Giải các phương trình 2x + x + 12 = 0.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


2 x - 1 2 + (2 – x)(2x – 1) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(2x – 1) + (2 – x)(2x – 1) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)[(2x – 1) + (2 – x)] = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(2x – 1 + 2 – x) = 0
⇔ (2x – 1)(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ 2x – 1 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
2x – 1 = 0 ⇔ x = 0,5
x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = - 1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 0,5 hoặc x = - 1

(2x2 + x – 4)2 – (2x – 1)2 = 0
⇔ (2x2 + x – 4 – 2x + 1)(2x2 + x – 4 + 2x – 1) = 0
⇔ (2x2 – x – 3)(2x2 + 3x – 5) = 0
⇔ 2x2 – x – 3 = 0 (1)
hoặc 2x2 + 3x – 5 = 0 (2)
+ Giải (1): 2x2 – x – 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -1; c = -3 ⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm x = -1 và x = -c/a = 3/2.
+ Giải (2): 2x2 + 3x – 5 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 3; c = -5 ⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm x = 1 và x = c/a = -5/2.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 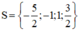

a) \(x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
b) \(x^2-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(2x^2+5x+3=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) \(x^2-x-12=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

`a,x^2 +4x-5=0`
`<=> x^2-x+5x-5=0`
`<=> x(x-1)+5(x-1)=0`
`<=>(x-1)(x+5)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
`b, x^2 -x-12=0`
`<=> x^2 +3x-4x-12=0`
`<=>(x^2+3x)-(4x+12)=0`
`<=>x(x+3)-4(x+3)=0`
`<=>(x+3)(x-4)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
`c, (2x-7)^2 - 6(2x-7)(x-3)=0`
`<=>(2x-7)(2x-7 -6x+18)=0`
`<=>(2x-7) ( -4x+11)=0`
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\-4x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=7\\-4x=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{11}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: =>(x+5)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-5
b: =>(x-4)(x+3)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-3
c: =>(2x-7)(2x-7-6x+18)=0
=>(2x-7)(-4x+11)=0
=>x=11/4 hoặc x=7/2
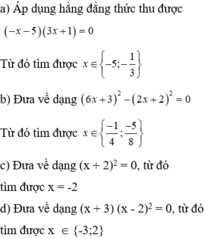
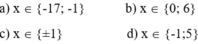
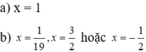
2x + x - 12 = 0 ⇔ 3x - 12 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 12 ⇔ x = 4
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {4}.