b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^3+a}{2}+\frac{-b^3-b}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow a^3-b^3+a-b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-b\right)\left(a^2+ab+b^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=b\)vì \(a^2+ab+b^2+1>0\forall a,b\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=\sqrt{5-2y}\Rightarrow4x^2=5-2y\Rightarrow y=\frac{5-4x^2}{2}\)
Thế y vào (2) ta có \(4x^2+\left(\frac{5-4x^2}{2}\right)^2+2.\sqrt{3-4x}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2+\left(5-4x^2\right)^2+8\sqrt{3-4x}=28\)\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2+25-40x^2+16x^4+8\sqrt{3-4x}-28=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^4-24x^2+8\sqrt{3-4x}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(16x^4-1\right)-\left(24x^2-6\right)+\left(8\sqrt{3-4x}-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2-1\right)\left(4x^2+1\right)-6\left(4x^2-1\right)+\left(8\sqrt{3-4x}-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2-1\right)\left(4x^2+1\right)-6\left(4x^2-1\right)+8.\frac{2-4x}{\sqrt{3-4x}+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(4x^2+1\right)-6\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)-8.2.\frac{2x-1}{\sqrt{3-4x}+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left[\left(2x+1\right)\left(4x^2+1\right)-6\left(2x+1\right)-\frac{16.1}{\sqrt{3-4x}+1}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left[\left(2x+1\right)\left(4x^2-5\right)-\frac{16}{\sqrt{3-4x}+1}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=0\)
Vì với \(y=\frac{5-4x^2}{2}\ge\frac{5}{2}\Rightarrow4x^2-5< 0\Rightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(4x^2-5\right)-\frac{16}{\sqrt{3-4x}+1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\frac{5-4\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2}{2}=2\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2};2\right)\)

1. 3x( x - 2 ) - ( x - 2 ) = 0
<=> ( x-2).(3x-1) = 0 => x = 2 hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
2. x( x-1 ) ( x2 + x + 1 ) - 4( x - 1 )
<=> ( x - 1 ).( x (x^2 + x + 1 ) - 4 ) = 0
(phần này tui giải được x = 1 thôi còn bên kia giải ko ra nha )
3 \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{5}x-2y=7\\\sqrt{5}x-5y=10\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\x=\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(1. 3x^2 - 7x +2=0\)
=>\(Δ=(-7)^2 - 4.3.2\)
\(= 49-24 = 25\)
Vì 25>0 suy ra phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1\)=\(\dfrac{-\left(-7\right)+\sqrt{25}}{2.3}=\dfrac{7+5}{6}=2\)
\(x_2\)=\(\dfrac{-\left(-7\right)-\sqrt{25}}{2.3}=\dfrac{7-5}{6}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)

Ta có x + y + z = 0
<=> (x + y + z)2 = 0
<=> \(x^2+y^2+z^2+2xy+2yz+2zx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow xy+yz+zx=-3\) (vì x2 + y2 + z2 = 6)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(y+z\right)+yz=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+yz=-3\Leftrightarrow yz=x^2-3\) (vì x + y + z = 0)
Khi đó \(x^3+y^3+z^3=x^3+(y+z).(y^2+z^2-yz)\)
\(=x^3-x.[6-x^2-(x^2-3)]\)
\(=x^3-x.(9-2x^2)=3x^3-9x=6\)
Ta được \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x-2=0\Leftrightarrow(x^3+1)-3(x+1)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow(x+1)(x^2-x-2)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với x = -1 ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+z=1\\y^2+z^2=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-z\\(1-z)^2+z^2=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-z\\z^2-z-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1-z\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}z=-1\\z=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\z=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\z=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với x = 2 ta có hệ : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+z=-2\\y^2+z^2=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2-z\\(-2-z)^2+z^2=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2-z\\z^2+2z+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2-z\\z=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow y=z=-1\)
Vậy (x;y;z) = (2;-1;-1) ; (-1 ; 2 ; -1) ; (-1 ; -1 ; 2)

Đưa hệ phương trình về hệ dạng tam giác bằng cách khử dần các ẩn.
Nhân phương trình (1) với 2 rồi cộng với phương trình (2) và nhân phương trình (3) với 4 rồi cộng với phương trình (2) ta được:
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm