Cho ∫ 0 π 4 x 1 + sin 2 x d x = a + b π 2 trong đó a,b là các hữu ỷ. Giá trị của 8 a + 3 b bằng
A. 131 32
B. - 61 32
C. 35 16
D. 67 32
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) √2 cos(x - π/4)
= √2.(cosx.cos π/4 + sinx.sin π/4)
= √2.(√2/2.cosx + √2/2.sinx)
= √2.√2/2.cosx + √2.√2/2.sinx
= cosx + sinx (đpcm)
b) √2.sin(x - π/4)
= √2.(sinx.cos π/4 - sin π/4.cosx )
= √2.(√2/2.sinx - √2/2.cosx )
= √2.√2/2.sinx - √2.√2/2.cosx
= sinx – cosx (đpcm).

a) 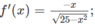
f′(x) > 0 trên khoảng (-4; 0) và f’(x) < 0 trên khoảng (0; 4).
Hàm số đạt cực đại tại x = 0 và f C Đ = 5
Mặt khác, ta có f(-4) = f(4) = 3
Vậy 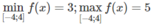
d) f(x) = | x 2 − 3x + 2| trên đoạn [-10; 10]
Khảo sát sự biến thiên và vẽ đồ thị của hàm số g(x) = x 2 – 3x + 2.
Ta có:
g′(x) = 2x − 3; g′(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 3/2
Bảng biến thiên:
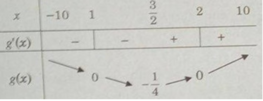
Vì
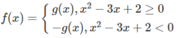
nên ta có đồ thị f(x) như sau:
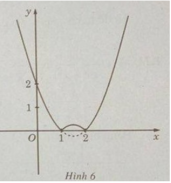
Từ đồ thị suy ra: min f(x) = f(1) = f(2) = 0; max = f(x) = f(−10) = 132
e) 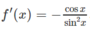
f′(x) < 0 nên và f’(x) > 0 trên (π/2; 5π/6] nên hàm số đạt cực tiểu tại x = π/2 và f C T = f(π/2) = 1
Mặt khác, f(π/3) = 2√3, f(5π/6) = 2
Vậy min f(x) = 1; max f(x) = 2
g) f(x) = 2sinx + sin2x trên đoạn [0; 3π/2]
f′(x) = 2cosx + 2cos2x = 4cos(x/2).cos3(x/2)
f′(x) = 0
⇔ 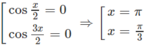
Ta có: f(0) = 0,
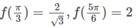
Từ đó ta có: min f(x) = −2 ; max f(x) = 3√3/2

a: pi/2<a<pi
=>sin a>0
\(sina=\sqrt{1-\left(-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(sin\left(a+\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)=sina\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)+sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)\cdot cosa\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{6}-2}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
b: \(cos\left(a+\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)=cosa\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)-sina\cdot sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
c: \(sin\left(a-\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=sina\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)-cosa\cdot sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
d: \(cos\left(a-\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)\)
\(=cosa\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)+sina\cdot sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{6}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}+\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}}{2\sqrt{3}}\)

\(sin^2x-2m.sinx.cosx-sinx.cosx+2mcos^2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(sinx-cosx\right)-2mcosx\left(sinx-cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sinx-cosx\right)\left(sinx-2m.cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=cosx\\sinx=2m.cosx\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=1\\tanx=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(tanx=1\) ko có nghiệm đã cho nên \(tanx=2m\) phải có nghiệm trên khoảng đã cho
\(\Rightarrow tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)< 2m< tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow1< 2m< \sqrt[]{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\) (hoặc có thể 1 đáp án là tập con của tập này cũng được)

\(\Leftrightarrow1-2sin^2x+\left(2m-3\right)sinx+m-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x-\left(2m-3\right)sinx-m+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x+sinx-2\left(m-1\right)sinx-\left(m-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\left(2sinx+1\right)-\left(m-1\right)\left(2sinx+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2sinx+1\right)\left(sinx-m+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\sinx=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Pt có đúng 2 nghiệm thuộc khoảng đã cho khi và chỉ khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\\-1\le m-1\le1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\\0\le m\le2\end{matrix}\right.\)


\(A=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}cos2x+\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}cos\left(2x+\frac{4\pi}{3}\right)+\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}cos\left(2x-\frac{4\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{2}cos2x+cos2x.cos\frac{4\pi}{3}\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{2}cos2x-\frac{1}{2}cos2x=\frac{3}{2}\)
\(B=\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}cos2x+\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}cos\left(2x+\frac{4\pi}{3}\right)+\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}cos\left(2x-\frac{4\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}-\frac{1}{2}cos2x-cos2x.cos\frac{4\pi}{3}\)
\(=\frac{3}{2}-\frac{1}{2}cos2x+\frac{1}{2}cos2x=\frac{3}{2}\)
Chọn đáp án D.